Related Research Articles
Czech, historically also Bohemian, is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German.

Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.

Slovak is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union.

This article is about the demographic features of the population of the Czech Republic, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, and religious affiliations.
A caron, háček or haček also known as a hachek, wedge, check, kvačica, strešica, mäkčeň, paukščiukas, inverted circumflex, inverted hat, flying bird, inverted chevron, is a diacritic (◌̌) commonly placed over certain letters in the orthography of some languages to indicate a change in the related letter's pronunciation.
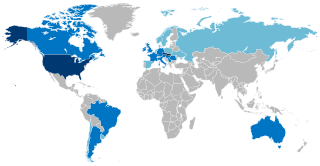
The Slovaks are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.

The QWERTZ or QWERTZU keyboard is a typewriter and keyboard layout widely used in Central Europe. The name comes from the first six letters at the top left of the keyboard:.
The Slovak language is a West Slavic language. Historically, it forms a dialect continuum with Czech. The written standard is based on the work of Ľudovít Štúr, published in the 1840s and codified in July 1843 in Hlboké.
The Dissolution of Czechoslovakia took effect on 1 January 1993, and was the self-determined split of the federal republic of Czechoslovakia into the independent countries of the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Both mirrored the Czech Socialist Republic and the Slovak Socialist Republic, which had been created in 1969 as the constituent states of the Czechoslovak Federal Republic.
Hungarian Sign Language is the sign language of Deaf people in Hungary. There is historical evidence that Hungarian and Austrian Sign Language are related, but Bickford (2005) found that Hungarian, Slovak, and Czech Sign formed a cluster with Romanian, Bulgarian, and Polish Sign rather than with Austrian. Bickford also noted that there are about seven dialects of Hungarian Sign Language, with the variation connected to the residential Deaf school where it is taught.

The Czech and Slovak languages form the Czech–Slovak subgroup within the West Slavic languages.

Czechoslovakism is a concept which underlines reciprocity of the Czechs and the Slovaks. It is best known as an ideology which holds that there is one Czechoslovak nation, though it might also appear as a political program of two nations living in one common state. The climax of Czechoslovakism fell on 1918-1938, when as a one-nation-theory it became the official political doctrine of Czechoslovakia; its best known representative was Tomáš Masaryk. Today Czechoslovakism as political concept or ideology is almost defunct; its remnant is a general sentiment of cultural affinity, present among many Czechs and Slovaks.

Moravian dialects are the varieties of Czech spoken in Moravia, a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic. There are more forms of the Czech language used in Moravia than in the rest of the Czech Republic. The main four groups of dialects are the Bohemian-Moravian group, the Central Moravian group, the Eastern Moravian group and the Lach (Silesian) group. While the forms are generally viewed as regional variants of Czech, some Moravians claim them to be one separate Moravian language.
The French Sign Language or Francosign family is a language family of sign languages which includes French Sign Language and American Sign Language.
This article describes ethnic minorities in Czechoslovakia from 1918 until 1992.

The Czechoslovak language was a political sociolinguistic concept used in Czechoslovakia in 1920–1938 for the definition of the state language of the country which proclaimed its independence as the republic of two nations, i.e. ethnic groups, Czechs and Slovaks.
Czech Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf community in the Czech Republic. It presumably emerged around the time of the first deaf school in Bohemia (1786). It belongs to the French sign-language family and is partially intelligible with French sign language. Despite the similarity of oral Czech and Slovak, it is not particularly close to Slovak Sign Language.
Ukrainian Sign Language (USL) is the sign language of the deaf community of Ukraine. Ukrainian Sign Language belongs to the family of French sign languages. Worldwide awareness of Ukrainian Sign Language rose sharply in 2014 after the release of a Ukrainian film The Tribe, where actors communicated in Ukrainian Sign Language with no spoken dialogue.
Bulgarian Sign Language is the language, or perhaps languages, of the deaf community in Bulgaria.
The City of the Sun is a 2005 comedy film written and directed by Martin Šulík and starring Oldřich Navrátil and Ľuboš Kostelný. The film won the main prize at the 2005 Finále Plzeň Film Festival. At the 2006 ceremony for The Sun in a Net Awards, the film won in six categories. The film was Slovakia's submission for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film for the 78th Academy Awards. The film won in two categories at the Czech Lion Awards, specifically for music and editing.
References
- ↑ Slovak Sign Language at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Bickford, 2005. The Signed Languages of Eastern Europe