
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies. It is mainly used as an analgesic. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual; via inhalation; injection into a muscle, injection under the skin, or injection into the spinal cord area; transdermal; or via rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine are available as MS-Contin, Kadian, and other brand names as well as generically.

Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, Thēbai (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar to both morphine and codeine, but has stimulatory rather than depressant effects. At high doses, it causes convulsions similar to strychnine poisoning. The synthetic enantiomer (+)-thebaine does show analgesic effects apparently mediated through opioid receptors, unlike the inactive natural enantiomer (−)-thebaine. While thebaine is not used therapeutically, it is the main alkaloid extracted from Papaver bracteatum and can be converted industrially into a variety of compounds, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, nalbuphine, naloxone, naltrexone, buprenorphine, butorphanol and etorphine.

Papaver somniferum, commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable ornamental plant grown in gardens. Its native range was east of the Mediterranean Sea, but has since been obscured and vastly expanded by introduction and cultivation from ancient times to the present day, being naturalized across much of Europe and Asia.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.

Noscapine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae. It lacks significant hypnotic, euphoric, or analgesic effects affording it with very low addictive potential. This agent is primarily used for its antitussive (cough-suppressing) effects.

Codeinone is an isoquinolone alkaloid found in the opium poppy. As an analgesic, it is one-third the potency of codeine. It is an important intermediate in the production of hydrocodone–a painkiller about three-quarters the potency of morphine–as well as of oxycodone, though the latter can also be synthesized from thebaine.
In enzymology, a codeinone reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.247) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridine reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.248) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a reticuline oxidase (EC 1.21.3.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a berbamunine synthase (EC 1.14.19.66, Formerly EC 1.1.3.34 and EC 1.14.21.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridine synthase (EC 1.14.21.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,2-dehydroreticulinium reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.5.1.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme (S)-norcoclaurine synthase (EC 4.2.1.78) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
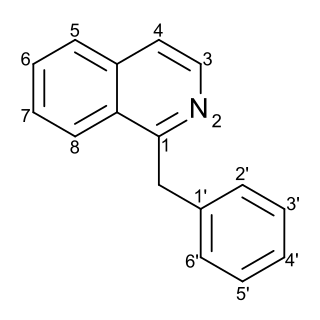
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine.

An opiate is an alkaloid substance derived from opium. It differs from the similar term opioid in that the latter is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions, with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Most opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America.

Synthesis of morphine-like alkaloids in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the natural morphinan class of alkaloids that includes codeine, morphine, oripavine, and thebaine and the closely related semisynthetic analogs methorphan, buprenorphine, hydromorphone, hydrocodone, isocodeine, naltrexone, nalbuphine, oxymorphone, oxycodone, and naloxone.

Erysodienone is a key precursor in the biosynthesis of many Erythrina-produced alkaloids. Early work was done by Derek Barton and co-workers to illustrate the biosynthetic pathways towards erythrina alkaloids. It was demonstrated that erysodienone could be synthesized from simple starting materials by a similar approach as its biosynthetic pathway, which led to the development of the biomimetic synthesis of erysodienone.
Morphinone reductase is an enzyme which catalyzes the NADH-dependent saturation of the carbon-carbon double bond of morphinone and codeinone, yielding hydromorphone and hydrocodone respectively. This saturation reaction is assisted by a FMN cofactor and the enzyme is a member of the α/β-barrel flavoprotein family. The sequence of the enzyme has been obtained from bacteria Pseudomonas putida M10 and has been successfully expressed in yeast and other bacterial species. The enzyme is reported to harbor high sequence and structural similarity to the Old Yellow Enzyme, a large group of flavin-dependent redox biocatalysts of yeast species, and an oestrogen-binding protein of Candida albicans. The enzyme has demonstrated value in biosynthesis of semi-opiate drugs in microorganisms, expanding the chemical diversity of BIA biosynthesis.
(S)-corytuberine synthase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme purified from the plant Coptis japonica, with EC number EC 1.14.19.51 and CYP Symbol CYP80G2, and catalyses an intramolecular C-C phenol coupling of (S)-reticuline in magnoflorine biosynthesis.










