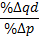In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded will equal the quantity supplied, resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics.

In economics, deadweight loss is the loss of societal economic welfare due to production/consumption of a good at a quantity where marginal benefit does not equal marginal cost – in other words, there are either goods being produced despite the cost of doing so being larger than the benefit, or additional goods are not being produced despite the fact that the benefits of their production would be larger than the costs. The deadweight loss is the net benefit that is missed out on. While losses to one entity often lead to gains for another, deadweight loss represents the loss that is not regained by anyone else. This loss is therefore attributed to both producers and consumers.

In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that will lead to the highest possible total profit. In neoclassical economics, which is currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, the firm is assumed to be a "rational agent" which wants to maximize its total profit, which is the difference between its total revenue and its total cost.
A good's price elasticity of demand is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good, but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price, holding everything else constant. If the elasticity is −2, that means a one percent price rise leads to a two percent decline in quantity demanded. Other elasticities measure how the quantity demanded changes with other variables.
In economics, the crosselasticity of demand measures the effect of changes in the price of one good on the quantity demanded of another good. This reflects the fact that the quantity demanded of good is dependent on not only its own price but also the price of other "related" good.

In microeconomics, substitute goods are two goods that can be used for the same purpose by consumers. That is, a consumer perceives both goods as similar or comparable, so that having more of one good causes the consumer to desire less of the other good. Contrary to complementary goods and independent goods, substitute goods may replace each other in use due to changing economic conditions. An example of substitute goods is Coca-Cola and Pepsi; the interchangeable aspect of these goods is due to the similarity of the purpose they serve, i.e. fulfilling customers' desire for a soft drink. These types of substitutes can be referred to as close substitutes.

The price elasticity of supply is a measure used in economics to show the responsiveness, or elasticity, of the quantity supplied of a good or service to a change in its price. Price elasticity of supply, in application, is the percentage change of the quantity supplied resulting from a 1% change in price. Alternatively, PES is the percentage change in the quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price.

In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on all else being equal, as the price of a good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change.

A demand curve is a graph depicting the inverse demand function, a relationship between the price of a certain commodity and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price. Demand curves can be used either for the price-quantity relationship for an individual consumer, or for all consumers in a particular market.

Marginal revenue is a central concept in microeconomics that describes the additional total revenue generated by increasing product sales by 1 unit. Marginal revenue is the increase in revenue from the sale of one additional unit of product, i.e., the revenue from the sale of the last unit of product. It can be positive or negative. Marginal revenue is an important concept in vendor analysis. To derive the value of marginal revenue, it is required to examine the difference between the aggregate benefits a firm received from the quantity of a good and service produced last period and the current period with one extra unit increase in the rate of production. Marginal revenue is a fundamental tool for economic decision making within a firm's setting, together with marginal cost to be considered.
In microeconomics, the Slutsky equation, named after Eugen Slutsky, relates changes in Marshallian (uncompensated) demand to changes in Hicksian (compensated) demand, which is known as such since it compensates to maintain a fixed level of utility.
In economics, the total revenue test is a means for determining whether demand is elastic or inelastic. If an increase in price causes an increase in total revenue, then demand can be said to be inelastic, since the increase in price does not have a large impact on quantity demanded. If an increase in price causes a decrease in total revenue, then demand can be said to be elastic, since the increase in price has a large impact on quantity demanded.
In economics, tax incidence or tax burden is the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Economists distinguish between the entities who ultimately bear the tax burden and those on whom the tax is initially imposed. The tax burden measures the true economic effect of the tax, measured by the difference between real incomes or utilities before and after imposing the tax, and taking into account how the tax causes prices to change. For example, if a 10% tax is imposed on sellers of butter, but the market price rises 8% as a result, most of the tax burden is on buyers, not sellers. The concept of tax incidence was initially brought to economists' attention by the French Physiocrats, in particular François Quesnay, who argued that the incidence of all taxation falls ultimately on landowners and is at the expense of land rent. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that ultimately bears the burden of, or ultimately suffers a loss from, the tax. The key concept of tax incidence is that the tax incidence or tax burden does not depend on where the revenue is collected, but on the price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply. As a general policy matter, the tax incidence should not violate the principles of a desirable tax system, especially fairness and transparency. The concept of tax incidence is used in political science and sociology to analyze the level of resources extracted from each income social stratum in order to describe how the tax burden is distributed among social classes. That allows one to derive some inferences about the progressive nature of the tax system, according to principles of vertical equity.
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. In economics "demand" for a commodity is not the same thing as "desire" for it. It refers to both the desire to purchase and the ability to pay for a commodity.
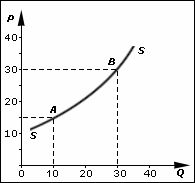
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, labour time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the price per unit on the vertical axis and quantity supplied as a function of price on the horizontal axis. This reversal of the usual position of the dependent variable and the independent variable is an unfortunate but standard convention.
In mathematics, the elasticity or point elasticity of a positive differentiable function f of a positive variable at point a is defined as
In economics, the income elasticity of demand (YED) is the responsivenesses of the quantity demanded for a good to a change in consumer income. It is measured as the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in income. For example, if in response to a 10% increase in income, quantity demanded for a good or service were to increase by 20%, the income elasticity of demand would be 20%/10% = 2.0.
Total revenue is the total receipts a seller can obtain from selling goods or services to buyers. It can be written as P × Q, which is the price of the goods multiplied by the quantity of the sold goods.
In mathematical economics, an isoelastic function, sometimes constant elasticity function, is a function that exhibits a constant elasticity, i.e. has a constant elasticity coefficient. The elasticity is the ratio of the percentage change in the dependent variable to the percentage causative change in the independent variable, in the limit as the changes approach zero in magnitude.

In microeconomics, a monopoly price is set by a monopoly. A monopoly occurs when a firm lacks any viable competition and is the sole producer of the industry's product. Because a monopoly faces no competition, it has absolute market power and can set a price above the firm's marginal cost.