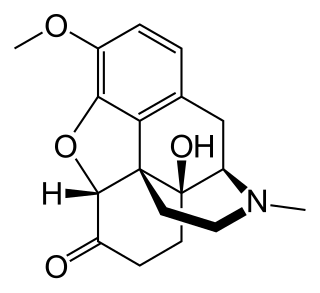
Oxycodone, sold under various brand names such as Roxicodone and OxyContin, is a strong, semi-synthetic opioid used medically for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and a commonly abused drug. It is usually taken by mouth, and is available in immediate-release and controlled-release formulations. Onset of pain relief typically begins within fifteen minutes and lasts for up to six hours with the immediate-release formulation. In the United Kingdom, it is available by injection. Combination products are also available with paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, naloxone, naltrexone, and aspirin.

Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an hour. It is also available by injection. It is available in combination with paracetamol (acetaminophen).

Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.

Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.
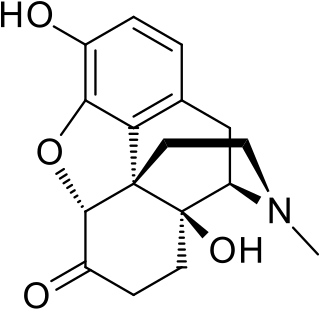
Oxymorphone is a highly potent opioid analgesic indicated for treatment of severe pain. Pain relief after injection begins after about 5–10 minutes, after oral administration it begins after about 30 minutes, and lasts about 3–4 hours for immediate-release tablets and 12 hours for extended-release tablets. The elimination half-life of oxymorphone is much faster intravenously, and as such, the drug is most commonly used orally. Like oxycodone, which metabolizes to oxymorphone, oxymorphone has a high potential to be abused.

The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."

Metandienone, also known as methandienone or methandrostenolone and sold under the brand name Dianabol (D-Bol) among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is still quite often used because of its affordability and effectiveness for bulking cycles. It is also used non-medically for physique- and performance-enhancing purposes. It is often taken by mouth.

Ruppia, also known as the widgeonweeds, ditch grasses or widgeon grass, is the only extant genus in the family Ruppiaceae, with eight known species. These are aquatic plants widespread over much of the world. The genus name honours Heinrich Bernhard Rupp, a German botanist (1688-1719). They are widespread outside of frigid zones and the tropics.

Morphinan is the prototype chemical structure of a large chemical class of psychoactive drugs, consisting of opiate analgesics, cough suppressants, and dissociative hallucinogens, among others.

Fluoxymesterone, sold under the brand names Halotestin and Ultandren among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, breast cancer in women, and anemia. It is taken by mouth.

Thebacon, or dihydrocodeinone enol acetate, is a semisynthetic opioid that is similar to hydrocodone and is most commonly synthesised from thebaine. Thebacon was invented in Germany in 1924, four years after the first synthesis of hydrocodone. Thebacon is a derivative of acetyldihydrocodeine, where only the 6–7 double bond is saturated. Thebacon is marketed as its hydrochloride salt under the trade name Acedicon, and as its bitartrate under Diacodin and other trade names. The hydrochloride salt has a free base conversion ratio of 0.846. Other salts used in research and other settings include thebacon's phosphate, hydrobromide, citrate, hydroiodide, and sulfate.
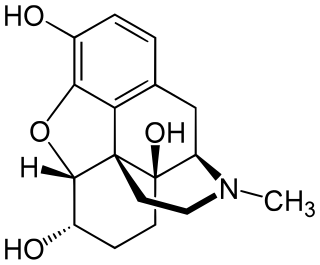
Hydromorphinol, also is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation, analgesia and respiratory depression, but is twice as potent as morphine and has a steeper dose-response curve and longer half-life. It is used in medicine as the bitartrate salt and hydrochloride

An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term opioid is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America.
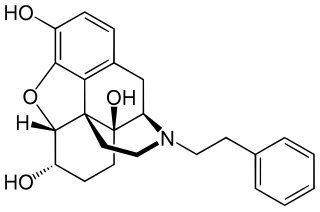
RAM-378(7,8-Dihydro-14-hydroxy-N-phenethylnormorphine) is an opioid analgesic. It is the N-phenethyl derivative of hydromorphinol.

14-Hydroxydihydrocodeine (RAM-318) is an opiate analgesic drug, which is also an active metabolite of oxycodone and hydromorphinol. 14-Hydroxydihydrocodeine is not currently marketed in any developed country, but has been of interest to pharmaceutical companies looking for new analgesics and antitussives.

4-Methylpregabalin is a drug developed by Pfizer and related to pregabalin, which similarly acts as an analgesic with effectiveness against difficult to treat "atypical" pain syndromes such as neuropathic pain. The effectiveness of pregabalin and its older relative gabapentin against pain syndromes of this kind has led to their widespread use, and these drugs have subsequently been found to be useful for many other medical applications, including as anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, anxiolytics and mood stabilisers.

U-47700, also known as U4, pink heroin, pinky, and pink, is an opioid analgesic drug developed by a team at Upjohn in the 1970s which has around 7.5 times the potency of morphine in animal models.
Cholesterol-5,6-oxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.11, cholesterol-epoxide hydrolase, ChEH) is an enzyme with systematic name 5,6alpha-epoxy-5alpha-cholestan-3beta-ol hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Noroxymorphone is an opioid which is both a metabolite of oxymorphone and oxycodone and is manufactured specifically as an intermediate in the production of narcotic antagonists such as naltrexone and others. It is a potent agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, but is poorly able to cross the blood-brain-barrier into the central nervous system, and for this reason, has only minimal analgesic activity.

16β,17α-Epiestriol, or 16,17-epiestriol, also known as 16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol, as well as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16β,17α-triol, is a minor and weak endogenous steroidal estrogen that is related to 17α-estradiol and estriol. Along with estriol, 16β,17α-epiestriol has been detected in the urine of women during the late pregnancy stage. It shows preferential affinity for the ERβ over the ERα.



















