Related Research Articles
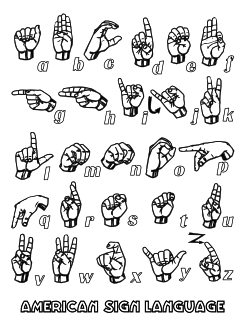
Fingerspelling is the representation of the letters of a writing system, and sometimes numeral systems, using only the hands. These manual alphabets, have often been used in deaf education, and have subsequently been adopted as a distinct part of a number of sign languages; there are about forty manual alphabets around the world. Historically, manual alphabets have had a number of additional applications—including use as ciphers, as mnemonics, and in silent religious settings.
Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language, as well as to produce and use words and sentences to communicate.

Sign languages are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulations in combination with non-manual elements. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and they are not mutually intelligible with each other, although there are also striking similarities among sign languages.

A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthetic device to provide a person with moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss a modified sense of sound. CI bypasses the normal acoustic hearing process to replace it with electric signals which directly stimulate the auditory nerve. A person with a cochlear implant receiving intensive auditory training may learn to interpret those signals as sound and speech. However, one third of deaf children do not develop language if they are on a CI program alone and have no sign language input.
Lip reading, also known as lipreading or speechreading, is a technique of understanding speech by visually interpreting the movements of the lips, face and tongue when normal sound is not available. It relies also on information provided by the context, knowledge of the language, and any residual hearing. Although lip reading is used most extensively by deaf and hard-of-hearing people, most people with normal hearing process some speech information from sight of the moving mouth.

The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.

Brodmann area 47, or BA47, is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Curving from the lateral surface of the frontal lobe into the ventral (orbital) frontal cortex. It is below areas BA10 and BA45, and beside BA11. This cytoarchitectonic region most closely corresponds to the gyral region the orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus, although these regions are not equivalent. Pars orbitalis is not based on cytoarchitectonic distinctions, and rather is defined according to gross anatomical landmarks. Despite a clear distinction, these two terms are often used liberally in peer-reviewed research journals.
Signing Exact English is a system of manual communication that strives to be an exact representation of English vocabulary and grammar. It is one of a number of such systems in use in English-speaking countries. It is related to Seeing Essential English (SEE-I), a manual sign system created in 1945, based on the morphemes of English words. SEE-II models much of its sign vocabulary from American Sign Language (ASL), but modifies the handshapes used in ASL in order to use the handshape of the first letter of the corresponding English word. The four components of signs are handshape, orientation, location, and movement.
Cued speech is a visual system of communication used with and among deaf or hard-of-hearing people. It is a phonemic-based system which makes traditionally spoken languages accessible by using a small number of handshapes, known as cues, in different locations near the mouth to convey spoken language in a visual format. The National Cued Speech Association defines cued speech as "a visual mode of communication that uses hand shapes and placements in combination with the mouth movements and speech to make the phonemes of spoken language look different from each other." It adds information about the phonology of the word that is not visible on the lips. This allows people with hearing or language difficulties to visually access the fundamental properties of language. It is now used with people with a variety of language, speech, communication, and learning needs. It is different from American Sign Language (ASL), which is a separate language from English. Cued speech is considered a communication modality but can be used as a strategy to support auditory rehabilitation, speech articulation, and literacy development.
Home sign is a gestural communication system, often invented spontaneously by a deaf child who lacks accessible linguistic input. Home sign systems often arise in families where a deaf child is raised by hearing parents and is isolated from the Deaf community. Because the deaf child does not receive signed or spoken language input, these children are referred to as linguistic isolates.
Auditory verbal agnosia (AVA), also known as pure word deafness, is the inability to comprehend speech. Individuals with this disorder lose the ability to understand language, repeat words, and write from dictation. Some patients with AVA describe hearing spoken language as meaningless noise, often as though the person speaking was doing so in a foreign language. However, spontaneous speaking, reading, and writing are preserved. The maintenance of the ability to process non-speech auditory information, including music, also remains relatively more intact than spoken language comprehension. Individuals who exhibit pure word deafness are also still able to recognize non-verbal sounds. The ability to interpret language via lip reading, hand gestures, and context clues is preserved as well. Sometimes, this agnosia is preceded by cortical deafness; however, this is not always the case. Researchers have documented that in most patients exhibiting auditory verbal agnosia, the discrimination of consonants is more difficult than that of vowels, but as with most neurological disorders, there is variation among patients.
Manually coded languages (MCLs) are a family of gestural communication methods which include gestural spelling as well as constructed languages which directly interpolate the grammar and syntax of oral languages in a gestural-visual form - that is, signed versions of oral languages. Unlike the sign languages that have evolved naturally in deaf communities, these manual codes are the conscious invention of deaf and hearing educators. MCLs mostly follow the grammar of the oral language—or, more precisely, of the written form of the oral language that they interpolate. They have been mainly used in deaf education in an effort to "represent English on the hands" and by sign language interpreters in K-12 schools, although they have had some influence on deaf sign languages where their implementation was widespread.
Ban Khor Sign Language (BKSL) is a village sign language used by at least 400 people of a rice-farming community in the village of Ban Khor in a remote area of Isan. Known locally as pasa kidd, it developed in the 1930s due to a high number of deaf people. Estimated number of users in 2009 was 16 deaf and approximately 400 hearing out of 2741 villagers. It is a language isolate, independent of the other sign languages of Thailand such as Old Bangkok Sign Language and the national Thai Sign Language.
Bimodal bilingualism is an individual or community's bilingual competency in at least one oral language and at least one sign language. A substantial number of bimodal bilinguals are Children of Deaf Adults or other hearing people who learn sign language for various reasons. Deaf people as a group have their own sign language and culture, but invariably live within a larger hearing culture with its own oral language. Thus, "most deaf people are bilingual to some extent in [an oral] language in some form". In discussions of multilingualism in the United States, bimodal bilingualism and bimodal bilinguals have often not been mentioned or even considered, in part because American Sign Language, the predominant sign language used in the U.S., only began to be acknowledged as a natural language in the 1960s. However, bimodal bilinguals share many of the same traits as traditional bilinguals, as well as differing in some interesting ways, due to the unique characteristics of the Deaf community. Bimodal bilinguals also experience similar neurological benefits as do unimodal bilinguals, with significantly increased grey matter in various brain areas and evidence of increased plasticity as well as neuroprotective advantages that can help slow or even prevent the onset of age-related cognitive diseases, such as Alzheimer's and dementia.
Auditory agnosia is a form of agnosia that manifests itself primarily in the inability to recognize or differentiate between sounds. It is not a defect of the ear or "hearing", but rather a neurological inability of the brain to process sound meaning. It is caused by bilateral damage to the anterior superior temporal gyrus, which is part of the auditory pathway responsible for sound recognition, the auditory "what" pathway.
John D. Bonvillian was a psychologist and associate professor - emeritus in the Department of Psychology and Interdepartmental Program in Linguistics at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, Virginia. He was known for his contributions to the study of sign language, childhood development, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition. Much of his research worked with typically developing children, deaf children, or children with disabilities.
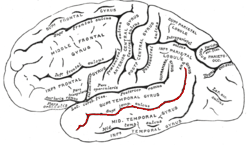
The superior temporal sulcus (STS) is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe of the brain. A sulcus is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, and a gyrus is the a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum.
Language acquisition is a natural process in which infants and children develop proficiency in the first language or languages that they are exposed to. The process of language acquisition is varied among deaf children. Deaf children born to deaf parents are typically exposed to a sign language at birth and their language acquisition following a typical developmental timeline. However, at least 90% of deaf children are born to hearing parents who use a spoken language at home. Hearing loss prevents many deaf children from hearing spoken language to the degree necessary for language acquisition. For many deaf children, language acquisition is delayed until the time that they are exposed to a sign language or until they begin using amplification devices such as hearing aids or cochlear implants. Deaf children who experience delayed language acquisition, sometimes called language deprivation, are at risk for lower language and cognitive outcomes.
The machine translation of sign languages has been possible, albeit in a limited fashion, since 1977. When a research project successfully matched English letters from a keyboard to ASL manual alphabet letters which were simulated on a robotic hand. These technologies translate signed languages into written or spoken language, and written or spoken language to sign language, without the use of a human interpreter. Sign languages possess different phonological features than spoken languages, which has created obstacles for developers. Developers use computer vision and machine learning to recognize specific phonological parameters and epentheses unique to sign languages, and speech recognition and natural language processing allow interactive communication between hearing and deaf people.
References
- ↑ "Iranian Sign Language". Ethnologue. Retrieved 4 February 2021.