The Alismatales (alismatids) are an order of flowering plants including about 4,500 species. Plants assigned to this order are mostly tropical or aquatic. Some grow in fresh water, some in marine habitats. Perhaps the most important food crop in the order is the corm of the taro plant, Colocasia esculenta.

The Laurales are an order of flowering plants. They are magnoliids, related to the Magnoliales.

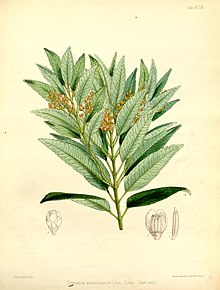
The Magnoliales are an order of flowering plants.

The dicotyledons, also known as dicots, are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, that the seed has two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. There are around 200,000 species within this group. The other group of flowering plants were called monocotyledons, typically each having one cotyledon. Historically, these two groups formed the two divisions of the flowering plants.

Smilacaceae, the greenbriers, is a family of flowering plants. While they were often assigned to a more broadly defined family Liliaceae, most recent botanists have accepted the two as distinct families, diverging around 55 million years ago during the Early Paleogene. One characteristic that distinguishes Smilacaceae from most of the other members of the Liliaceae-like Liliales is that it has true vessels in its conducting tissue. Another is that the veins of the leaves, between major veins, are reticulate (net-shaped), rather than parallel as in most monocots.

Proteales is an order of flowering plants consisting of three families. The Proteales have been recognized by almost all taxonomists.

Illiciales is an order of flowering plants that is not recognized by the current most widely used system of plant classification, the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group's APG III system. The order was comprised differently in various systems of plant taxonomy, but is composed of 2-4 families of shrubs, trees, and lianas native to Australasia, south eastern Asia, and the southeastern United States. The families all contain species with essential oils, and flowers with a perianth with bracts, sepals, and petals incompletely distinguished from each other and not arranged in definite whorls. The families of the order had been variably placed in other orders in different taxonomies.

Amborella is a monotypic genus of understory shrubs or small trees endemic to the main island, Grande Terre, of New Caledonia in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The genus is the only member of the family Amborellaceae and the order Amborellales and contains a single species, Amborella trichopoda. Amborella is of great interest to plant systematists because molecular phylogenetic analyses consistently place it as the sister group to all other flowering plants.

Colchicaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes 15 genera with a total of about 285 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016.

The Xyridaceae are a family of flowering plants. This family has been recognized by many taxonomists and is known as the yellow-eyed grass family.

Austrobaileya is the sole genus consisting of a single species that constitutes the entire flowering plant family Austrobaileyaceae. The species Austrobaileya scandens grows naturally only in the Wet Tropics rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia.

Nelumbonaceae is a family of aquatic flowering plants. Nelumbo is the sole extant genus, containing Nelumbo lutea, native to North America, and Nelumbo nucifera, widespread in Asia. At least five other genera, Nelumbites, Exnelumbites, Paleonelumbo, Nelumbago, and Notocyamus are known from fossils.

The Calycanthaceae are a small family of flowering plants in the order Laurales. The family contains three genera and only 10 known species, restricted to warm temperate and tropical regions:

Schisandraceae is a family of flowering plants with 3 known genera and a total of 92 known species. Such a family has been recognized by most taxonomists, at least for the past several decades. Before that, the plants concerned were assigned to family Magnoliaceae and Illiciaceae.

Trochodendraceae is the only family of flowering plants in the order Trochodendrales. It comprises two extant genera, each with a single species along with up to five additional extinct genera and a number of extinct species. The living species are native to south east Asia. The two living species both have secondary xylem without vessel elements, which is quite rare in angiosperms. As the vessel-free wood suggests primitiveness, these two species have attracted much taxonomic attention.

Chloranthaceae is a family of flowering plants (angiosperms), the only family in the order Chloranthales. It is not closely related to any other family of flowering plants, and is among the early-diverging lineages in the angiosperms. They are woody or weakly woody plants occurring in Southeast Asia, the Pacific, Madagascar, Central and South America, and the West Indies. The family consists of four extant genera, totalling about 77 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016. Some species are used in traditional medicine. The type genus is Chloranthus. The fossil record of the family, mostly represented by pollen such as Clavatipollenites, extends back to the dawn of the history of flowering plants in the Early Cretaceous, and has been found on all continents.

Cyclanthaceae is a family of flowering plants.

The Rapateaceae are a family of flowering plants. The botanical name has been recognized by most taxonomists.

Magnoliids are a clade of flowering plants. With more than 10,000 species, including magnolias, nutmeg, bay laurel, cinnamon, avocado, black pepper, tulip tree and many others, it is the third-largest group of angiosperms after the eudicots and monocots. The group is characterized by trimerous flowers, pollen with one pore, and usually branching-veined leaves.

The basal angiosperms are the flowering plants which diverged from the lineage leading to most flowering plants. In particular, the most basal angiosperms were called the ANITA grade, which is made up of Amborella, Nymphaeales and Austrobaileyales.