
The 1848 United States presidential election was the 16th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1848. In the aftermath of the Mexican–American War, General Zachary Taylor of the Whig Party defeated Senator Lewis Cass of the Democratic Party.

The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott. A third party candidate from the Free Soil party, John P. Hale, also ran and came in third place, but got no electoral votes.

The 1860 United States presidential election was the 19th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin won a national popular plurality, a popular majority in the North where states already had abolished slavery, and a national electoral majority comprising only Northern electoral votes. Lincoln's election thus served as the main catalyst of the states that would become the Confederacy seceding from the Union. This marked the first time that a Republican was elected president. It was also the first presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1904, 1920, 1940, 1944, and 2016.

The Free Soil Party was a short-lived coalition political party in the United States active from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party. The party was largely focused on the single issue of opposing the expansion of slavery into the western territories of the United States.

The Constitutional Union Party was a United States political party active during the 1860 elections. It consisted of conservative former Whigs, largely from the Southern United States, who wanted to avoid secession over the slavery issue and refused to join either the Republican Party or the Democratic Party. The Constitutional Union Party campaigned on a simple platform "to recognize no political principle other than the Constitution of the country, the Union of the states, and the Enforcement of the Laws".

James Chamberlain Jones was an American politician who served as the tenth governor of Tennessee from 1841 to 1845, and as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 1851 to 1857. A Whig, Jones twice defeated future U.S. President James K. Polk for the governorship, in 1841 and 1843. He was the first native-born Tennessean to be elected governor of the state.

The 1852 Whig National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held from June 16 to June 21, in Baltimore, Maryland. It nominated the Whig Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1852 election. The convention selected General-in-Chief Winfield Scott for president and U.S. secretary of the navy William A. Graham for vice president.
The following table indicates the party of elected officials in the U.S. state of Maine:

The 1850–51 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1850 and 1851, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The political career of John C. Breckinridge included service in the state government of Kentucky, the Federal government of the United States, as well as the government of the Confederate States of America. In 1857, 36 years old, he was inaugurated as Vice President of the United States under James Buchanan. He remains the youngest person to ever hold the office. Four years later, he ran as the presidential candidate of a dissident group of Southern Democrats, but lost the election to the Republican candidate Abraham Lincoln.

The 1845 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, May 26, 1845, to elect the first United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 29th Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including the gubernatorial election, the senatorial elections, and various state and local elections.

The 1846 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 5, 1846 to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 30th Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including various state and local elections. The party primaries were held on June 20, 1846.

The 1848 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 2, 1848, to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 31st Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including the presidential election, the senatorial election, the gubernatorial election, and various state and local elections.

The 1850 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 7, 1846 to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 32nd Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including the senatorial election and various state and local elections.

The 1854 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 2, 1854 to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 34th Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including the senatorial election and various state and local elections.

The 1856 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 6, 1856 to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 35th Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including the presidential election, the senatorial election, the gubernatorial election, and various state and local elections.

The 1858 United States House of Representatives election in Florida was held on Monday, October 4, 1858 to elect the single United States Representative from the state of Florida, one from the state's single at-large congressional district, to represent Florida in the 36th Congress. The election coincided with the elections of other offices, including various state and local elections.
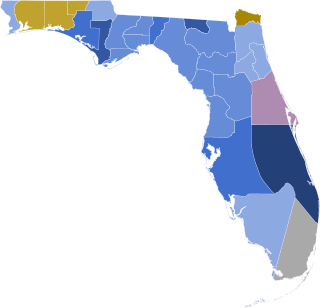
The 1852 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 2, 1852, as part of the 1852 United States presidential election. Voters chose three representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for President and Vice President.

William Archer Cocke was an American attorney and politician who served as the 13th Florida Attorney General. Cocke was placed into the national spotlight due to his role in the controversy following the 1876 presidential election.

A special election to the United States House of Representatives for Florida's at-large congressional district was held October 6, 1845.






















