In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
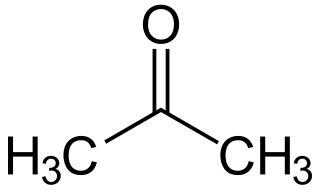
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=O, sometimes abbreviated as MeCH=O. It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body.

In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical or unsymmetrical.

An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine. Enamines are versatile intermediates.

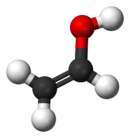
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of Functional group or intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula C=C(OH). The term enol is an abbreviation of alkenol, a portmanteau deriving from "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol". Many kinds of enols are known.

In chemistry, tautomers are structural isomers of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life.

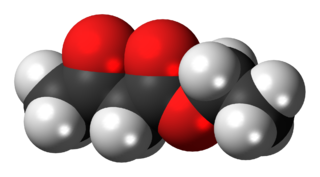
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed polyphenols.
The organic compound ethyl acetoacetate (EAA) is the ethyl ester of acetoacetic acid. It is a colorless liquid. It is widely used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a wide variety of compounds.

In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include the reagent 3,4-dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether.

Glycolaldehyde is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2−CHO. It is the smallest possible molecule that contains both an aldehyde group and a hydroxyl group. It is a highly reactive molecule that occurs both in the biosphere and in the interstellar medium. It is normally supplied as a white solid. Although it conforms to the general formula for carbohydrates, Cn(H2O)n, it is not generally considered to be a saccharide.

Cyclopropanone is an organic compound with molecular formula (CH2)2CO consisting of a cyclopropane carbon framework with a ketone functional group. The parent compound is labile, being highly sensitive toward even weak nucleophiles. Surrogates of cyclopropanone include the ketals.
In enzymology, phenylpyruvate tautomerase or Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Johann Georg Anton Geuther was a German chemist. His work in organic and inorganic chemistry influenced the development of coordination chemistry. Geuther spent most of his academic career at the University of Jena where he discovered ethyl acetoacetate, a key compound for chemical synthesis and for the discovery of tautomerism.
Living cationic polymerization is a living polymerization technique involving cationic propagating species. It enables the synthesis of very well defined polymers and of polymers with unusual architecture such as star polymers and block copolymers and living cationic polymerization is therefore as such of commercial and academic interest.

Vinylsulfonic acid is the organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH2=CHSO3H. It is the simplest unsaturated sulfonic acid. The C=C double bond is a site of high reactivity. Polymerization gives polyvinylsulfonic acid, especially when used as a comonomer with functionalized vinyl and (meth)acrylic acid compounds. It is a colorless, water-soluble liquid, although commercial samples can appear yellow or even red.

Thioformic acid is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH2OS. As the simplest thiocarboxylic acid, it has been the subject of studies on its properties which may be extrapolated to more complex thiocarboxylic acids.

1,2-Cyclopentanedione is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(CO)2. It is one of two isomeric cyclopentanediones, the other being 1,3-cyclopentanedione. It was first prepared by base-induced condensation of di ethylglutarate with diethyloxalate, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting diketodiester followed by decarboxylation. The enol is predicted to be about 1-3 kcal/mol more stable than the diketo form. The enol structure has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.