
Andesaurus is a genus of basal titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which existed during the middle of the Cretaceous Period in South America. Like most sauropods, belonging to one of the largest animals ever to walk the Earth, it would have had a small head on the end of a long neck and an equally long tail.

Huabeisaurus was a genus of dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It was a sauropod which lived in what is present-day northern China. The type species, Huabeisaurus allocotus, was first described by Pang Qiqing and Cheng Zhengwu in 2000. Huabeisaurus is known from numerous remains found in the 1990s, which include teeth, partial limbs and vertebrae. Due to its relative completeness, Huabeisaurus represents a significant taxon for understanding sauropod evolution in Asia. Huabeisaurus comes from Kangdailiang and Houyu, Zhaojiagou Town, Tianzhen County, Shanxi province, China. The holotype was found in the unnamed upper member of the Huiquanpu Formation, which is Late Cretaceous (?Cenomanian–?Campanian) in age based on ostracods, charophytes, and fission-track dating.
Gobititan is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Aptian faunal stage of the Early Cretaceous. The name of this genus is derived from the Gobi desert region and the Titans of Greek mythology, which is a reference to its large body size. The specific name shenzhouensis, is derived from "Shenzhou", an ancient name for China.

Jiangshanosaurus is a genus of herbivorous titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur that lived in China approximately 92-88 million years ago, during the Turonian-Coniacian stage of the Late Cretaceous.

Phuwiangosaurus is a genus of titanosaur dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Hauterivian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The type species, P. sirindhornae, was described by Martin, Buffetaut, and Suteethorn in a 1993 press release and was formally named in 1994. The species was named to honor Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn of Thailand, who was interested in the geology and palaeontology of Thailand, while the genus was named after the Phu Wiang area, where the fossil was discovered.

Huanghetitan, is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the early Cretaceous Period. It was a basal titanosauriform which lived in what is now Gansu, China.

Ruyangosaurus is a genus of titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur recovered from the Early Cretaceous Haoling Formation of China. The type species is R. giganteus, described in 2009 by Lü Junchang et al.

Baotianmansaurus is a genus of titanosaur sauropod dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in Upper Cretaceous rocks in Henan, China, within the Gaogou Formation. The type species is B. henanensis, described in 2009. The holotype is 41H III-0200. Remains of the fossils were vertebrae, ribs and scapula fragments. It was probably a close relative of Opisthocoelicaudia and Dongyangosaurus in Saltasauridae.

Wintonotitan is a genus of titanosauriform dinosaur from Cenomanian -age Winton Formation of Australia. It is known from partial postcranial remains.

Xianshanosaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) of the Ruyang Basin in Henan Province, China. Its type and only species is Xianshanosaurus shijiagouensis. It was described in 2009 by a team of paleontologists led by Lü Junchang. Xianshanosaurus may be a titanosaur, and Daxiatitan may be its closest relative, but its evolutionary relationships remain controversial.
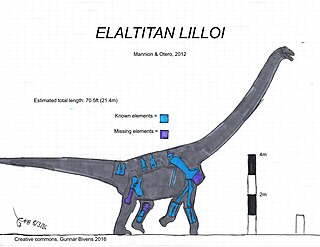
Elaltitan is an extinct genus of large lithostrotian titanosaur sauropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous of Chubut Province, southern Argentina. It contains a single species, Elaltitan lilloi.
Dongyangopelta is an monospecific genus of nodosaurid dinosaur that lived in China during the Early to Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Chaochuan Formation. The type and only known species, Dongyangopelta yangyanensis, is known from a partial postcranial skeleton preserving osteoderms and ossified tendons. It was named in 2013 by Rongjun Chen, Wenjie Zheng, Yoichi Azuma, Masateru Shibata, Tianling Lou, Qiang Jin and Xinsheng Jin. Dongyangopelta represents one of the only nodosaurids known from Asia, along with Taohelong and Sauroplites.
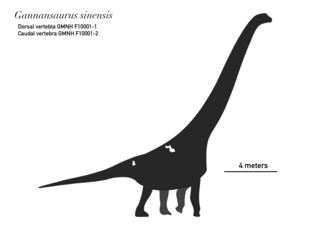
Gannansaurus is an extinct genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur known from the latest Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of Ganzhou Basin, Jiangxi Province of southern China. It is known from specimen GMNH F10001 which consists of a single, nearly complete dorsal vertebra and a mid-caudal vertebra. Gannansaurus was first named by Lü Junchang, Yi Laiping, Zhong Hui and Wei Xuefang in 2013 and the type species is Gannansaurus sinensis. Gannansaurus shares some characters with Euhelopus, indicating that it is more closely related to it rather than to other titanosauriforms.

Yongjinglong is an extinct genus of titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur known from the Early Cretaceous of Lanzhou-Minhe Basin of Gansu Province, China. It contains a single species, Yongjinglong datangi.
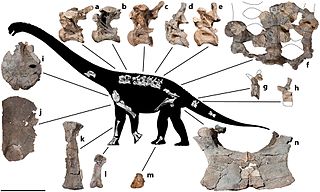
Savannasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Winton Formation of Queensland, Australia. It contains one species, Savannasaurus elliottorum, named in 2016 by Stephen Poropat and colleagues. The holotype and only known specimen, originally nicknamed "Wade", is the most complete specimen of an Australian sauropod, and is held at the Australian Age of Dinosaurs museum. Dinosaurs known from contemporary rocks include its close relative Diamantinasaurus and the theropod Australovenator; associated teeth suggest that Australovenator may have fed on the holotype specimen.

Mierasaurus is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Utah, United States. The taxon was first described and named in 2017 by Rafael Royo-Torres and colleagues, from a mostly complete skeleton including a disarticulated partial skull and mandible, teeth, multiple vertebrae from along the length of the body, both scapulae, radius and ulna bones, a left manus, a complete pelvis, both femora and the entire left hindlimb. Additionally, they referred a lower jaw and femur from juvenile individuals, which were found nearby, to the genus. Collectively, Mierasaurus is among the most completely known North American sauropods. The genus name honours Bernardo de Miera y Pacheco, the first European scientist to enter what is now Utah. The type species for Mierasaurus is Mierasaurus bobyoungi, named after Robert Glen Young, a paleontologist who researched the Early Cretaceous of Utah.
The Chaochuan Formation is a geologic formation in China. It is made up of purplish red calcarenaceous, muddy siltstone, fine-grained sandstone with interbeds of tuffaceous sandstone and conglomerate or rhyolitic tuff.
The Fangyan Formation is a geologic formation in China (Dongyang). It is made up of mainly conglomerates. It preserves dinosaur fossils dating back to the Late Cretaceous.

Dzharatitanis is a genus of sauropod from the Bissekty Formation in Uzbekistan, dating to the Turonian age of the Late Cretaceous. The genus contains a single species, Dzharatitanis kingi, named after geologist Christopher King, who contributed to the Cretaceous geology of Asia. It is currently one of two known sauropods from the Bissekty Formation, alongside an indeterminate titanosaur. In its original publication it was considered to be a member of Rebbachisauridae, but later papers considered it to be a titanosaur.
Ruixinia is an extinct genus of somphospondylan titanosauriform dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) Yixian Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, Ruixinia zhangi. The Ruixinia holotype is a partial articulated skeleton with the most complete series of caudal vertebrae known from any Asian titanosauriform.



























