Related Research Articles
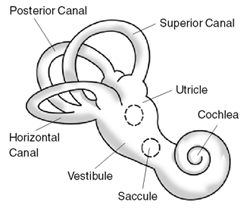
Ménière's disease (MD) is a disease of the inner ear that is characterized by potentially severe and incapacitating episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Typically, only one ear is affected initially, but over time, both ears may become involved. Episodes generally last from 20 minutes to a few hours. The time between episodes varies. The hearing loss and ringing in the ears can become constant over time.
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but this is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearing, or is associated with other problems. The word tinnitus comes from the Latin tinnire, "to ring". In some people, it interferes with concentration, and can be associated with anxiety and depression.

A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech understanding in both quiet and noisy environments. A CI bypasses acoustic hearing by direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Through everyday listening and auditory training, cochlear implants allow both children and adults to learn to interpret those signals as speech and sound.

Otosclerosis is a condition of the middle ear where portions of the dense enchondral layer of the bony labyrinth remodel into one or more lesions of irregularly-laid spongy bone. As the lesions reach the stapes the bone is resorbed, then hardened (sclerotized), which limits its movement and results in hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo or a combination of these. The term otosclerosis is something of a misnomer: much of the clinical course is characterized by lucent rather than sclerotic bony changes, so the disease is also known as otospongiosis.
Unilateral hearing loss (UHL) is a type of hearing impairment where there is normal hearing in one ear and impaired hearing in the other ear.

JAMA Otolaryngology—Head & Neck Surgery is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by the American Medical Association and covering all aspects of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases of the head, neck, ear, nose, and throat. The editor-in-chief is Jay F. Piccirillo. It was established in 1925 as the Archives of Otolaryngology and renamed A.M.A. Archives of Otolaryngology in 1950, then renamed Archives of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery in 1960, before obtaining its current name in 2013.
A mastoidectomy is a procedure performed to remove the mastoid air cells, air bubbles in the skull, near the middle ear. This can be done as part of treatment for mastoiditis, chronic suppurative otitis media or cholesteatoma. In addition, it is sometimes performed as part of other procedures or for access to the middle ear. There are classically five different types of mastoidectomy:
Milind is an Indian male given name. Notable people with this name include:
Neurotology or neuro-otology is a subspecialty of otolaryngology—head and neck surgery, also known as ENT medicine. Neuro-otology is closely related to otology, clinical neurology and neurosurgery.

Claus-Frenz Claussen, was a German ENT-Medician and University teacher, author, editor, artist and inventor. He was the first university teacher for neurotology to be appointed in Germany.
The International Tinnitus Journal is a peer-reviewed medical journal that was established in 1995. It covers all aspects of tinnitus. Until 2010, the journal was published by the Martha Entenmann Tinnitus Research Center in cooperation with the Neurootologisches Forschungsinstitut der 4-G-Forschung e.V., and edited by Claus-Frenz Claussen, Abraham Shulman, Barbara Goldstein, and Michael Seidman. It is published biannually and is the official journal of the Neurootological and Equilibriometric Society. The journal is abstracted and indexed in Index Medicus/MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, and Chemical Abstracts.

Henryk Skarzynski is a Polish doctor otolaryngologist, audiologist and phoniatrist, creator and director of Warsaw Institute of Physiology and Pathology of Hearing and World Hearing Center in Kajetany.

William Fouts House was an American otologist, physician and medical researcher who developed and invented the cochlear implant. The cochlear implant is considered to be the first invention to restore not just the sense of hearing, but any of the absent five senses in humans. Dr. House also pioneered approaches to the lateral skull base for removal of tumors, and is considered "the Father of Neurotology".

Yog Raj Sharma is an Indian ophthalmologist and ex-chief of Dr. Rajendra Prasad Centre for Ophthalmic Sciences of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, the apex body of the National Programme for the Control of Blindness, a Government of India initiative to reduce the prevalence of blindness in India. He is the Chairman of the Task Force on Prevention and Control of Diabetic Retinopathy Group and the Co-Chairman of the National Task Force on Prevention of Blindness from Retinopathy of Prematurity under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare of the Government of India. An advisor to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India. Sharma was honored by the Government of India in 2015 with Padma Shri, the fourth highest Indian civilian award. In 2005, Yog Raj Sharma's published article on "Pars plana vitrectomy vs scleral buckling in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment" in Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica and in November 2021, American society of retina specialists cited it as top 100 publications on retinal detachment management in the last ~121 years. Of these top hundred publications, only nineteen countries contributed, three of the contributing countries were Asian and from India this study was the sole contribution. Dr Sharma called it 'the singular biggest achievement of his career" in an article published in Daily Excelsior, Jammu in December 2021.
Thomas J. Balkany is an American ear surgeon, otolaryngologist and neurotologist specializing in cochlear implantation.

Mohan Kameswaran is an Indian otorhinolaryngologist, medical academic and the founder of MERF Institute of Speech and Hearing, a Chennai-based institution providing advanced training in audiology and speech-language pathology. He is one of the pioneers of cochlear implant surgery in India and a visiting professor at Rajah Muthiah Medical College of the Annamalai University and Sri Ramachandra Medical College and Research Institute, Chennai. He has many firsts to his credit such as the performance of the first auditory brain stem implantation surgery in South and South East Asia, the first pediatric brain stem implantation surgery in Asia, the first totally implantable hearing device surgery in Asia Pacific region, and the first to introduce KTP/532 laser-assisted ENT surgery in India. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2006, for his contributions to Indian medicine.

Dr. Charles Limb is a surgeon, neuroscientist, and musician at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) who has carried out research on the neural basis of musical creativity and the impact of cochlear implants on music perception in hearing impaired individuals. As an otologic surgeon and otolaryngologist, he specializes in treatment of ear disorders.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a disorder where pressure abnormalities in the middle ear result in symptoms.
Muaaz Tarabichi is a Syrian otolaryngologist, lecturer, researcher, and author. He is recognized around the world as the father of endoscopic ear surgery. He is the co-founder of Tarabichi Stammberger Ear and Sinus Institute. He was elected as the chairman of the International Advisory Board of the American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.
Cochlear hydrops is a condition of the inner ear involving a pathological increase of fluid affecting the cochlea. This results in swelling that can lead to hearing loss or changes in hearing perception. It is a form of endolymphatic hydrops and related to Ménière's disease. Cochlear hydrops refers to a case of inner-ear hydrops that only involves auditory symptoms and does not cause vestibular issues.
References
- ↑ "Padma 2014". Press Information Bureau, Government of India. 25 January 2014. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved October 28, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Sehat". Sehat. 2014. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "St Xaviers". St Xaviers College. 2014. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- 1 2 "India Medical Times". India Medical Times. 2014. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- ↑ "List of Fellows - NAMS" (PDF). National Academy of Medical Sciences. 2016. Retrieved March 19, 2016.
- ↑ Suresh D. Isloor (Editor), Milind V. Kirtane (Foreword) (2014). Lacrimal Drainage Surgery. JP Medical. p. 91. ISBN 978-9350906507.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ↑ Bachi T. Hathiram (Editor), Vicki S. Khattar (Editor), Jatin P. Shah (Foreword), Milind V. Kirtane (Foreword) (2013). Atlas of Operative Otorhinolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery. JP Medical. p. 1653. ISBN 978-9351522973.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ V. Anqand (Author), Milind V. Kirtane (Foreword), Ravi Nayar (Foreword) (2011). ENT, Head and Neck Diseases Made Easy. JP Medical. p. 160. ISBN 978-8184485950.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Claus-Frenz Claussen (Author), Milind V. Kirtane (Editor) (1991). Vertigo, Nausea, Tinnitus, and Hypoacusia Due to Head and Neck Trauma: Proceedings of the Xviith Scientific Meeting of the Neurootological and Equil (International Congress Series). Excerpta Medica. p. 466. ISBN 978-0444811509.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ↑ Claus-Frenz Claussen (Author), Milind V. Kirtane (Author), Klaus Schlitter (Author) (1988). Vertigo, Nausea, Tinnitus, and Hypoacusia in Metabolic Disorders: Proceedings (International Congress Series). Excerpta Medica. p. 650. ISBN 978-0444810243.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Milind V Kirtane (1982). Electronystagmography: A Systematic Approach. Dr M V Kirtane. ASIN B001A1MHR2.