The Beyond Einstein program is a NASA project designed to explore the limits of General theory of Relativity of Albert Einstein. The project includes two space observatories, and several observational cosmology probes. The program culminates with the Einstein Vision probes, after completion of the Great Observatories program.
Constellation-X Observatory (Con-X) and the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) have been promoted by NASA as the Einstein Great Observatories, to differentiate them from the current generation. However, they are not a part of the Great Observatories program. [1]
The science of the Dark Energy Probe was folded into the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (WFIRST) mission upon recommendation by a National Research Council committee in 2010.
Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers, and falls in between visible radiation, which ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers, and submillimeter waves.

A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with galactic clusters (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters within galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and clusters can themselves cluster together to form superclusters.

The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is a proposed space probe to detect and accurately measure gravitational waves—tiny ripples in the fabric of spacetime—from astronomical sources. LISA would be the first dedicated space-based gravitational wave detector. It aims to measure gravitational waves directly by using laser interferometry. The LISA concept has a constellation of three spacecraft arranged in an equilateral triangle with sides 2.5 million kilometres long, flying along an Earth-like heliocentric orbit. The distance between the satellites is precisely monitored to detect a passing gravitational wave.
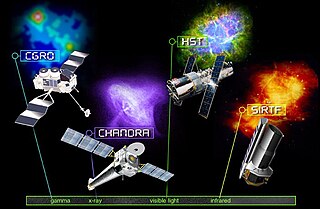
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.

Cornelis A. "Neil" Gehrels was an American astrophysicist specializing in the field of gamma-ray astronomy. He was Chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) from 1995 until his death, and was best known for his work developing the field from early balloon instruments to today's space observatories such as the NASA Swift mission, for which he was the Principal investigator. He was leading the WFIRST wide-field infrared telescope forward toward a launch in the mid-2020s. He was a member of the National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
The Joint Dark Energy Mission (JDEM) was an Einstein probe that planned to focus on investigating dark energy. JDEM was a partnership between NASA and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).

The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is a NASA infrared space telescope in development and scheduled to launch by May 2027. Roman was recommended in 2010 by the United States National Research Council Decadal Survey committee as the top priority for the next decade of astronomy. On 17 February 2016, WFIRST was approved for development and launch.

The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey is a review of astronomy and astrophysics literature produced approximately every ten years by the National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences in the United States. The report surveys the current state of the field, identifies research priorities, and makes recommendations for the coming decade. The decadal survey represents the recommendations of the research community to governmental agencies on how to prioritize scientific funding within astronomy and astrophysics. The editing committee is informed by topical panels and subcommittees, dedicated conferences, and direct community input in the form of white papers summarizing the state of the art in each subdiscipline. The most recent report, Astro2020, was released in 2021.

The International X-ray Observatory (IXO) is a cancelled X-ray telescope that was to be launched in 2021 as a joint effort by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). In May 2008, ESA and NASA established a coordination group involving all three agencies, with the intent of exploring a joint mission merging the ongoing XEUS and Constellation-X Observatory (Con-X) projects. This proposed the start of a joint study for IXO. NASA was forced to cancel the observatory due to budget constrains in fiscal year 2012. ESA however decided to reboot the mission on its own developing Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics as a part of Cosmic Vision program.

Enduring Quests and Daring Visions is a vision for astrophysics programs chartered by then-Director of NASA's Astrophysics Division, Paul Hertz, and released in late 2013. It lays out plans over 30 years as long-term goals and missions. Goals include mapping the Cosmic Microwave Background and finding Earth like exoplanets, to go deeper into space-time studying the Large Scale Structure of the Universe, extreme physics, and looking back farther in time. The panel that produced the vision included many notable American astrophysicists, including: Chryssa Kouveliotou, Eric Agol, Natalie Batalha, Misty Bentz, Alan Dressler, Scott Gaudi, Olivier Guyon, Enectali Figueroa-Feliciano, Feryal Ozel, Aki Roberge, Amber Straughn, and Joan Centrella.

LISA Pathfinder, formerly Small Missions for Advanced Research in Technology-2 (SMART-2), was an ESA spacecraft that was launched on 3 December 2015 on board Vega flight VV06. The mission tested technologies needed for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA), an ESA gravitational wave observatory planned to be launched in 2037. The scientific phase started on 8 March 2016 and lasted almost sixteen months. In April 2016 ESA announced that LISA Pathfinder demonstrated that the LISA mission is feasible.
Ann Hornschemeier is an American astronomer specializing in X-ray emission from X-ray binary populations. She is the Chief Scientist for the Physics of the Cosmos program at NASA.

SPHEREx is a future near-infrared space observatory that will perform an all-sky survey to measure the near-infrared spectra of approximately 450 million galaxies. In February 2019, SPHEREx was selected by NASA for its next Medium-Class Explorers mission, beating out two competing mission concepts: Arcus and FINESSE. As of August 2022, SPHEREx is targeted to launch no earlier than April 2025 on a Falcon 9 launch vehicle from Vandenberg Space Force Base. The principal investigator is James Bock at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, California.

The Science Programme of the European Space Agency is a long-term programme of space science and space exploration missions. Managed by the agency's Directorate of Science, The programme funds the development, launch, and operation of missions led by European space agencies and institutions through generational campaigns. Horizon 2000, the programme's first campaign, facilitated the development of eight missions between 1985 and 1995 including four "cornerstone missions" – SOHO and Cluster II, XMM-Newton, Rosetta, and Herschel. Horizon 2000 Plus, the programme's second campaign, facilitated the development of Gaia, LISA Pathfinder, and BepiColombo between 1995 and 2005. The programme's current campaign since 2005, Cosmic Vision, has so far funded the development of ten missions including three flagship missions, JUICE, Athena, and LISA. The programme's upcoming fourth campaign, Voyage 2050, is currently being drafted. Collaboration with agencies and institutions outside of Europe occasionally occur in the Science Programme, including a collaboration with NASA on Cassini–Huygens and the CNSA on SMILE.
Cosmic Vision is the third campaign of space science and space exploration missions in the Science Programme of the European Space Agency (ESA). Formulated in 2005 as Cosmic Vision: Space Science for Europe 2015–2025, the campaign succeeded the Horizon 2000 Plus campaign and envisioned a number of missions in the fields of astronomy and solar system exploration beyond 2015. Ten missions across four funding categories are planned to be launched under Cosmic Vision, with the first being CHEOPS in December 2019. A mission to the Galilean moons (JUICE), the first deep space mission with an opportunistic target, and one of the first gravitational-wave space observatories (LISA), are planned for launch as part of the Cosmic Vision campaign.