
Sign languages are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are also similarities among different sign languages.

French Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf in France and French-speaking parts of Switzerland. According to Ethnologue, it has 100,000 native signers.

Irish Sign Language is the sign language of Ireland, used primarily in the Republic of Ireland. It is also used in Northern Ireland, alongside British Sign Language (BSL). Irish Sign Language is more closely related to French Sign Language (LSF) than to BSL, though it has influence from both languages. It has influenced sign languages in Australia and South Africa, and has little relation to either spoken Irish or English. ISL is unique among sign languages for having different gendered versions due to men and women being taught it at different schools all over Ireland.
Hungarian Sign Language is the sign language of Deaf people in Hungary. There is historical evidence that Hungarian and Austrian Sign Language are related, but Bickford (2005) found that Hungarian, Slovak, and Czech Sign formed a cluster with Romanian, Bulgarian, and Polish Sign rather than with Austrian. Bickford also noted that there are about seven dialects of Hungarian Sign Language, with the variation connected to the residential Deaf school where it is taught.
Polish Sign Language is the language of the deaf community in Poland. Polish Sign Language uses a distinctive one-handed manual alphabet based on the alphabet used in Old French Sign Language and therefore appears to be related to French Sign Language. It may also have common features with Russian Sign Language and German Sign Language, which is related to the history of Poland during the Partitions, when Russification and Germanization significantly influenced the Polish language, and may also have borrowings from the sign language used in the Austrian partition. Its lexicon and grammar are distinct from the Polish language, although there is a manually coded version of Polish known as System Językowo-Migowy, which is often used by interpreters on television and by teachers in schools.

Senegal is a multilingual country: Ethnologue lists 36 languages, Wolof being the most widely spoken language.
Argentine Sign Language is used in Argentina. Deaf people attend separate schools, and use local sign languages out of class. A manual alphabet for spelling Spanish has been developed.
Salvadoran Sign language is a language used by the deaf community in El Salvador. Its main purpose is to communicate. There are three distinct forms of sign language. American Sign Language was brought over to El Salvador from the United States by missionaries who set up small communal schools for the deaf. The government has also created a school for the deaf, teaching by means of their own modified Salvadoran Sign Language. The third type of sign language used is a combination of American Sign Language and Salvadoran Sign language. Most deaf understand and rely upon both. Their own unique Salvadoran Sign language is based on their language and is most useful in regular encounters; however, American Sign Language is often relied on within education due to the larger and more specific vocabulary. This is the reason that the deaf community within El Salvador sometimes relies upon both ASL and SSL in a combined form.
Danish Sign Language is the sign language used in Denmark.
The French Sign Language or Francosign family is a language family of sign languages which includes French Sign Language and American Sign Language.
Algerian Sign Language is the sign language most commonly used in Algeria. It was officially recognized by the Algerian law on the protection and promotion of persons with a disability enacted on May 8, 2002.
Armenian Sign Language is the deaf sign language of Armenia.
The Swedish Sign Language family is a language family of sign languages, including Swedish Sign Language, Portuguese Sign Language, and Finnish Sign Language.
A number of Ethiopian sign languages have been used in various Ethiopian schools for the deaf since 1971, and at the primary level since 1956. Ethiopian Sign Language, presumably a national standard, is used in primary, secondary, and—at Addis Ababa University—tertiary education, and on national television. The Ethiopian Deaf Community uses the language as a marker of identity.
The Slovak Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf community in Slovakia. It belongs to the French sign-language family. Bickford (2005) found that Slovak, Czech, and Hungarian Sign formed a cluster with Romanian, Bulgarian, and Polish Sign.
Tunisian Sign Language is the sign language used by deaf people in Tunisia. It derives from Italian Sign Language, mixed with indigenous sign.
Hanoi Sign Language is the deaf-community sign language of the city of Hanoi in Vietnam. It is about 50% cognate with the other sign languages of Vietnam, and its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by the French Sign Language once taught in Vietnamese schools for the deaf.
Algerian Jewish Sign Language (AJSL), also known as Ghardaia Sign Language, is a moribund village sign language originally of Ghardaïa, Algeria that is now used in Israel and possibly also in France.
Bulgarian Sign Language is the language, or perhaps languages, of the deaf community in Bulgaria.
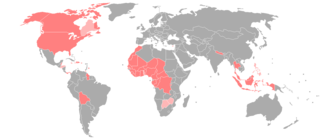
American Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States and Canada, but has spread around the world. Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.





