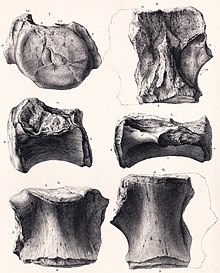
Titanosaurus is a dubious genus of sauropod dinosaurs, first described by Richard Lydekker in 1877. It is known from the Maastrichtian Lameta Formation of India.

Pelorosaurus is a genus of titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur. Remains referred to Pelorosaurus date from the Early Cretaceous period, about 140-125 million years ago, and have been found in England and Portugal. Thomas Holtz estimated its length at 24 meters.

The Brachiosauridae are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the leaves of tall trees that other sauropods would have been unable to reach. In addition, they possessed thick spoon-shaped teeth which helped them to consume tough plants more efficiently than other sauropods. They have also been characterized by a few unique traits or synapomorphies; dorsal vertebrae with 'rod-like' transverse processes and an ischium with an abbreviated pubic peduncle.

Cetiosaurus meaning 'whale lizard', from the Greek keteios/κήτειος meaning 'sea monster' and sauros/σαυρος meaning 'lizard', is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period, living about 168 million years ago in what is now Britain.

Cetiosauriscus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived between 166 and 164 million years ago during the Callovian in what is now England. A herbivore, Cetiosauriscus had – by sauropod standards – a moderately long tail, and longer forelimbs, making them as long as its hindlimbs. It has been estimated as about 15 m (49 ft) long and between 4 and 10 t in weight.

Janenschia is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Lindi Region, Tanzania around 155 million years ago.

Paranthodon is a genus of stegosaurian dinosaur that lived in what is now South Africa during the Early Cretaceous, between 139 and 131 million years ago. Discovered in 1845, it was one of the first stegosaurians found. Its only remains, a partial skull, isolated teeth, and fragments of vertebrae, were found in the Kirkwood Formation. British paleontologist Richard Owen initially identified the fragments as those of the pareiasaur Anthodon. After remaining untouched for years in the British Museum of Natural History, the partial skull was identified by South African paleontologist Robert Broom as belonging to a different genus; he named the specimen Palaeoscincus africanus. Several years later, Hungarian paleontologist Franz Nopcsa, unaware of Broom's new name, similarly concluded that it represented a new taxon, and named it Paranthodon owenii. Since Nopcsa's species name was assigned after Broom's, and Broom did not assign a new genus, both names are now synonyms of the current binomial, Paranthodon africanus. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek para (near) with the genus name Anthodon, to represent the initial referral of the remains.
Volkheimeria is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now Argentina during the Early Jurassic, 178–179 million years ago. Its type and only species is Volkheimeria chubutensis.
Eucamerotus was a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Barremian-age Lower Cretaceous Wessex Formation (Wealden) of the Isle of Wight, England.
Marmarospondylus is a dubious genus of sauropod dinosaur from Middle Jurassic deposits in the English Midlands.

Ornithopsis is a genus of sauropod dinosaur, from the Early Cretaceous of England. The type species, which is the only species seen as valid today, is O. hulkei, which is only known from fragmentary remains, and has been regarded by many authors as dubious.
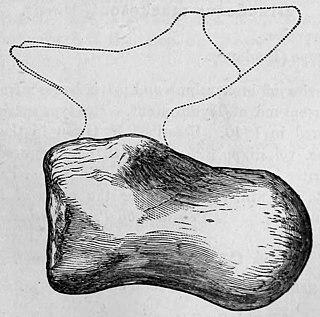
Iuticosaurus is a genus of titanosaur sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of the Isle of Wight. Two species have been named: I. valdensis and I. lydekkeri. I. valdensis was found in the Wessex Formation and I. lydekkeri in the younger Upper Greensand.

Lapparentosaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic. Its fossils were found in Madagascar. The type species is L. madagascariensis.

Turiasauria is an unranked clade of basal sauropod dinosaurs known from Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous deposits in Europe, North America, and Africa.

Neosauropoda is a clade within Dinosauria, coined in 1986 by Argentine paleontologist José Bonaparte and currently described as Saltasaurus loricatus, Diplodocus longus, and all animals directly descended from their most recent common ancestor. The group is composed of two subgroups: Diplodocoidea and Macronaria. Arising in the early Jurassic and persisting until the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, Neosauropoda contains the majority of sauropod genera, including genera such as Apatosaurus, Brachiosaurus, and Diplodocus. It also includes giants such as Argentinosaurus, Patagotitan and Sauroposeidon, and its members remain the largest land animals ever to have lived.
The Isalo III Formation is a geological formation in Madagascar, off the eastern coast of Africa. It dates back to the Middle Jurassic. The use of the term "Isalo III" is somewhat controversial as the two prior units Isalo I and II are Triassic cross-bedded sandstone units that form a continuous depositional sequence, while the "Isalo III" sandstones are not part of the same depositional sequence, and were deposited considerably later. and are perhaps better treated as part of several separate formations. It is traditionally divided into two subunits the lower, Bajocian aged Isalo IIIa unit also known as the Beronono Formation and the upper, Bathonian aged Isalo IIIb unit also known as the Sakaraha Formation or Sakahara Formation. The Sakaraha Formation consists of sandstones, marls and carbonates and represents a coastal plain environment, and is laterally equivalent to the predominantly carbonate Bemaraha Formation, which represents a coastal barrier lagoon complex. The formation is found in the northwest and in the southeast of the country and has provided a variety of fossils.

Haestasaurus is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur, belonging to the Macronaria, that during the Early Cretaceous lived in the area of present-day England. The only species is Haestasaurus becklesii.

Vouivria is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur, belonging to the Brachiosauridae, that lived in the area of present France during the Late Jurassic. The type species is Vouivria damparisensis.
Wamweracaudia is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania, Africa, 155-145 million years ago.

Narindasaurus is a genus of turiasaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Isalo III Formation of Madagascar. The type species, N. thevenini was formally described by Royo-Torres et al. in 2020. The holotype, which consists of one specimen, is currently stored at the Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle and has been since 1906 or 1907.