











The following timeline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of Arizona .












The following timeline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of Arizona .
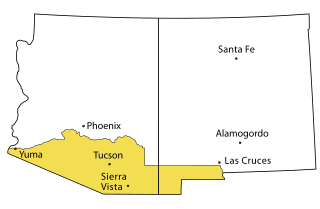
The Gadsden Purchase is a 29,640-square-mile (76,800 km2) region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lands south of the Gila River and west of the Rio Grande where the United States wanted the construction of what is now known as the Sunset Route, a transcontinental railroad, to be carried out, which the Southern Pacific Railroad later completed in 1881–1883. The purchase also aimed to resolve other border issues.

The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo officially ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). It was signed on 2 February 1848 in the town of Guadalupe Hidalgo.

James Gadsden was an American diplomat, soldier and businessman after whom the Gadsden Purchase is named, pertaining to land which the United States bought from Mexico, and which became the southern portions of Arizona and New Mexico. James Gadsden served as Adjutant General of the U.S. Army from August 13, 1821 – March 22, 1822. Between 1853 and 1856, he served as U.S. Minister to Mexico. He was known commonly as General Gadsden, although he never had a rank above colonel.

The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of Nuevo México becoming part of the American frontier after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. It existed with varying boundaries until the territory was admitted to the Union as the U.S. state of New Mexico in 1912. This jurisdiction was an organized, incorporated territory of the US for nearly 62 years, the longest period of any territory in the contiguous United States.

The Mexican Cession is the region in the modern-day Western United States that Mexico previously controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. This region had not been part of the areas east of the Rio Grande that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas, which had been claiming independence since its Texas Revolution of 1836 and subsequent brief war for independence, followed afterwards a decade later by the American annexation and admitted statehood in 1845. It had not specified the southern and western boundary of the new state of Texas with New Mexico consisting of roughly 529,000 square miles (1,370,000 km2), not including any Texas lands, the Mexican Cession was the third-largest acquisition of territory in U.S. history, surpassed only by the 827,000-square-mile (2,140,000 km2) Louisiana Purchase of 1803 and the later 586,000-square-mile (1,520,000 km2) Alaska Purchase from Russia in 1867.

The Territory of Arizona, commonly known as the Arizona Territory, was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Arizona. It was created from the western half of the New Mexico Territory during the American Civil War.

Estado de Occidente was a Mexican state established in 1824. The constitution was drafted in that year and the government was initially established with its capital at El Fuerte, Sinaloa. The first governor was Juan Miguel Riesgo. The state consisted of modern Sonora and Sinaloa, and also modern Arizona more or less south of the Gila River.

The United States Court of Private Land Claims (1891–1904) was an ad-hoc court created to decide land claims guaranteed by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, in the territories of New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah, and in the states of Nevada, Colorado, and Wyoming.

New Mexico Territory's at-large congressional district is an obsolete congressional district representing the New Mexico Territory, which was created in 1850. After New Mexico's admission to the Union as the 47th state by act of Congress on January 6, 1912, this district was dissolved and replaced by New Mexico's at-large congressional district.

The Pious Fund of the Californias is a endowment, originating in 1696, to sponsor the Roman Catholic Jesuit Spanish missions in Baja California, Dominican missions in upper Baja California, and Franciscan Spanish missions in Alta California in the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1697 to 1834, and originally administered by the Jesuits. It became the object of litigation between the US and Mexican governments in the 19th century, with the resolution making legal history in The Hague in 1902.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Arizona:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Nevada:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of New Mexico:
The area currently occupied by the U.S. State of New Mexico has undergone numerous changes in occupancy and territorial claims and designations. This geographic chronology traces the territorial evolution of New Mexico.

The following outline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of Wyoming.

The following timeline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of Utah.

The following outline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of Nevada.

The following timeline traces the territorial evolution of California, the thirty-first state admitted to the United States of America, including the process of removing Indigenous Peoples from their native lands, or restricting them to reservations.
Hispanic and Latino Arizonans are residents of the state of Arizona who are of Hispanic or Latino ancestry. As of the 2010 U.S. Census, Hispanics and Latinos of any race were 30% of the state's population.