
Aeolosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. Like most sauropods, it would have been a quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and tail. Aeolosaurus is well known for a titanosaur, as it is represented by the remains of several individuals belonging to at least two species. However, like most titanosaurs, no remains of the skull are known. The holotype of Aeolosaurus rionegrinus consists of a series of seven tail vertebrae, as well as parts of both forelimbs and the right hindlimb. It was discovered in the Angostura Colorada Formation in Argentina, which dates from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 83 to 74 million years ago. The species A. maximus was transferred over to the new genus Arrudatitan in 2021.
Agustinia is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of South America. The genus contains a single species, A. ligabuei, known from a single specimen that was recovered from the Lohan Cura Formation of Neuquén Province in Argentina. It lived about 116–108 million years ago, in the Aptian–Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous Period.

Bonitasaura is a genus of titanosaurian dinosaur hailing from uppermost layers of the Late Cretaceous (Santonian) Bajo de la Carpa Formation, Neuquén Group of the eastern Neuquén Basin, located in Río Negro Province, Northwestern Patagonia, Argentina. The remains, consisting of a partial sub-adult skeleton jumbled in a small area of fluvial sandstone, including a lower jaw with teeth, a partial vertebrae series, and limb bones, were described by Sebastian Apesteguía in 2004.

Isisaurus is a genus of titanosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Lameta Formation of India and Pab Formation of Pakistan. The genus contains a single species, Isisaurus colberti.
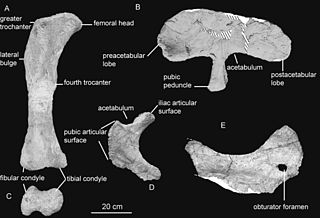
Rocasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod that lived in South America. Rocasaurus was discovered in Argentina in 2000, within the Allen Formation which is dated to be middle Campanian to early Maastrichtian in age. This genus grew up to 8 metres (26 ft) long, making it one of the smaller sauropods. It seems to be closely related to saltasaurid dinosaurs, like Saltasaurus and Neuquensaurus.
The Plottier Formation is a geologic formation that outcrops in the Argentine Patagonian provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén. It is the younger of two formations belonging to the Río Neuquén Subgroup within the Neuquén Group of the Neuquén Basin, with the oldest rocks dating from the late Coniacian and its youngest maybe from the very start of the Santonian. Formerly, that subgroup was treated as a formation, and the Plottier Formation was known as the Plottier Member.

The Bajo de la Carpa Formation is a geologic formation of the Neuquén Basin that crops out in northern Patagonia, in the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén, Argentina. It is the oldest of two formations belonging to the Río Colorado Subgroup within the Neuquén Group. Formerly, that subgroup was treated as a formation, and the Bajo de la Carpa Formation was known as the Bajo de la Carpa Member.

The Anacleto Formation is a geologic formation with outcrops in the Argentine Patagonian provinces of Mendoza, Río Negro, and Neuquén. It is the youngest formation within the Neuquén Group and belongs to the Río Colorado Subgroup. Formerly that subgroup was treated as a formation, and the Anacleto Formation was known as the Anacleto Member.
Pitekunsaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Anacleto Formation of Neuquén, Argentina. It was described by L. Filippi and A. Garrido in 2008. The type species is P. macayai. The generic name is derived from Mapudungun pitekun, meaning "to discover", the epitheton honours the discoverer, oil company explorer Luis Macaya, who found the fossil in April 2004.

Lognkosauria is a clade of giant long-necked sauropod dinosaurs within the clade Titanosauria. It includes some of the largest and heaviest dinosaurs known. They lived in South America and likely Asia during the Late Cretaceous period.

Petrobrasaurus is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur. It is a titanosaur which lived during the upper Cretaceous period in what is now Rincón de los Sauces, Patagonia, Argentina. It is known from the holotype MAU-Pv-PH-449 — a partial disarticulated skeleton recovered from the Plottier Formation, Argentina. This genus was named by Leonardo S. Filippi, José Ignacio Canudo, Leonardo J. Salgado, Alberto C. Garrido, Rodolfo A. Garcia, Ignacio A. Cerda and Alejandro Otero in 2011, and the type species is Petrobrasaurus puestohernandezi. The generic name is derived from "Petrobras" and saurus, "lizard". The specific name refers to the Puesto Hernández oil field, where the fossil remains were found.

Aeolosaurini is an extinct clade of titanosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous period of Argentina and Brazil. Rodrigo M. Santucci and Antonio C. de Arruda-Campos (2011) in their cladistic analysis found Aeolosaurus, Gondwanatitan, Maxakalisaurus, Panamericansaurus and Rinconsaurus to be aeolosaurids.

Overosaurus is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaurs, containing only a single species, Overosaurus paradasorum. This species lived approximately 86 to 84 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Patagonia. Overosaurus paradasorum was relatively small compared to other sauropods from Patagonia, like the saltasaurids and other aeolosaurines, estimated as approximately 10 m (33 ft). It was a ground-dwelling herbivore.

Eutitanosauria is a clade of titanosaurs, encompassing the more derived members of the group and characterized by the absence of the hyposphene-hypantrum articulation and possibly the presence of osteoderms. The group was first named by Sanz and colleagues in 1999, who used it to unite the group of Argyrosaurus, Lirainosaurus, Saltasaurus and the Peiropolis titanosaur. However, this definition was not used as it made the group equivalent to Saltasauridae, so Saldago redefined it in 2003 to be all titanosaurs closer to Saltasaurus than Epachthosaurus. This definition created Eutitanosauria as the sister group to Epachthosaurinae, but was problematic due to the variable nature of Epachthosaurus. Eutitanosauria was often broadly similar to Lithostrotia, and has often been unused or unlabelled on phylogenies. Sometimes Epachthosaurus would be more primitive than Malawisaurus, making Eutitanosauria more encompassing than Lithostrotia, or Epachthosaurus could nest close to Colossosauria and limit Eutitanosauria to a smaller group of saltasauroids. Because of the flexible nature of Epachthosaurus in basal titanosaur phylogeny, Carballido and colleagues redefined the group in 2022 to include the smallest clade of both Patagotitan, a colossosaur, and Saltasaurus, creating a node-stem clade with Colossosauria and Saltasauroidea, presenting the informal cladogram of stable titanosaur clades below.

Brasilotitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Adamantina Formation of Brazil. The type species is Brasilotitan nemophagus. Brasilotitan was a small titanosaur with a squared-off snout, and may be closely related to another Brazilian titanosaur, Uberabatitan.

Notocolossus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from late Cretaceous strata of Mendoza Province, Argentina.

Rinconsauria is an extinct clade of giant titanosaurian sauropods known from the late Cretaceous period of Argentina.
The Sierra Barrosa Formation is a geologic formation of the Neuquén Basin in the northern Patagonian provinces of Mendoza and Neuquén. The formation dates to the Late Cretaceous, middle to late Coniacian, and belongs to the Río Neuquén Subgroup of the Neuquén Group. The formation overlies the Los Bastos Formation and is overlain by the Plottier Formation. As the underlying Los Bastos Formation, the Sierra Barrosa Formation comprises mudstones and sandstones deposited in a fluvial environment.
Teratopodus is an ichnogenus of titanosaurian sauropod footprint. It includes a single species, T. malarguensis, known from prints found in the Late Cretaceous Anacleto Formation of Argentina. The Teratopodus tracks represent some of the best sauropod pes tracks currently known from South America.

Inawentu is an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Bajo de la Carpa Formation of Argentina. The genus contains a single species, I. oslatus, known from a partial articulated skeleton including the skull. The square-shaped jaw of Inawentu demonstrates convergent characteristics with rebbachisaurids.


























