
The Polygonaceae are a family of flowering plants known informally as the knotweed family or smartweed—buckwheat family in the United States. The name is based on the genus Polygonum, and was first used by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu in 1789 in his book, Genera Plantarum. The name may refer to the many swollen nodes the stems of some species have, being derived from Greek [poly meaning 'many' and gony meaning 'knee' or 'joint']. Alternatively, it may have a different origin, meaning 'many seeds'.

Meliaceae, the mahogany family, is a flowering plant family of mostly trees and shrubs in the order Sapindales.

Ceratophyllaceae is a cosmopolitan family of flowering plants including one living genus commonly found in ponds, marshes, and quiet streams in tropical and in temperate regions. It is the only extant family in the order Ceratophyllales. Species are commonly called coontails or hornworts, although hornwort is also used for unrelated plants of the division Anthocerotophyta.

Dilleniaceae is a family of flowering plants with 11 genera and about 430 known species. Such a family has been universally recognized by taxonomists. It is known to gardeners for the genus Hibbertia, which contains many commercially valuable garden species.
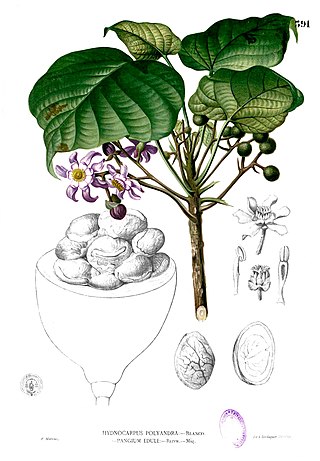
Achariaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of 32-33 genera with about 155 species of tropical herbs, shrubs, and trees. The APG IV system has greatly expanded the scope of the family by including many genera previously classified in Flacourtiaceae. Molecular data strongly support the inclusion of this family in the order Malpighiales.

Siparunaceae is a family of flowering plants in the magnoliid order Laurales. It consists of two genera of woody plants, with essential oils: Glossocalyx in West Africa and Siparuna in the neotropics. Glossocalyx is monospecific and Siparuna has about 74 known species.

Peridiscaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Saxifragales. Four genera comprise this family: Medusandra, Soyauxia, Peridiscus, and Whittonia., with a total of 12 known species. It has a disjunct distribution, with Peridiscus occurring in Venezuela and northern Brazil, Whittonia in Guyana, Medusandra in Cameroon, and Soyauxia in tropical West Africa. Whittonia is possibly extinct, being known from only one specimen collected below Kaieteur Falls in Guyana. In 2006, archeologists attempted to rediscover it, however, it proved unsuccessful.

The Achatocarpaceae are a family of woody flowering plants consisting of two genera and 11 known species, and has been recognized by most taxonomists. The family is found from the southwestern United States south to tropical and subtropical South America.

Ixiolirion is a genus of flowering plants native to central and southwest Asia, first described as a genus in 1821. Recent classifications place the group in the monogeneric family Ixioliriaceae in the order Asparagales of the monocots. In earlier systems of classification, it was usually placed in the family Amaryllidaceae.

The Molluginaceae are a family of flowering plants recognized by several taxonomists. It was previously included in the larger family Aizoaceae. The APG III system of 2009 made no change in the status of the family as compared to the APG II system of 2003 and the APG system of 1998, apart from a reassignment of several genera, such as the placement of Corrigiola and Telephium into Caryophyllaceae, Corbichonia in Lophiocarpaceae, Microtea into Microteaceae and Limeum in Limeaceae, because the family was found to be widely polyphyletic in Caryophyllales. In addition Macarthuria was found not to be related to Limeum as previously thought and thus it was placed in Macarthuriaceae, and similarly species formerly placed in Hypertelis, apart from type species Hypertelis spergulacea, a true Molluginaceae, were found to belong elsewhere and were described as Kewa in the family Kewaceae, named for the Royal Botanic Gardens Kew. Molluginaceae is still assigned to the order Caryophyllales in the clade core eudicots, although the generic circumscription is difficult because Mollugo is not monophyletic.

Caryophyllales is a diverse and heterogeneous order of flowering plants that includes the cacti, carnations, amaranths, ice plants, beets, and many carnivorous plants. Many members are succulent, having fleshy stems or leaves. The betalain pigments are unique in plants of this order and occur in all its families with the exception of Caryophyllaceae and Molluginaceae.

Oncotheca is a genus of tree endemic to New Caledonia. There are two species, Oncotheca balansae and Oncotheca humboldtiana.

Hydrostachys is a genus of about 22 species of flowering plants native to Madagascar and southern and central Africa. It is the only genus in the family Hydrostachyaceae. All species of Hydrostachys are aquatic, growing on rocks in fast-moving water. They have tuberous roots, usually pinnately compound leaves, and highly reduced flowers on dense spikes.

Frankenia is the only genus in the Frankeniaceae family of flowering plants. Other genera have been recognized within the family, such as Anthobryum, Hypericopsis and Niederleinia, but molecular phylogenetic studies have consistently shown that they all belong inside Frankenia. Frankenia comprises about 70–80 species of shrubs, subshrubs and herbaceous plants, adapted to saline and dry environments throughout temperate and subtropical regions. A few species are in cultivation as ornamental plants.

Talinaceae is a family of two genera and 28 species of flowering plants comprising shrubs, lianas, and herbaceous species native to the Americas, Africa and Madagascar. The family is newly recognized through research by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group III system to deal with long-standing phylogenetic difficulties in placing various genera within the Caryophyllales.

Peraceae Klotzsch is a family of flowering plants in the eudicot order Malpighiales. The family was segregated from the Euphorbiaceae by Johann Friedrich Klotzsch in 1859, and its uniqueness was affirmed by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew's Euphorbiaceae expert, Airy Shaw.

Kewa is a genus of flowering plants, consisting of eight species of succulent sub-woody plants, native to eastern and southern Africa, including Saint Helena and Madagascar. These are small shrubs or herbs that form cushions and have edible, acid-tasting leaves. Kewa is the only genus in the family Kewaceae.
Hypertelis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Molluginaceae. Most of its former species have been transferred to the new genus Kewa, and the remaining species, Hypertelis spergulacea, may also need a different placement. Hypertelis spergulacea is a woody-based plant, up to 30 cm (1 ft) high, with whorled greyish green leaves. It is found on the border between Namibia and the Northern Cape province of South Africa.

Macarthuriaceae is a family of plants in the order Caryophyllales and consists of a single genus, Macarthuria.

Pharnaceum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Molluginaceae, found in southern Africa. Some are annual or perennial herbs, others are shrubs or subshrubs.


















