
Willmore Wilderness Park, located in Alberta, Canada, is a 4,600-square-kilometre (1,800 sq mi) wilderness area adjacent to Jasper National Park. It is lesser known and less visited than Jasper National Park. There are no public roads, bridges or buildings. There are, however, several ranger cabins in the park that are available as a courtesy to visitors.

The Peace River is a 1,923-kilometre-long (1,195 mi) river in Canada that originates in the Rocky Mountains of northern British Columbia and flows to the northeast through northern Alberta. The Peace River joins the Athabasca River in the Peace-Athabasca Delta to form the Slave River, a tributary of the Mackenzie River. The Finlay River, the main headwater of the Peace River, is regarded as the ultimate source of the Mackenzie River. The combined Finlay–Peace–Slave–Mackenzie river system is the 13th longest river system in the world.
Height of the Rockies Provincial Park is a provincial park in the Canadian Rockies of south eastern British Columbia, Canada. It is located west of the Continental Divide, adjacent to Elk Lakes Provincial Park.

Kakwa Provincial Park and Protected Area is a 170,890 ha provincial park in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. The park preserves the southernmost portion of the Hart Ranges and the northernmost portion of the Continental Ranges. The park also preserves significant marine fossil deposits located in the region.

The Municipal District of Greenview No. 16 is a municipal district (MD) in northwest Alberta, Canada. It covers the full extent of Census Division 18, and with an area of 32,984 km2 (12,735 sq mi), it is the largest municipal district in Alberta. Its administrative office is located in the Town of Valleyview.

The Hart Ranges are a major subrange of the Canadian Rockies located in northeastern British Columbia and western Alberta. The mountains constitute the southernmost portion of the Northern Rocky Mountains.

The Great Divide Trail (GDT) is a wilderness hiking trail in the Canadian Rockies. The trail closely follows the Great Divide between Alberta and British Columbia, crossing the divide more than 30 times. Its southern terminus is in Waterton Lakes National Park at the Canada–US border and its northern terminus is at Kakwa Lake in Kakwa Provincial Park, north of Jasper National Park. The trail is 1,130 km (700 mi) long and ranges in elevation from 1,055 m (3,461 ft) at Old Fort Point trailhead near Jasper to 2,590 m (8,500 ft) at an unnamed pass above Michele Lakes just south of the White Goat Wilderness Area.
Chinchaga Wildland Park is a protected 800 km2 (310 sq mi) tract of land in the 5,000 km2 (1,900 sq mi) of the greater Chinchaga wilderness area in a disjunct outlier of the Foothills Natural Region of Alberta, in a remote area of northwest Alberta, Canada, about 140 kilometres (87 mi) west of Manning. It was designated as a Wildlife Park in December 1999. The greater Chinchaga area was identified in 1995 as an Environmentally Significant Area. It was designated by the Alberta Government as a protected area in 2000, under the "Special Places" program. "Elevations in the Park range from 650 m adjacent to the Chinchaga River to 915 m at the height of land atop Halverson Ridge."
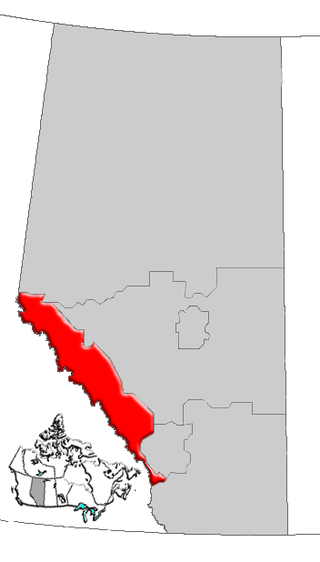
Alberta's Rockies comprise the Canadian Rocky Mountains in Alberta, Canada. On the southwestern part of the province along the British Columbia border, the region covers all but the south of Census Division 15.
Rock Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park in Alberta, Canada, located on the shores of Rock Lake, 64 km (40 mi) north-west from Hinton, north on the Bighorn Highway and 39 km west on an access road.
The Northern Rocky Mountains, usually referred to as the Northern Rockies, are a subdivision of the Canadian Rockies comprising the northern half of the Canadian segment of the Rocky Mountains. While their northward limit is easily defined as the Liard River, which is the northward terminus of the whole Rockies, the southward limit is debatable, although the area of Mount Ovington and Monkman Pass is mentioned in some sources, as south from there are the Continental Ranges, which are the main spine of the Rockies forming the boundary between British Columbia and Alberta. Some use the term to mean only the area north of the Peace Arm of the Williston Reservoir, and in reference to Northern Rocky Mountains Provincial Park, while others consider the term to extend all the way south, beyond the limit of the Hart Ranges at Mount Ovington, to include the McBride area, the Sir Alexander Group and Mount Robson.

The Montane Cordillera Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is an ecozone in south-central British Columbia and southwestern Alberta, Canada. A rugged and mountainous ecozone spanning 473,000 square kilometres, it still contains "two of the few significant agricultural areas of the province", the Creston Valley and the Okanagan Valley. Primarily a mountainous region, it consists of rugged ecosystems such as alpine tundra, dry sagebrush and dense conifer forests. The interior plains are encircled by a ring of mountains. The area has a mild climate throughout the year, with typically dry summers and wet winters.
The Kakwa River is a tributary of the Smoky River in western Alberta, Canada.
Jarvis Pass is a mountain pass in Kakwa Provincial Park in the Northern Rockies of British Columbia, Canada, located to the north of Kakwa Lake, on the British Columbia-Alberta boundary, and therefore is on the Continental Divide. It was one of the many passes surveyed as a route for the Canadian Pacific Railway in the 1870s.
Intersection Mountain is a 2,452-metre (8,045 ft) mountain on the Continental Divide. The mountain is so named because it lies at the intersection of the 120th meridian where the British Columbia and Alberta border diverges from its line along the Divide northwards along the meridian. The mountain is in Kakwa Provincial Park in British Columbia and Willmore Wilderness Park in Alberta and is near Casket Pass.

The Alberta Mountain forests are a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of Western Canada, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system.
Don Getty Wildland Provincial Park is a wildland provincial park in Kananaskis Country, Alberta, Canada. It was created on 24 July 2001 and has an area of 62,775 hectares. The park was named for the 11th premier of Alberta, Don Getty. The park was designated as part of the Special Places 2000: Alberta’s Natural Heritage initiative.










