
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 4, 1924. Incumbent Republican President Calvin Coolidge won election to a full term. Coolidge was the second vice president, after Theodore Roosevelt, to ascend to the presidency and then win a full term.
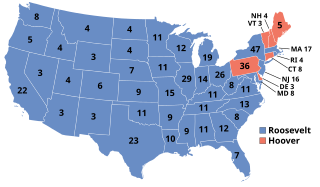
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1932. Against the backdrop of the Great Depression, incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the governor of New York and the vice presidential nominee of the 1920 presidential election. Roosevelt was the first Democrat in 80 years to simultaneously win an outright majority of the electoral college and popular vote, a feat last accomplished by Franklin Pierce in 1852, as well as the first Democrat in 56 years to win a majority of the popular vote, which was last achieved by Samuel J. Tilden in 1876. Roosevelt was the last sitting governor to be elected president until Bill Clinton in 1992. Hoover became the first incumbent president to lose an election to another term since William Howard Taft in 1912, the last to do so until Gerald Ford lost 44 years later, and the last elected incumbent president to do so until Jimmy Carter lost 48 years later. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans. It was the first time since 1916 that a Democrat was elected president.

The Democratic National Convention (DNC) is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1832 by the United States Democratic Party. They have been administered by the Democratic National Committee since the 1852 national convention. The primary goal of the Democratic National Convention is to officially nominate a candidate for president and vice president, adopt a comprehensive party platform, and unify the party. Pledged delegates from all fifty U.S. states, the District of Columbia, and the American territories, and superdelegates which are unpledged delegates representing the Democratic establishment, attend the convention and cast their votes to choose the party's presidential candidate. Like the Republican National Convention, the Democratic National Convention marks the formal end of the primary election period and the start of the general election season. Since the 1980s, national conventions have become mostly inaugural events for the winning candidate, since winners are announced long before the convention. In 2020, both major parties, and many minor parties, replaced their usual in-person conventions with virtual programs due to the COVID-19 pandemic.

The 1920 Republican National Convention nominated Ohio Senator Warren G. Harding for president and Massachusetts Governor Calvin Coolidge for vice president. The convention was held in Chicago, Illinois, at the Chicago Coliseum from June 8 to June 12, 1920, with 940 delegates. Under convention rules, a majority plus one, or at least 471 of the 940 delegates, was necessary for a nomination.

The 1924 Republican National Convention was held in Cleveland, Ohio, at the Public Auditorium, from June 10 to 12.
This article contains the results of the 2008 Republican presidential primaries and caucuses.
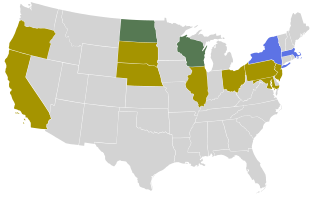
From January 23 to June 4, 1912, delegates to the 1912 Republican National Convention were selected through a series of primaries, caucuses, and conventions to determine the party's nominee for president in the 1912 election. Incumbent president William Howard Taft was chosen over former president Theodore Roosevelt. Taft's victory at the national convention precipitated a fissure in the Republican Party, with Roosevelt standing for the presidency as the candidate of an independent Progressive Party, and the election of Democrat Woodrow Wilson over the divided Republicans.

Presidential primaries and caucuses were organized by the Democratic Party to select the 4,051 delegates to the 2016 Democratic National Convention held July 25–28 and determine the nominee for President in the 2016 United States presidential election. The elections took place within all fifty U.S. states, the District of Columbia, five U.S. territories, and Democrats Abroad and occurred between February 1 and June 14, 2016. Between 2008 and 2020, this was the only Democratic Party primary in which the nominee had never been nor had ever become President of the United States. This was the first time the Democratic primary had nominated a woman for president.

The nomination of Robert M. La Follette for president took place at a convention held in Cleveland, Ohio from July 4-5, 1924. The convention was called by the Conference for Progressive Political Action (CPPA) and included accredited delegates from national trade unions, state branches of the CPPA, and other political organizations. Members of the Socialist Party of America played a prominent role in the organization of the July convention and the subsequent La Follette presidential campaign; representatives of the Communist Workers Party of America were banned.
This article includes the entire 2016 Democratic Party presidential primary schedule in a format that includes result tabulation. Below are the vote totals for everyone that appeared on the ballot during the 2016 Democratic presidential primaries. Two candidates, Bernie Sanders and Hillary Clinton, appeared on all 57 ballots. Two others, Martin O'Malley and Rocky De La Fuente, appeared in over 30 states and six others appeared on between two and ten states. Nearly 20 appeared on only New Hampshire's ballot. As of June 8, Hillary Clinton was considered the presumptive nominee according to media organizations. On July 26, the second day of the Democratic National Convention, Clinton was confirmed the Democratic nominee for the 2016 United States presidential election.

The 2016 United States presidential election in Virginia was held on November 8, 2016, as part of the 2016 general election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Virginia voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting the Republican nominee, businessman Donald Trump, and running mate Indiana Governor Mike Pence against Democratic nominee, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton and her running mate, Virginia Senator Tim Kaine.

From March 12 to June 27, 1940, voters of the Democratic Party elected delegates to the 1940 Democratic National Convention through a series of primaries, caucuses, and conventions. Incumbent President Franklin D. Roosevelt was selected as the party's presidential nominee despite not formally declaring a campaign for a third term. Supporters effectively drafted Roosevelt, who was non-committal about seeking re-election, amid rising concerns over war in Europe.

From March 9 to June 5, 1920, voters of the Republican Party elected delegates to the 1920 Republican National Convention for the purpose of choosing the party's nominee for president in the 1920 election.

From February 9 to June 6, through a series of primaries and caucuses, voters of the Republican Party elected delegates to the 1916 Republican National Convention, held June 7 to June 10, 1916, in Chicago, Illinois to choose the party's nominee for President of the United States. The delegate election process was inconclusive, with a majority of delegates not pledged to any candidate and a small plurality supporting Associate Justice of the Supreme Court Charles Evans Hughes. Hughes eventually secured the nomination at the convention on the third ballot.

The 1924 United States presidential election in Ohio was held on November 4, 1924, as part of the 1924 United States presidential election. State voters chose twenty-four electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
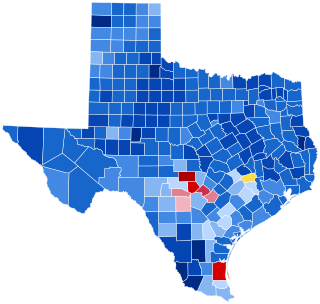
The 1944 United States presidential election in Texas took place on November 7, 1944, as part of the 1944 United States presidential election. State voters chose 23 electors to represent the state in the Electoral College, which chose the president and vice president.

The 1924 United States presidential election in Idaho took place on November 4, 1924, as part of the 1924 United States presidential election. State voters chose four representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1924 United States presidential election in Tennessee took place on November 4, 1924, as part of the 1924 United States presidential election. Tennessee voters chose 12 representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
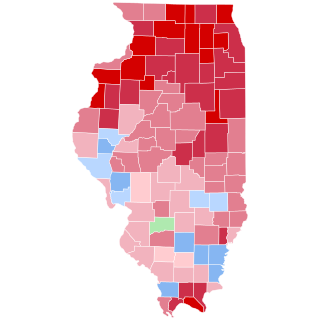
The 1924 United States presidential election in Illinois took place on November 4, 1924, as part of the 1924 United States presidential election. State voters chose 29 representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
This is a list of endorsements for declared candidates in the Republican primaries for the 1928 United States presidential election.





















