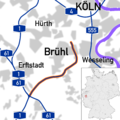
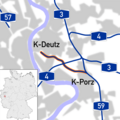
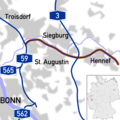
The German federal motorways are now numbered according to a clear system. Since the mid-1970s there has been a numbering system for motorways, which sets out which number is replaced by a new motorway. Motorways with a single-digit number (e.g. A 1) are of national or even cross-border significance. Highways with a two-digit number (e.g. A 20) are usually of overriding national importance. Highways with three digits (e.g. A 999) are generally of regional or urban significance; often these motorways are feeders or detours. If there is more than one digit, the first digit indicates the approximate location of the motorway (A 10 to A 19 for Berlin; A 20 in the north to A99 in the south, A 100 for Berlin; A 200 in the north to A 999 in the south). Usually highways with even numbers predominantly run east–west, and those with odd numbers run north–south. Exceptions include the A14 and the A15.