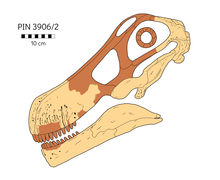
Tarbosaurus is a genus of large tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 70 million years ago. It contains the single type species: Tarbosaurus bataar, which is known from the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia, with more fragmentary remains found further afield in the Subashi Formation of China. Tarbosaurus is represented by dozens of fossil specimens, including several complete skulls and skeletons. These remains have allowed studies focusing on its phylogeny, skull mechanics, and brain structure. Further fossil remains have been reported from other geologic formations of Asia, however, these remains are fragmentary and can not be confidently assigned to Tarbosaurus or the type species.

Nemegtosauridae is a family of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaurs based on their diplodocid-like skulls. Only three species are known: Nemegtosaurus, Quaesitosaurus and possibly Tapuiasaurus, each from the Cretaceous.

Avimimus, meaning "bird mimic", is a genus of oviraptorosaurian theropod dinosaur, named for its bird-like characteristics, that lived in the late Cretaceous in what is now Mongolia, around 85 to 70 million years ago.

Bonitasaura is a genus of titanosaurian dinosaur hailing from uppermost layers of the Late Cretaceous (Santonian) Bajo de la Carpa Formation, Neuquén Group of the eastern Neuquén Basin, located in Río Negro Province, Northwestern Patagonia, Argentina. The remains, consisting of a partial sub-adult skeleton jumbled in a small area of fluvial sandstone, including a lower jaw with teeth, a partial vertebrae series, and limb bones, were described by Sebastian Apesteguía in 2004.

Alioramus is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period of Asia. It currently contains two species. The type species, A. remotus is known from a partial skull and three foot bones recovered from the Mongolian Nemegt Formation, which was deposited in a humid floodplain about 70 million years ago. These remains were named and described by Soviet paleontologist Sergei Kurzanov in 1976. A second species, A. altai, known from a much more complete skeleton also from the Nemegt Formation, was named and described by Stephen L. Brusatte and colleagues in 2009. Its relationships to other tyrannosaurid genera were at first unclear, with some evidence supporting a hypothesis that Alioramus was closely related to the contemporary species Tarbosaurus bataar. However, the discovery of Qianzhousaurus indicates that it belongs to a distinct branch of tyrannosaurs, namely the tribe Alioramini.

Nemegtosaurus was a sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now Mongolia. It was named after the Nemegt Basin in the Gobi Desert, where the remains — a single skull — were found. The skull resembles diplodocoids in being long and low, with pencil-shaped teeth. However, recent work has shown that Nemegtosaurus is in fact a titanosaur, closely related to animals such as Saltasaurus, Alamosaurus and Rapetosaurus.

Opisthocoelicaudia is a genus of sauropod dinosaur of the Late Cretaceous Period discovered in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. The type species is Opisthocoelicaudia skarzynskii. A well-preserved skeleton lacking only the head and neck was unearthed in 1965 by Polish and Mongolian scientists, making Opisthocoelicaudia one of the best known sauropods from the Late Cretaceous. Tooth marks on this skeleton indicate that large carnivorous dinosaurs had fed on the carcass and possibly had carried away the now-missing parts. To date, only two additional, much less complete specimens are known, including part of a shoulder and a fragmentary tail. A relatively small sauropod, Opisthocoelicaudia measured about 11.4–13 m (37–43 ft) in length. Like other sauropods, it would have been characterised by a small head sitting on a very long neck and a barrel shaped trunk carried by four column-like legs. The name Opisthocoelicaudia means "posterior cavity tail", alluding to the unusual, opisthocoel condition of the anterior tail vertebrae that were concave on their posterior sides. This and other skeletal features lead researchers to propose that Opisthocoelicaudia was able to rear on its hindlegs.

Bagaceratops is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. Bagaceratops remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of Bagaceratops in the Djadochta Formation.
Jeffrey A. Wilson, also known as JAW, is a paleontologist and professor of geological sciences and assistant curator at the Museum of Paleontology at the University of Michigan.

Breviceratops is a genus of protoceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Barun Goyot Formation, Mongolia.

Udanoceratops is a genus of large leptoceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period of Mongolia.

Tylocephale is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur, a group of dome-headed, herbivorous ornithischians, that lived during the Late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous in what is now Mongolia. It is known from a partial skull and associated mandible that were unearthed in 1971 by a Polish-Mongolian Expedition to the Barun Goyot Formation of the Gobi Desert. The specimen was described in 1974 by Polish paleontologists Teresa Maryańska and Halszka Osmólska as a new genus and species.

Kuru is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod from the Late Cretaceous Barun Goyot Formation of Mongolia. The genus contains only a single species, the type species Kuru kulla, which is known from a fragmentary skeleton including a partial skull.

The Barun Goyot Formation is a geological formation dating to the Late Cretaceous Period. It is located within and is widely represented in the Gobi Desert Basin, in the Ömnögovi Province of Mongolia.

Minotaurasaurus is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Djadochta Formation. The type and only species, Minotaurasaurus ramachandrani, is known from two skulls, a cervical vertebra and a cervical half ring. It was named and described in 2009 by Clifford Miles and Clark Miles. The first fossils of Minotaurasaurus were illegally exported out of Mongolia.It has been suggested to be a synonym of Tarchia but more recent publications consider it as a distinct genus.

Ceratonykus is a monospecific genus of alvarezsaurid dinosaur from Mongolia that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Barun Goyot Formation. The type and only species, Ceratonykus oculatus, is known from a fragmentary skeleton, including an incomplete skull, of an adult individual. It was named and described in 2009 by Vladimir Alifanov and Rinchen Barsbold. Its describers questioned the traditional placement of alvarezsaurs in Theropoda, instead suggesting they were ornithischians, but this has not been accepted since. Ceratonykus has an estimated length of 75 centimetres and weight of 760 grams. It has been considered as a possible junior synonym of Parvicursor.
Khulsanurus is an extinct genus of alvarezsaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Barungoyot Formation of the Khulsan Locality in the Gobi Desert region of Mongolia. The type and only species is Khulsanurus magnificus.

Ondogurvel is a genus of alvarezsaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) Barun Goyot Formation in southern Mongolia. The type and only species is O. alifanovi, known from a partial skeleton consisting of fragments of two last dorsal vertebrae, three anterior sacral vertebrae, right ilium, left and right pubis and ischium, articulated right tibia, fibula, metatarsals II and IV, and phalanges IV-1 and IV-2, right carpometacarpus, left and right manual phalanx II-1, right femur, left pedal phalanx II-1, and fragments of unidentified phalanges.

Natovenator is a genus of halszkaraptorine dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Barun Goyot Formation of Mongolia. The genus is known from a single species, N. polydontus. Natovenator is crucial to the understanding of halszkaraptorines due to it providing more support for the semi-aquatic lifestyle that has been proposed for this clade. This discovery is important as the semi-aquatic lifestyles of halszkaraptorines was contested in early 2022.

Jaculinykus is an extinct genus of alvarezsaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Baruungoyot Formation of Mongolia. The genus contains a single species, J. yaruui, known from a nearly complete articulated skeleton including bones of the skull. Jaculinykus is notable for its unique hand, which has a hypertrophied first digit and greatly reduced second digit, which is intermediate between the tridactyl hand of Shuvuuia and monodactyl hand of Linhenykus.