
Melanthiaceae, also called the bunchflower family, is a family of flowering herbaceous perennial plants native to the Northern Hemisphere. Along with many other lilioid monocots, early authors considered members of this family to belong to the family Liliaceae, in part because both their sepals and petals closely resemble each other and are often large and showy like those of lilies, while some more recent taxonomists have placed them in a family Trilliaceae. The most authoritative modern treatment, however, the APG III system of 2009, places the family in the order Liliales, in the clade monocots. Circumscribed in this way, the family includes up to 17 genera.

Alstroemeriaceae is a family of flowering plants, with 254 known species in four genera, almost entirely native to the Americas, from Central America to southern South America. One species of Luzuriaga occurs in New Zealand, and the genus Drymophila is endemic to south-eastern Australia.

Petrosaviaceae is a family of flowering plants belonging to a monotypic order, Petrosaviales. Petrosaviales are monocots, and are grouped within the lilioid monocots. Petrosaviales is a very small order – one family, two genera and four species were accepted in 2016 – ) of photosynthetic (Japonolirion) and rare, leafless, achlorophyllous, mycoheterotrophic plants (Petrosavia), found in low-light montane rainforests in Japan, China, Southeast Asia and Borneo. They are characterised by having bracteate racemes, pedicellate flowers, six persistent tepals, septal nectaries, three almost-distinct carpels, simultaneous microsporogenesis, monosulcate pollen, and follicular fruit.

Nartheciaceae is a family of flowering plants. The APG III system places it in the order Dioscoreales, in the clade monocots. As circumscribed by APG IV (2016) it includes 35 species of herbaceous plants in the following five genera:

Colchicaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes 15 genera with a total of about 285 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016.

The Xyridaceae are a family of flowering plants. This family has been recognized by many taxonomists and is known as the yellow-eyed grass family.

Haemodoraceae is a family of perennial herbaceous flowering plants with 14 genera and 102 known species. It is sometimes known as the "bloodroot family". Primarily a Southern Hemisphere family, they are found in South Africa, Australia and New Guinea, and in the Americas. Perhaps the best known are the widely cultivated and unusual kangaroo paws from Australia, of the two closely related genera Anigozanthos and Macropidia.

Asphodelaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Asparagales. Such a family has been recognized by most taxonomists, but the circumscription has varied widely. In its current circumscription in the APG IV system, it includes about 40 genera and 900 known species. The type genus is Asphodelus.

Hypoxidaceae is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots.

The Thurniaceae are a family of flowering plants composed of two genera with four species. The botanical name has been recognized by most taxonomists.

Dasypogonaceae is a family of flowering plants based on the type genus Dasypogon, one that has traditionally not been commonly recognized by taxonomists; the plants it contains were usually included in the family Xanthorrhoeaceae. If valid, Dasypogonaceae includes four genera with 16 species. The family is endemic to Australia. The best known representative is Kingia australis.

Cyclanthaceae is a family of flowering plants.

The Rapateaceae are a family of flowering plants. The botanical name has been recognized by most taxonomists.

Corsiaceae is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants. The APG II system (2003) treats the family in the order Liliales, in the clade monocots. This is a slight change from the APG system, of 1998, which left the family unplaced as to order, but did assign it also to the monocots.
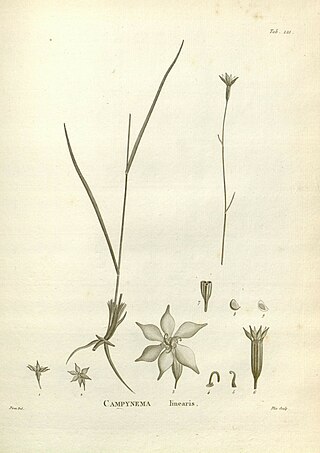
Campynemataceae (Campynemaceae) is a family of flowering plants. The family consists of two genera and four species of perennial herbaceous plants endemic to New Caledonia and Tasmania.

Philydraceae is a family of flowering plants composed of three genera and a total of six known species. Such a family has not been recognized by many taxonomists.

Boryaceae is a family of highly drought-tolerant flowering plants native to Australia, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. The family includes two genera, with twelve species in total in Australia.

Tecophilaeaceae is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. It consists of nine genera with a total of 27 species.

The Ecdeiocoleaceae comprise a family of flowering plants with two genera and three species. The botanical name has rarely been recognized by taxonomists.

Huaceae is a family of plant in the rosids group, which has been classed in the orders Malpighiales, Malvales, and Violales or in its own order Huales. The APG II system placed it in the clade eurosids I, whereas the APG III system of 2009 and APG IV (2016) place it within the Oxalidales. The family is endemic to central Africa. It contains four species in the following two genera:




















