This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it . Please introduce links to this page from related articles ; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (June 2025) |
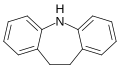 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names 10,11-Dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.080 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H13N | |
| Molar mass | 195.26 g/mol |
| Density | g/cm3 (20°C) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Iminodibenzyl is an aromatic organic compound with a multitude of uses in medicinal chemistry. Iminodibenzyl is a fundamental building block used mainly in the construction of tricyclic antidepressants. Chemically speaking, it is almost the same as for iminostilbene, but differs in that the 2 carbon bridge between the two phenyl rings is saturated (with hydrogen), and does not contain an olefin.

