
Christiaan Neethling Barnard was a South African cardiac surgeon who performed the world's first human-to-human heart transplant operation. On 3 December 1967, Barnard transplanted the heart of accident victim Denise Darvall into the chest of 54-year-old Louis Washkansky, who regained full consciousness and was able to talk easily with his wife, before dying 18 days later of pneumonia, largely brought on by the anti-rejection drugs that suppressed his immune system. Barnard had told Mr. and Mrs. Washkansky that the operation had an 80% chance of success, an assessment which has been criticised as misleading. Barnard's second transplant patient, Philip Blaiberg, whose operation was performed at the beginning of 1968, returned home from the hospital and lived for a year and a half.

Organ donation is the process when a person authorizes an organ of their own to be removed and transplanted to another person, legally, either by consent while the donor is alive, through a legal authorization for deceased donation made prior to death, or for deceased donations through the authorization by the legal next of kin.

Gopal Krishna Gokhale was an Indian political leader and a social reformer during the Indian independence movement, and political mentor of Indian freedom fighter Mahatma Gandhi.
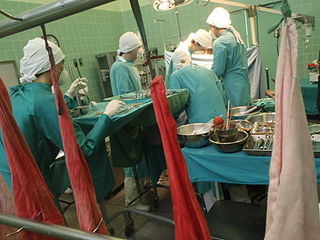
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source.
Hand transplantation, or simply a hand transplant, is a surgical procedure to transplant a hand from one human to another. The donor hand, usually from a brain-dead donor, is transplanted to a recipient amputee. Most hand transplants to date have been performed on below-elbow amputees, although above-elbow transplants are gaining popularity. Hand transplants were the first of a new category of transplants where multiple organs are transplanted as a single functional unit, now termed vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA).

Joseph Edward Murray was an American plastic surgeon who is known as the "father of transplantation" for major milestones in the field of transplantation, including performing the first successful human kidney transplant, defining brain death, the organization of the first international conference on human kidney transplants and founding of the National Kidney Registry, the forerunner of the current United Network Of Organ Sharing (UNOS). By 2013, more than one million patients are estimated to have benefitted from organ transplantation around the world.

A face transplant is a medical procedure to replace all or part of a person's face using tissue from a donor. Part of a field called "Vascularized Composite Tissue Allotransplantation" (VCA) it involves the transplantation of facial skin, the nasal structure, the nose, the lips, the muscles of facial movement used for expression, the nerves that provide sensation, and, potentially, the bones that support the face. The recipient of a face transplant will take life-long medications to suppress the immune system and fight off rejection.

Devanahalli Venkataramanaiah Gundappa, popularly known as DVG, was an Indian writer, poet and philosopher in Kannada-language. He is one of the stalwarts of modern Kannada literature. His most notable work is the Mankuthimmana Kagga, which is similar to the wisdom poems of the late medieval poet Sarvajna.

Vikram Gokhale was an Indian film, television and stage actor, noted for his roles in Marathi theatre, Hindi films and television. He was the son of the Veteran Marathi theatre and film actor, Chandrakant Gokhale.

Vladimir Petrovich Demikhov was a Soviet Russian scientist and organ transplantation pioneer, who performed several transplants in the 1940s and 1950s, including the transplantation of a heart into an animal and a heart–lung replacement in an animal. He is also well known for his dog head transplants, which he conducted during the 1950s, resulting in two-headed dogs. This ultimately led to the head transplants in monkeys by Robert White, who was inspired by Demikhov's work.
Penis transplantation is a surgical transplant procedure in which a penis is transplanted to a patient. The penis may be an allograft from a human donor, or it may be grown artificially, though the latter has not yet been transplanted onto a human.
A uterine transplant is a surgical procedure whereby a healthy uterus is transplanted into an organism of which the uterus is absent or diseased. As part of normal mammalian sexual reproduction, a diseased or absent uterus does not allow normal embryonic implantation, effectively rendering the female infertile. This phenomenon is known as absolute uterine factor infertility (AUFI). Uterine transplant is a potential treatment for this form of infertility.

Enterobacter cloacae is a clinically significant Gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium.

Dr. Arvinder Singh Soin is an Indian surgeon and the Chief Hepatobiliary and Liver Transplant Surgeon & Chairman of the Institute of Liver Transplantation and Regenerative Medicine, Medanta-The Medicity. Known for his work in the field of liver transplantation, Soin also runs the Liver Transplant institute at the Sir H. N. Reliance Foundation Hospital, Mumbai. He has performed more than 3500 living donor liver transplants in India, which is the highest in the country, and the second-highest in the world.

A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. As of 2018, the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart, with or without both lungs, from a recently deceased organ donor and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed and replaced with the donor heart or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart.
Richard Rowland Lower was an American pioneer of cardiac surgery, particularly in the field of heart transplantation. Lower was born in Detroit, attended Amherst College, and received his medical degree from Cornell University in 1955. Lower and Norman Shumway developed many of the techniques required to conduct successful heart transplantation, including the use of hypothermia and the orthotopic technique, which became the standard technique for cardiac transplantation.

Prafulla Kumar Sen MD was an Indian vascular and cardiothoracic surgeon, who led the world's sixth attempt of human heart transplant and India's first in 1968. It dubbed him the fourth surgeon in the world to carry out this operation.

R.N. Kao: Gentleman Spymaster is a biography of Rameshwar Nath Kao, the founding chief of India's external intelligence agency, the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW). Written by Nitin A. Gokhale, the book was published by Bloomsbury India in November 2019. The book is being adapted into a movie by Karan Johar.

Things to Leave Behind is a historical novel written by Namita Gokhale. It was published in 2016 by Penguin Random House India.














