
The rosids are members of a large clade of flowering plants, containing about 70,000 species, more than a quarter of all angiosperms.

Sarcococca is a genus of 11 species of flowering plants in the box family Buxaceae, native to eastern and southeastern Asia and the Himalayas. They are slow-growing, monoecious, evergreen shrubs 1–2 m (3–7 ft) tall. The leaves are borne alternately, 3–12 cm long and 1–4 cm broad.
The APG II system of plant classification is the second, now obsolete, version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy that was published in April 2003 by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. It was a revision of the first APG system, published in 1998, and was superseded in 2009 by a further revision, the APG III system.

Aphloia is a genus of flowering plants that contains a single species, Aphloia theiformis, the sole species of the monogeneric family Aphloiaceae. It is a species of evergreen shrubs or small trees occurring in East Africa, Madagascar, the Mascarene Islands and the Seychelles.

Rhodiola is a genus of perennial plants in the family Crassulaceae that resemble Sedum and other members of the family. Like sedums, Rhodiola species are often called stonecrops. Some authors merge Rhodiola into Sedum.

Bonnetia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bonnetiaceae. Most of the roughly 30 species are shrubs. The remaining species, all trees, are among the dominant species in the forest vegetation on the tepui plateaus of northern South America, such as B. roraimae on the summit of Mount Roraima.

Phedimus spurius, the Caucasian stonecrop or two-row stonecrop, is a species of flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It is still widely listed in the literature as Sedum spurium.

Hylotelephium is a genus of flowering plants in the stonecrop family Crassulaceae. It includes about 33 species distributed in Asia, Europe, and North America.

Aizopsis is a genus of the succulent family Crassulaceae, found in east Asia.

Petrosedum is a genus of the succulent family Crassulaceae.

Phedimus is a genus of the succulent family Crassulaceae, with about 18 species, distributed in eastern Europe and Asia. The genus is described with two subgenera, but one of these is also recognized as a separate genus, Aizopsis. Phedimus kamtschaticus is widely grown as an ornamental ground cover and has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.

Petrosedum is a genus of the succulent plant family Crassulaceae.
Tanakaea radicans, the Japanese foam flower, is a member of the Saxifrage family native to Japan, and is the sole species in the genus Tanakaea. It is named after the Japanese botanist Tanaka Yoshio. It was initially described by Ludovic Savatier and Adrien René Franchet.

Berberidopsis beckleri is a species of climbing plant found in cool rainforests in eastern Australia. Its common name is the montane tape vine. Ferdinand von Mueller described the plant as Streptothamnus beckleri from collections at the Clarence River.
Afrovivella is a monotypic genus of the succulent plant family Crassulaceae. The sole species is Afrovivella semiensis.

Peridiscus lucidus is a species of flowering plant, the only species in the genus Peridiscus, which is one of four genera within the family Peridiscaceae. It grows in Venezuela and northern Brazil, in evergreen, sometimes riverine forests. It was originally described by Bentham and Hooker in 1862. The taxonomic history of Peridiscus and of Peridiscaceae is complex, and has been resolved by molecular phylogenetic analysis.
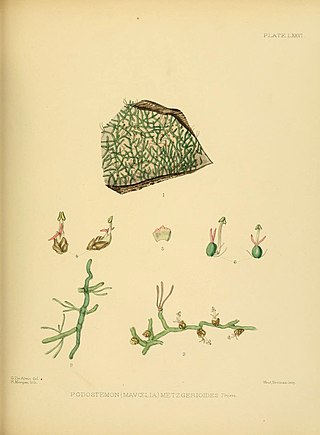
Farmeria is a genus of flowering plants in the riverweed family Podostemaceae, native to Sri Lanka and India. They attach to rocks using holdfasts, and their flowers are protected by boat-shaped spathella until they emerge.















