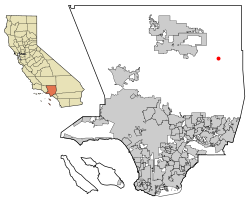
Palmdale is a city in northern Los Angeles County in the U.S. state of California. The city lies in the Antelope Valley of Southern California. The San Gabriel Mountains separate Palmdale from the Los Angeles Basin to the south.

The San Gabriel Mountains comprise a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Transverse Ranges and lies between the Los Angeles Basin and the Mojave Desert, with Interstate 5 to the west and Interstate 15 to the east. The range lies in, and is surrounded by, the Angeles and San Bernardino National Forests, with the San Andreas Fault as its northern border.

The San Gabriel Valley, often referred to by its initials as SGV, is one of the principal valleys of Southern California, with the city of Los Angeles directly bordering it to the west, and occupying the vast majority of the southeastern part of Los Angeles County. Surrounding landforms and other features include the following:

The Antelope Valley is located in northern Los Angeles County, California, United States, and the southeast portion of California's Kern County, and constitutes the western tip of the Mojave Desert. It is situated between the Tehachapi, Sierra Pelona, and the San Gabriel Mountains. The valley was named for the pronghorns that roamed there until they were all eliminated in the 1880s, mostly by hunting, or resettled in other areas. The principal cities in the Antelope Valley are Palmdale and Lancaster.

State Route 14 (SR 14) is a north–south state highway in the U.S. state of California that connects Los Angeles to the northern Mojave Desert. The southern portion of the highway is signed as the Antelope Valley Freeway. Its southern terminus is at Interstate 5 in the Los Angeles neighborhoods of Granada Hills and Sylmar just immediately to the south of the border of the city of Santa Clarita. SR 14's northern terminus is at U.S. Route 395 (US 395) near Inyokern. Legislatively, the route extends south of I-5 to SR 1 in the Pacific Palisades area of Los Angeles; however, the portion south of the junction with I-5 has not been constructed. The southern part of the constructed route is a busy commuter freeway serving and connecting the cities of Santa Clarita, Palmdale, and Lancaster to the rest of the Greater Los Angeles area. The northern portion, from Vincent to US 395, is legislatively named the Aerospace Highway, as the highway serves Edwards Air Force Base, once one of the primary landing strips for NASA's Space Shuttle, as well as the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake that supports military aerospace research, development and testing. This section is rural, following the line between the hot Mojave desert and the forming Sierra Nevada mountain range. Most of SR 14 is loosely paralleled by a rail line originally built by the Southern Pacific Railroad, and was once the primary rail link between Los Angeles and Northern California. While no longer a primary rail line, the southern half of this line is now used for the Antelope Valley Line of the Metrolink commuter rail system.

State Route 138 is an east–west state highway in the U.S. state of California that generally follows the northern foothills of the San Gabriel Mountains and the western Mojave Desert. The scenic highway begins in the west at its junction with Interstate 5 located south of Gorman in the Sierra Pelona Mountains, continues eastward through the Antelope Valley and Cajon Pass, to its junction with State Route 18 in the east, located in the San Bernardino Mountains south of Crestline.

The Ridge Route, officially the Castaic–Tejon Route and colloquially known as the Grapevine, was a two-lane highway between Los Angeles County and Kern County, California. Opened in 1915 and paved with concrete between 1917 and 1921, the road was the first paved highway directly linking the Los Angeles Basin with the San Joaquin Valley over the Tejon Pass and the rugged Sierra Pelona Mountains ridge south of Gorman. Much of the old road runs through the Angeles National Forest, and passes many historical landmarks, including the National Forest Inn, Reservoir Summit, Kelly's Half Way Inn, Tumble Inn, and Sandberg's Summit Hotel. North of the forest, the Ridge Route passed through Deadman's Curve before ending at Grapevine.

Pearblossom is an unincorporated community located in the Antelope Valley of the Mojave Desert, in northern Los Angeles County, California, United States.

The San Gabriel River is a mostly-urban waterway flowing 58 miles (93 km) southward through Los Angeles and Orange Counties, California, in the United States. It is the central of three major rivers draining the Greater Los Angeles Area, the others being the Los Angeles River and Santa Ana River. The river's watershed stretches from the rugged San Gabriel Mountains to the heavily-developed San Gabriel Valley and a significant part of the Los Angeles coastal plain, emptying into the Pacific Ocean between the cities of Long Beach and Seal Beach.

The Angeles Crest Highway is a two-lane highway over the San Gabriel Mountains, in Los Angeles County, California. Its route is to/through the San Gabriel Mountains National Monument and the Angeles National Forest. With the exception of a 1,000 feet (300 m)-long section in La Cañada Flintridge, the entire route is part of California State Route 2.

State Route 18 is a state highway in the U.S. state of California. It serves as a primary route into the San Bernardino Mountains, both from the Riverside–San Bernardino metropolitan area from the south and the Mojave Desert from the north. SR 18 runs from State Route 210 in San Bernardino to State Route 138 in Llano. It has two discontinuities: one in Big Bear Lake, the other in Victorville.

The Victor Valley is a valley in the Mojave Desert and subregion of the Inland Empire, in San Bernardino County in Southern California.
Piñon Hills is a census-designated place in San Bernardino County, California, near the Los Angeles County line. It is located along Pearblossom Highway, 28 miles east of Palmdale, and 15 miles west of the Cajon Pass where Pearblossom Highway meets Interstate 15. The town lies within 25 miles of Hesperia and Victorville. Piñon Hills is in a tri-community that consists of Piñon Hills, Phelan, and Wrightwood. The elevation is 4,173 feet (1,272 m). The population was 7,272 at the 2010 census.
The Imperial Highway is a west-east thoroughfare in the counties of Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, San Diego, and Imperial in the U.S. state of California. The main portion of the existing route begins at Vista Del Mar in Los Angeles near the Los Angeles International Airport and ends at the Anaheim–Orange city line at Via Escola where it becomes Cannon Street. Historically, the Imperial Highway extended from Vista Del Mar to Calexico, where a portion of the highway still exists. The original route was replaced with other highways, leading the older portions of the Imperial Highway to fall out of use.

U.S. Route 101 (US 101) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway, stretching from Los Angeles, California, to Tumwater, Washington. The California portion of US 101 is one of the last remaining and longest U.S. Routes still active in the state, and the longest highway of any kind in California. US 101 was also one of the original national routes established in 1926. Significant portions of US 101 between the Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area follow El Camino Real, the commemorative route connecting the former Alta California's 21 missions.

Western Avenue is a major four-lane street in the city of Los Angeles and through the center portion of Los Angeles County, California. It is one of the longest north–south streets in Los Angeles city and county, apart from Sepulveda Boulevard. It is about 29 miles (47 km) long.

Llano del Rio was a commune located in what is now Llano, California, east of Palmdale in the Antelope Valley, Los Angeles County. The colony was devised by lawyer and socialist politician Job Harriman after he had failed his bid to become the mayor of Los Angeles in 1911. The colony's land was acquired in 1913 and it was formally launched on May 1, 1914.

Wilsona was a 20th-century settlement in the Antelope Valley section of Los Angeles County, California. It lay in the vicinity of Big Rock Wash, at an elevation of 2726 feet in the far northeastern corner of the county, the near the border junction of Los Angeles, Kern, and San Bernardino Counties. Wilsona had a post office beginning in 1916 between the Llano and Gray Mountain post offices. Circa 1929, Valyermo, Llano, Wilsona, Neenach, Domino, and Muroc, were all described as "post offices that serve scattered ranches. All these communities are reached by automobile, and roads lead from the [Antelope Valley] to desert towns lying to the north and east." A 1939 guide to Los Angeles County stated "Antelope Valley has many small communities, among which are Acton, Littlerock, Fairmont, Vincent, Harold, Pearblossom, Llano, Valyermo, Wilsona, Hi Vista, Tierra Bonita, Roosevelt, Redman, Del Sur, Esperanza, Rogers, Lake Hughes, Neenach, Sandberg, and Gorman. Most of these are trading centers for populations, most of which are active either in mining or agricultural pursuits."

There are 9 routes assigned to the "N" zone of the California Route Marker Program, which designates county routes in California. The "N" zone includes county highways lying in Los Angeles and Orange counties.