
Titanosaurs were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thriving at the time of the extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous. This group includes some of the largest land animals known to have ever existed, such as Patagotitan, estimated at 37 m (121 ft) long with a weight of 69 tonnes, and the comparably-sized Argentinosaurus and Puertasaurus from the same region.

Antarctosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. The type species, Antarctosaurus wichmannianus, and a second species, Antarctosaurus giganteus, were described by prolific German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1929. Three additional species of Antarctosaurus have been named since then but later studies have considered them dubious or unlikely to pertain to the genus.

Rhabdodon is a genus of ornithopod dinosaur that lived in Europe approximately 70-66 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous. It is similar in build to a very robust "hypsilophodont", though all modern phylogenetic analyses find this to be an unnatural grouping, and Rhabdodon to be a basal member of Iguanodontia. It was large amongst its relatives, measuring 4 m (13 ft) long and weighing 250 kg (550 lb), with some specimens possibly reaching up to 6 m (20 ft) long.

Ampelosaurus is a titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now France. Its type species is A. atacis, named by Le Loeuff in 1995. Its remains were found in a level dating from 71.5 million years ago representing the early Maastrichtian.

Epachthosaurus was a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It was a basal lithostrotian titanosaur. Its fossils have been found in Central and Northern Patagonia in South America.

Neuquensaurus is a genus of saltasaurid sauropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 80 million years ago in Argentina in South America. Its fossils were recovered from outcrops of the Anacleto Formation around Cinco Saltos, near the Neuquén river from which its name is derived.

Lirainosaurus is a genus of titanosaur sauropod which lived in what is now Spain. The type species, Lirainosaurus astibiae, was described by Sanz, Powell, Le Loeuff, Martinez, and Pereda-Suberbiola in 1999. It was a relatively small sauropod, measuring 4 metres (13 ft) long, possibly up to 6 metres (20 ft) long for the largest individuals, and weighed about 2–4 metric tons.

Puertasaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous Period. It is known from a single specimen recovered from sedimentary rocks of the Cerro Fortaleza Formation in southwestern Patagonia, Argentina, which probably is Campanian or Maastrichtian in age. The only species is Puertasaurus reuili. Described by the paleontologist Fernando Novas and colleagues in 2005, it was named in honor of Pablo Puerta and Santiago Reuil, who discovered and prepared the specimen. It consists of four well-preserved vertebrae, including one cervical, one dorsal, and two caudal vertebrae. Puertasaurus is a member of Titanosauria, the dominant group of sauropods during the Cretaceous.

Lithostrotia is a clade of derived titanosaur sauropods that lived during the Early Cretaceous and Late Cretaceous. The group was defined by Upchurch et al. in 2004 as the most recent common ancestor of Malawisaurus and Saltasaurus and all the descendants of that ancestor. Lithostrotia is derived from the Ancient Greek lithostros, meaning "inlaid with stones", referring to the fact that many known lithostrotians are preserved with osteoderms. However, osteoderms are not a distinguishing feature of the group, as the two noted by Unchurch et al. include caudal vertebrae with strongly concave front faces (procoely), although the farthest vertebrae are not procoelous.
Muyelensaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Argentina. It was more slender than other titanosaurs. Fossils have been recovered in the Neuquén province of Patagonia and were originally assigned to the Portezuelo Formation but further research showed that these layers belong to the Plottier Formation. The type species is M. pecheni. The name Muyelensaurus first appeared in a 2007 paper by Argentine paleontologists Jorge Calvo of the Universidad Nacional del Comahue and Bernardo González Riga of the Laboratorio de Paleovertebrados, and Brazilian paleontologist Juan Porfiri of the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro.

Diamantinasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod from Australia that lived during the early Late Cretaceous, about 94 million years ago. The type species of the genus is D. matildae, first described and named in 2009 by Scott Hocknull and colleagues based on fossil finds in the Winton Formation. Meaning "Diamantina lizard", the name is derived from the location of the nearby Diamantina River and the Greek word sauros, "lizard". The specific epithet is from the Australian song Waltzing Matilda, also the locality of the holotype and paratype. The known skeleton includes most of the forelimb, shoulder girdle, pelvis, hindlimb and ribs of the holotype, and one shoulder bone, a radius and some vertebrae of the paratype.

The Villalba de la Sierra Formation is a Campanian to Maastrichtian geologic formation in Spain. Fossil dinosaur eggs have been reported from the formation, that comprises gypsiferous, grey, argillaceous mudstones and sandstones, deposited in a floodplain environment characterised by high seasonality and variability in water availability.

Atsinganosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which existed in what is now France during the Late Cretaceous. Well-preserved remains of Atsinganosaurus were collected from the Grès à Reptiles Formation of the Aix-en-Provence Basin. The type and only species is A. velauciensis.

Paludititan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived in the area of present Romania during the Late Cretaceous. It existed in the island ecosystem known as Hațeg Island.

Austroposeidon is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Presidente Prudente Formation of Brazil. It contains one species, Austroposeidon magnificus.
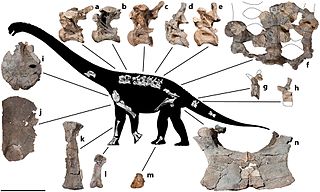
Savannasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Winton Formation of Queensland, Australia. It contains one species, Savannasaurus elliottorum, named in 2016 by Stephen Poropat and colleagues. The holotype and only known specimen, originally nicknamed "Wade", is the most complete specimen of an Australian sauropod, and is held at the Australian Age of Dinosaurs museum. Dinosaurs known from contemporary rocks include its close relative Diamantinasaurus and the theropod Australovenator; associated teeth suggest that Australovenator may have fed on the holotype specimen.

Lirainosaurinae is a subfamily of lithostrotian titanosaur sauropods from the Late Cretaceous of France, Spain, and Romania.

Lusovenator is a genus of carcharodontosaurian theropod dinosaur, from the Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) Praia de Amoreira Porto-Novo Member and the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous (Tithonian-Berriasian) Assenta Member of the Lourinhã Formation in present-day Portugal. It includes one species, Lusovenator santosi.

Abditosaurus is an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Tremp Group of Catalonia, Spain. The type and only species is Abditosaurus kuehnei. Phylogenetic analyses recover it within a clade of South American and African saltasaurines, distinct from other insular dwarf sauropods from the European archipelago. Abditosaurus inhabited the Ibero-Armorican Island, a prehistoric island made up of what is now Spain, Portugal, and southern France, and would have been the largest titanosaur species in its environment.

Garumbatitan is an extinct genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur from the Cretaceous Arcillas de Morella Formation of Spain. The genus contains a single species, G. morellensis, known from multiple partial skeletons.

































