
Mamenchisaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur known for their remarkably long necks which made up nearly half the total body length. Numerous species have been assigned to the genus; however, the validity of these assignments has been questioned. Fossils have been found in the Sichuan Basin and Yunnan Province in China. Several species from the Upper Shaximiao Formation, whose geologic age is uncertain, have been described. However, evidence suggests this formation to be no earlier than the Oxfordian stage of the Late Jurassic. M. sinocanadorum dates to the Oxfordian stage, and M. anyuensis to the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Most species were medium-large to large sauropods, measuring roughly 15 to 26 meters in length—possibly up to 35 meters (115 ft), based on two undescribed vertebrae.

Abrosaurus is a genus of macronarian sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period of what is now Asia, one of many dinosaurs found at the Dashanpu Quarry in the Sichuan Province of China. Like most sauropods, Abrosaurus was a quadrupedal herbivore but it was rather small for a sauropod, not much more than 30 feet (9.1 m) long. Its head was boxy and topped with a tall bony arch containing the nostrils.

Macronaria is a clade of sauropod dinosaurs. Macronarians are named after the large diameter of the nasal opening of their skull, known as the external naris, which exceeded the size of the orbit, the skull opening where the eye is located. Fossil evidence suggests that macronarian dinosaurs lived from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) through the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian). Macronarians have been found globally, including discoveries in Argentina, the United States, Portugal, China, and Tanzania. Like other sauropods, they are known to have inhabited primarily terrestrial areas, and little evidence exists to suggest that they spent much time in coastal environments. Macronarians are diagnosed through their distinct characters on their skulls, as well as appendicular and vertebral characters. Macronaria is composed of several subclades and families notably including Camarasauridae and Titanosauriformes, among several others. Titanosauriforms are particularly well known for being some of the largest terrestrial animals to ever exist.

Haplocanthosaurus is a genus of intermediate sauropod dinosaur. Two species, H. delfsi and H. priscus, are known from incomplete fossil skeletons. It lived during the late Jurassic period, 155 to 152 million years ago. The type species is H. priscus, and the referred species H. delfsi was discovered by a young college student named Edwin Delfs in Colorado, United States. Haplocanthosaurus specimens have been found in the very lowest layer of the Morrison Formation, along with Hesperosaurus mjosi, Brontosaurus yahnahpin, and Allosaurus jimmadseni.

Xuanhanosaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived during the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) of the Sichuan Basin, China, around 166 million years ago. This taxon represents one of the various non-coelurosaurian tetanuran taxa found on the Middle Jurassic of the region, uncovered in the Lower Shaximiao Formation. Although it has been known for more than 40 years, this taxon has been the subject of very few studies, although most seem to agree that it is a tetanuran, possibly a basal allosauroid, highlighting the fact that it has a vestigial fourth metacarpal.

Omeisaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period of what is now China. Its name comes from Mount Emei, where it was discovered in the lower Shaximiao Formation of Sichuan Province.
Volkheimeria is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now Argentina during the Early Jurassic, 178–179 million years ago. Its type and only species is Volkheimeria chubutensis.
Bashunosaurus is a genus of potentially macronarian sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation of Kaijiang, China. The type and only species is Bashunosaurus kaijiangensis.
Dashanpusaurus is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the middle of the Jurassic period. The dinosaur was described in 2005 by Peng Guangzhao, Ye Yong, Gao Yuhui, Shu Chunkang, and Jiang Shan. Its type and only species is Dashanpusaurus dongi, named in honor of the paleontologist Dong Zhiming.

The Shaximiao Formation is a Middle to Late Jurassic aged geological formation in Sichuan, China, most notable for the wealth of dinosaurs fossils that have been excavated from its strata. The Shaximiao Formation is exposed in and around the small township of Dashanpu, situated seven kilometres north-east from Sichuan's third largest city, Zigong, in the Da'an District.

Camarasauridae is a family of sauropod dinosaurs. Among sauropods, camarasaurids are small to medium-sized, with relatively short necks. They are visually identifiable by a short skull with large nares, and broad, spatulate teeth filling a thick jaw. Based on cervical vertebrae and cervical rib biomechanics, camarasaurids most likely moved their necks in a vertical, rather than horizontal, sweeping motion, in contrast to most diplodocids.

Neosauropoda is a clade within Dinosauria, coined in 1986 by Argentine paleontologist José Bonaparte and currently described as Saltasaurus loricatus, Diplodocus longus, and all animals directly descended from their most recent common ancestor. The group is composed of two subgroups: Diplodocoidea and Macronaria. Arising in the early Jurassic and persisting until the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Neosauropoda contains the majority of sauropod genera, including genera such as Apatosaurus, Brachiosaurus, and Diplodocus. It also includes giants such as Argentinosaurus, Patagotitan and Sauroposeidon, and its members remain the largest land animals ever to have lived.
The Zhiluo Formation is a geological formation in China, it is also alternatively considered a geological group under the name Zhiluo Group. It dates to the Middle Jurassic. It consists of sandstone, mudstone and siltstone of varying colours. It has received scientific attention for its uranium ore bodies present in the lower part of the formation. Fossil theropod tracks have been reported from the formation. These were described from two footprints found in Jiaoping Coal Mine by C. C. Young in 1966 as Shensipus tungchuanensis. These were in 2015 suggested to belong to Anomoepus. The dinosaur Lingwulong has been suggested to have come from the strata of this formation, previously having been attributed to the underlying Yanan Formation.
Isaberrysaura is a genus of stegosaurian ornithischian dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Los Molles Formation of Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, I. mollensis, described by Salgado et al. in 2017 from a single specimen. Although initially classified as a basal neornithischian, subsequent analysis has allied it with the Stegosauria; the morphology of its skull resembles those of other members of the group.

Lingwulong is a genus of dicraeosaurid sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of what is now Lingwu, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China. The type and only species is L. shenqi, known from several partial skeletons. It is the earliest-aged neosauropod ever discovered, as well as the only definite diplodocoid from east Asia.
The Yanan Formation, alternatively spelled the Yan'an Formation, is a geological formation in China, it is also alternatively considered a group. The age of the formation is uncertain, with estimates ranging from Toarcian to Bajocian. It is divided up into 5 members, with the designation of Y1 through Y5. Y2, Y3 and Y4 are predominantly dark shales, while Y1 and Y5 are composed of sandstones, coal beds and interbedded mudstones. The depositional environment at the time was when the Ordos Basin formed a large inland lake, surrounded by floodplains. The dark shales have been explored for the potential of producing shale gas. The coal has also been explored for the production of coalbed methane. The formation is also notable for its fossil content, with dinosaur footprints having been found in the formation. The dinosaur Lingwulong was formerly thought to have been found in this formation, but the strata was later attributed to the overlying Zhiluo Formation.
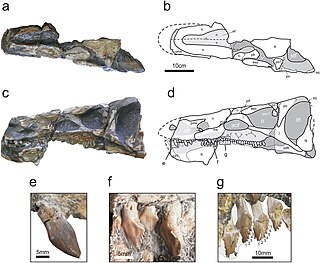
Sanxiasaurus is a genus of neornithischian dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Xintiangou Formation in the Chongqing Municipality of China. The type and only species is S. modaoxiensis. The holotype is a partial postcranial skeleton consisting of "55 bones including two cervical vertebrae, 11 dorsal vertebrae, 4 sacral vertebrae, 18 caudal vertebrae, both humeri, radii and ulnas, partial right ilium, partial right ischium, both femora and tibiae, left fibula, 3 metatarsi and 4 phalanges." In a phylogenetic analysis, it was found to be a basal neornithischian, more derived than Lesothosaurus and less derived than Hexinlusaurus.
The Xintiangou Formation is a geological formation in China. Part of the stratigraphy of the Sichuan Basin, it is of an uncertain Middle Jurassic age, with preliminary U-Pb estimates giving an age range of 170 ma. It predominantly consists of interbedded mudstone and sandstone, with subordinate shelly limestone. At the Laojun site remains of lungfish, bony fish, freshwater sharks, temnospondyls, plesiosaurs, crocodyliformes, the Xinjiangchelyid turtle Protoxinjiangchelys and tritylodontids are known. The dinosaurs Sanxiasaurus,Yunyangosaurus, and indeterminate sauropods are also known from the formation. Theropod and ornithopod tracks have also been reported from the formation.
Yunyangosaurus is a genus of possible megalosauroid dinosaur from the Xintiangou Formation in Chongqing, China. The type and only species is Yunyangosaurus puanensis. The name was first published in the 2019 SVP abstract book by Dai (2019) before it was formally described by Dai et al. (2020).

Bashanosaurus is an extinct genus of stegosaurian dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation of Yunyang County, China. The genus contains a single species, Bashanosaurus primitivus, known from incomplete skeletons belonging to three individuals. It is one of the basalmost stegosaurs, as well as one of the oldest known stegosaurs, along with Adratiklit, Isaberrysaura, and Thyreosaurus.

























