
Mamenchisaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur known for their remarkably long necks which made up nearly half the total body length. Numerous species have been assigned to the genus; however, the validity of these assignments has been questioned. Fossils have been found in the Sichuan Basin and Yunnan Province in China. Several species from the Upper Shaximiao Formation, whose geologic age is uncertain, have been described. However, evidence suggests this formation to be no earlier than the Oxfordian stage of the Late Jurassic. M. sinocanadorum dates to the Oxfordian stage, and M. anyuensis to the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Most species were medium-large to large sauropods, measuring roughly 15 to 26 meters in length—possibly up to 35 meters (115 ft), based on two undescribed vertebrae.

Agilisaurus is a genus of ornithischian dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period of what is now eastern Asia. It was about 3.5–4 ft long, 2 ft in height and 40 kg in weight.

Chialingosaurus is a genus of herbivorous stegosaurian dinosaur similar to Kentrosaurus from the Upper Shaximiao Formation, Late Jurassic beds in Sichuan Province in China. Its age makes it one of the oldest species of stegosaurs, living about 160 million years ago. Since it was an herbivore, scientists think that Chialingosaurus probably ate ferns and cycads, which were plentiful during the period when Chialingosaurus was alive.

Lufengosaurus is a genus of massospondylid dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic period in what is now southwestern China.

Shunosaurus, meaning "Lizard from Sichuan", is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) beds in Sichuan Province in China, from 161 to 157 Million years ago. The name derives from "Shu", an ancient name for the Sichuan province.

Yang Zhongjian, also Yang Chung-chien, courtesy name Keqiang (克强), also known as C.C. Young, was a Chinese paleontologist and zoologist. He was one of China's foremost vertebrate paleontologists. He has been called the "Father of Chinese Vertebrate Paleontology".

Yunnanosaurus is an extinct genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived approximately 199 to 183 million years ago in what is now the Yunnan Province, in China, for which it was named. Yunnanosaurus was a large sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could also walk bipedally, and ranged in size from 7 meters (23 feet) long and 2 m (6.5 ft) high to 4 m (13 ft) high in the largest species.

Sinosaurus is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic Period. It was a bipedal carnivore similar to Dilophosaurus, with proportionally large limbs to its slender body. Fossils of the animal were found at the Lufeng Formation, in the Yunnan Province of China.

Gyposaurus is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur from the early Jurassic of South Africa. It is usually considered to represent juveniles of other prosauropods, but "G." sinensis is regarded as a possibly valid species.
Fulengia is a dubious genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Early Jurassic Lufeng Formation of China.
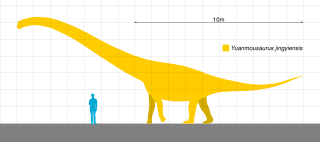
Yuanmousaurus was a sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic period of China. It is known from incomplete remains, recovered in 2000 from the Zhanghe Formation in Yuanmou County in Yunnan Province. Yuanmousaurus was a relatively large sauropod and may have reached about 17 meters (56 ft) in length. It was a basal member of the Sauropoda, but its exact systematic position is unclear. A recent study placed Yuanmousaurus within the family Mamenchisauridae. It may be a dubious genus. The only and type species was Yuanmousaurus jiangyiensis.
The Lufeng Formation is a Lower Jurassic sedimentary rock formation found in Yunnan, China. It has two units: the lower Dull Purplish Beds/Shawan Member are of Hettangian age, and Dark Red Beds/Zhangjia'ao Member are of Sinemurian age. It is known for its fossils of early dinosaurs. The Dull Purplish Beds have yielded the possible therizinosaur Eshanosaurus, the possible theropod Lukousaurus, and the "prosauropods" "Gyposaurus" sinensis, Lufengosaurus, Jingshanosaurus, and Yunnanosaurus. Dinosaurs discovered in the Dark Red Beds include the theropod Sinosaurus triassicus, the "prosauropods" "Gyposaurus", Lufengosaurus, and Yunnanosaurus, indeterminate remains of sauropods, and the early armored dinosaurs Bienosaurus and Tatisaurus.

The Lufeng Dinosaur Museum is located in Jingshan, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, China.

Dibothrosuchus is a genus of sphenosuchian, a type of basal crocodylomorph, the clade that comprises the crocodilians and their closest kin. It is known from several partial skeletons and skulls. These fossils were found in Lower Jurassic rocks of Yunnan, China. Dibothrosuchus was a small terrestrial crocodylomorph that probably had a keen sense of hearing, and thus was probably a vocal animal like modern crocodilians.

Ursavus is an extinct genus of bear that existed in North America, Europe, and Asia during the Miocene period, about 23–5.3 million years ago (Mya), existing for roughly 17.7 million years. The genus apparently dispersed from Asia into North America about 20 Mya, becoming the earliest member of the subfamily Ursinae in the New World. Qiu points out that if a questionable 29 million-year-old specimen of Ursavus reported in North America is validated, Ursavus may have evolved in North America and dispersed westward into Asia. The higher number of fossils in Europe grading toward eastern Asia make the westward dispersal unlikely.
Tonganosaurus is a genus of mamenchisaurid sauropod dinosaur, similar to Omeisaurus. It is known from one specimen consisting of twenty vertebrae, a front limb and pectoral girdle, and a complete hind limb with partial hip. It was discovered in the Yimen Formation, China. The horizon of the specimen and the age of the Yimen Formation is controversial. The formation has been divided into three levels, and Tonganosaurus appears to be of late Early Jurassic (Pliensbachian) age. Tonganosaurus is the oldest known member of the mamenchisaurids, being almost 15 million years older than the next-oldest members of the group. It was first named by Li Kui, Yang Chun-Yan, Liu Jian and Wang Zheng-Xin in 2010 and the type species is Tonganosaurus hei.

Yizhousaurus is a genus of basal sauropodiform dinosaurs which existed in what is now Lufeng Formation, Yunnan Province of southern China during the lower Jurassic period. Identified from a nearly complete and exquisitely preserved skeleton, it is the most complete basal sauropod currently known with intact skull. Although its name was revealed in a 2010 Geological Society of America abstract by Sankar Chatterjee, T. Wang, S.G. Pan, Z. Dong, X.C. Wu, and Paul Upchurch, it wasn't validly named and described until 2018. The type species is Yizhousaurus sunae.
Chuxiongosaurus is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic Period. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Lower Lufeng Formation, Yunnan Province, southern China. Identified from the holotype CMY LT9401 a nearly complete skull with some similarities to Thecodontosaurus, it was described as the "first basal sauropod dinosaur from the Early Jurassic of China," more basal than Anchisaurus. It was named by Lü Junchang, Yoshitsugu Kobayashi, Li Tianguang and Zhong Shimin in 2010, and the type species is Chuxiongosaurus lufengensis. It is a possible junior synonym of Jingshanosaurus.

Nebulasaurus is an extinct genus of basal eusauropod dinosaur known from the early Middle Jurassic Zhanghe Formation of Yunnan Province, China. It is known only from the holotype braincase LDRC-v.d.1. A phylogenetic analysis found Nebulasaurus to be a sister taxon to Spinophorosaurus from the Middle Jurassic of Africa. This discovery is significant paleontologically because it represents a clade of basal eusauropods previously unknown from Asia.
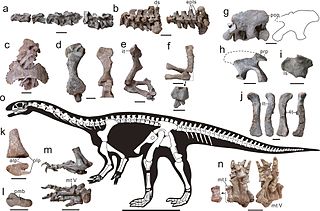
Xingxiulong is a genus of bipedal sauropodiform from the Early Jurassic of China. It contains a single species, X. chengi, described by Wang et al. in 2017 from three specimens, two adults and an immature individual, that collectively constitute a mostly complete skeleton. Adults of the genus measured 4–5 metres (13–16 ft) long and 1–1.5 metres tall. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that Xingxiulong is most closely related to its contemporary Jingshanosaurus, although an alternative position outside of both the Sauropodiformes and Massospondylidae is also plausible.





























