
The Nymphaeales are an order of flowering plants, consisting of three families of aquatic plants, the Hydatellaceae, the Cabombaceae, and the Nymphaeaceae. It is one of the three orders of basal angiosperms, an early-diverging grade of flowering plants. At least 10 morphological characters unite the Nymphaeales. One of the traits is the absence of a vascular cambium, which is required to produce both xylem (wood) and phloem, which therefore are missing. Molecular synapomorphies are also known.

Nymphaeaceae is a family of flowering plants, commonly called water lilies. They live as rhizomatous aquatic herbs in temperate and tropical climates around the world. The family contains five genera with about 70 known species. Water lilies are rooted in soil in bodies of water, with leaves and flowers floating on or rising from the surface. Leaves are oval and heart-shaped in Barclaya. Leaves are round, with a radial notch in Nymphaea and Nuphar, but fully circular in Victoria and Euryale.

The Cornaceae are a cosmopolitan family of flowering plants in the order Cornales. The family contains approximately 85 species in two genera, Alangium and Cornus. They are mostly trees and shrubs, which may be deciduous or evergreen, although a few species are perennial herbs. Members of the family usually have opposite or alternate simple leaves, four- or five-parted flowers clustered in inflorescences or pseudanthia, and drupaceous fruits. The family is primarily distributed in northern temperate regions and tropical Asia. In northern temperate areas, Cornaceae are well known from the dogwoods Cornus.

Ceratophyllum is a cosmopolitan genus of flowering plants commonly found in ponds, marshes, and quiet streams in tropical and in temperate regions. It is the only extant genus in the family Ceratophyllaceae, itself the only extant family in the order Ceratophyllales. They are usually called coontails or hornworts, although hornwort is also used for unrelated plants of the division Anthocerotophyta.

Nyssaceae is a family of flowering trees sometimes included in the dogwood family (Cornaceae). Nyssaceae is composed of 37 known species in the following five genera:

Petrosaviaceae is a family of flowering plants belonging to a monotypic order, Petrosaviales. Petrosaviales are monocots, and are grouped within the lilioid monocots. Petrosaviales is a very small order composed of one family, two genera and four species accepted in 2016. Some species are photosynthetic (Japonolirion) and others are rare, leafless, chlorophyllous, mycoheterotrophic plants (Petrosavia). The family is found in low-light montane rainforests in Japan, China, Southeast Asia and Borneo. They are characterised by having bracteate racemes, pedicellate flowers, six persistent tepals, septal nectaries, three almost-distinct carpels, simultaneous microsporogenesis, monosulcate pollen, and follicular fruit.

The Berberidaceae are a family of 18 genera of flowering plants commonly called the barberry family. This family is in the order Ranunculales. The family contains about 700 known species, of which the majority are in the genus Berberis. The species include trees, shrubs and perennial herbaceous plants.

Nelumbonaceae is a family of aquatic flowering plants. Nelumbo is the sole extant genus, containing Nelumbo lutea, native to North America, and Nelumbo nucifera, widespread in Asia. At least five other genera, Nelumbites, Exnelumbites, Paleonelumbo, Nelumbago, and Notocyamus are known from fossils.

The Calycanthaceae are a small family of flowering plants in the order Laurales. The family contains three genera and only 10 known species, restricted to warm temperate and tropical regions:

Lardizabalaceae is a family of flowering plants.

Siparunaceae is a family of flowering plants in the magnoliid order Laurales. It consists of two genera of woody plants, with essential oils: Glossocalyx in West Africa and Siparuna in the neotropics. Glossocalyx is monospecific and Siparuna has about 74 known species.

Trochodendraceae is the only family of flowering plants in the order Trochodendrales. It comprises two extant genera, each with a single species along with up to five additional extinct genera and a number of extinct species. The living species are native to south east Asia. The two living species both have secondary xylem without vessel elements, which is quite rare in angiosperms. As the vessel-free wood suggests primitiveness, these two species have attracted much taxonomic attention.

Chloranthaceae is a family of flowering plants (angiosperms), the only family in the order Chloranthales. It is not closely related to any other family of flowering plants, and is among the early-diverging lineages in the angiosperms. They are woody or weakly woody plants occurring in Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Madagascar, Central and South America, and the West Indies. The family consists of four extant genera, totalling about 77 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016. Some species are used in traditional medicine. The type genus is Chloranthus. The fossil record of the family, mostly represented by pollen such as Clavatipollenites, extends back to the dawn of the history of flowering plants in the Early Cretaceous, and has been found on all continents.
Ctenolophon is the only genus in the flowering plant family Ctenolophonaceae. It has two recognized species:

The Cabombaceae are a family of aquatic, herbaceous flowering plants. A common name for its species is water shield. The family is recognised as distinct in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group IV system (2016). The family consists of two genera of aquatic plants, Brasenia and Cabomba, totalling six species.

Trimeniaceae is a family of flowering plants recognized by most taxonomists, at least for the past several decades. It is a small family of one genus, Trimenia, with eight known species of woody plants, bearing essential oils. The family is subtropical to tropical and found in Southeast Asia, eastern Australia and on several Pacific Islands.
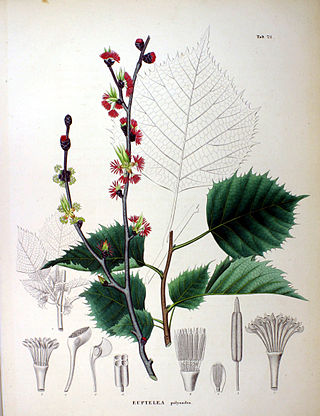
Euptelea is a genus of two species of flowering plants in the monogeneric family Eupteleaceae. The genus is found from Assam east through China to Japan, and consists of shrubs or small trees:

Myrothamnus is a genus of flowering plants, consisting of two species of small xerophytic shrubs, in the southern parts of tropical Africa and in Madagascar. Myrothamnus is recognized as the only genus in the family Myrothamnaceae.

Ixiolirion is a genus of flowering plants native to central and southwest Asia, first described as a genus in 1821. Recent classifications place the group in the monogeneric family Ixioliriaceae in the order Asparagales of the monocots. In earlier systems of classification, it was usually placed in the family Amaryllidaceae.

Tecophilaeaceae is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. It consists of nine genera with a total of 27 species.




















