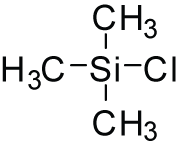In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula CnH2n−2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic.
Cyclopropene is an organic compound with the formula C3H4. It is the simplest cycloalkene. Because the ring is highly strained, cyclopropene is difficult to prepare and highly reactive. This colorless gas has been the subject for many fundamental studies of bonding and reactivity. It does not occur naturally, but derivatives are known in some fatty acids. Derivatives of cyclopropene are used commercially to control ripening of some fruit.
In organic chemistry, the Wurtz reaction, named after Charles Adolphe Wurtz, is a coupling reaction in which two alkyl halides are treated with sodium metal to form a higher alkane.

A polyyne is any organic compound with alternating single and triple bonds; that is, a series of consecutive alkynes, (−C≡C−)n with n greater than 1. These compounds are also called polyacetylenes, especially in the natural products and chemical ecology literature, even though this nomenclature more properly refers to acetylene polymers composed of alternating single and double bonds (−CR=CR′−)n with n greater than 1. They are also sometimes referred to as oligoynes, or carbinoids after "carbyne" (−C≡C−)∞, the hypothetical allotrope of carbon that would be the ultimate member of the series. The synthesis of this substance has been claimed several times since the 1960s, but those reports have been disputed. Indeed, the substances identified as short chains of "carbyne" in many early organic synthesis attempts would be called polyynes today.

Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCHN2. It is classified as a diazo compound. Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is commercially available as solutions in hexanes, DCM, and ether. It is a specialized reagent used in organic chemistry as a methylating agent for carboxylic acids. It is a safer replacement for diazomethane, which is a sensitive explosive gas, whereas trimethylsilyldiazomethane is a relatively stable liquid and thus easier to handle.
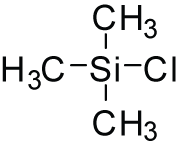
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound, with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.

Diethylaluminium cyanide is the organoaluminium compound with formula ( 2AlCN)n. This colorless compound is usually handled as a solution in toluene. It is a reagent for the hydrocyanation of α,β-unsaturated ketones.
The Glaser coupling is a type of coupling reaction. It is by far one of the oldest coupling reactions and is based on copper compounds like copper(I) chloride or copper(I) bromide and an additional oxidant like air. The base used in the original research paper is ammonia and the solvent is water or an alcohol. The reaction was first reported by Carl Andreas Glaser in 1869. He suggested the following process on his way to diphenylbutadiyne:

Trimethylsilylacetylene is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiC2H. A colorless liquid, "tms acetylene", as it is also called, is used as a source of "HC2−" in organic synthesis.

In organic chemistry, the thiol-yne reaction is an organic reaction between a thiol and an alkyne. The reaction product is an alkenyl sulfide.

tert-Butylphosphaacetylene is an organophosphorus compound. Abbreviated t-BuCP, it was the first example of an isolable phosphaalkyne. Prior to its synthesis, the double bond rule had suggested that elements of Period 3 and higher were unable to form double or triple bonds with lighter main group elements because of weak orbital overlap. The synthesis of t-BuCP discredited much of the double bond rule and opened new studies into the formation of unsaturated phosphorus compounds.

Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene (BTMSA) is an organosilicon compound with the formula Me3SiC≡CSiMe3 (Me = methyl). It is a crystalline solid that melts slightly above room temperature and is soluble in organic solvents. This compound is used as a surrogate for acetylene.
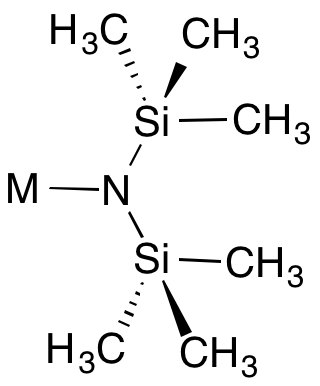
Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal M with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands (the −N 2 monovalent anion, or −N 2 monovalent group, and are part of a broader category of metal amides.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal alkyne complex is a coordination compound containing one or more alkyne ligands. Such compounds are intermediates in many catalytic reactions that convert alkynes to other organic products, e.g. hydrogenation and trimerization.

Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine is the simplest tris(trialkylsilyl)amine which are having the general formula (R3Si)3N, in which all three hydrogen atoms of the ammonia are replaced by trimethylsilyl groups (-Si(CH3)3). Tris(trimethylsilyl)amine has been for years in the center of scientific interest as a stable intermediate in chemical nitrogen fixation (i. e. the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen N2 into organic substrates under normal conditions).
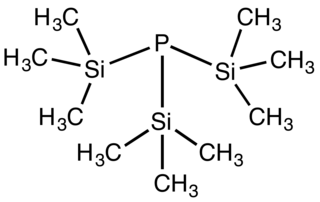
Tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(SiMe3)3 (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid that ignites in air and hydrolyses readily.

Zirconocene is a hypothetical compound with 14 valence electrons, which has not been observed or isolated. It is an organometallic compound consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound on a central zirconium atom. A crucial question in research is what kind of ligands can be used to stabilize the Cp2ZrII metallocene fragment to make it available for further reactions in organic synthesis.

Rosenthal's reagent is a metallocene bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene complex with zirconium (Cp2Zr) or titanium (Cp2Ti) used as central atom of the metallocene fragment Cp2M. Additional ligands such as pyridine or THF are commonly used as well. With zirconium as central atom and pyridine as ligand (Zirconocene bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene pyridine), a dark purple to black solid with a melting point of 125–126 °C is obtained. Synthesizing Rosenthal's reagent of a titanocene source yields golden-yellow crystals of the titanocene bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene complex with a melting point of 81–82 °C. This reagent enables the generation of the themselves unstable titanocene and zirconocene under mild conditions.
In chemistry, salt-free reduction describes methodology for reduction of metal halides by electron-rich trimethylsilyl reagents. Traditional reductions of metal halides are accomplished with alkali metals, a process that cogenerates alkali metal salts. Using the salt-free reduction, the reduction of metal halides is accompanied by formation of neutral organic compounds that can be easily removed from the inorganic or organometallic product. In addition to the reduction of metal halides, the reagents associated with this methodology are applicable to deoxygenation of organic substrates.