
The Willamette River is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is 187 miles (301 km) long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward between the Oregon Coast Range and the Cascade Range, the river and its tributaries form the Willamette Valley, a basin that contains two-thirds of Oregon's population, including the state capital, Salem, and the state's largest city, Portland, which surrounds the Willamette's mouth at the Columbia.

Thomas Lawson McCall was an American statesman, politician and journalist in the state of Oregon, serving as the state's thirtieth governor from 1967 to 1975. A progressive Republican, he was known as a staunch environmentalist and an advocate of sustainable development.

Governor Tom McCall Waterfront Park is a 36.59-acre (148,100 m2) park located in downtown Portland, Oregon, along the Willamette River. After the 1974 removal of Harbor Drive, a major milestone in the freeway removal movement, the park was opened to the public in 1978. The park covers 13 tax lots and is owned by the City of Portland. The park was renamed in 1984 to honor Tom McCall, the Oregon governor who pledged his support for the beautification of the west bank of the Willamette River—harkening back to the City Beautiful plans at the turn of the century which envisioned parks and greenways along the river. The park is bordered by RiverPlace to the south, the Steel Bridge to the north, Naito Parkway to the west, and Willamette River to the east. In October 2012, Waterfront Park was voted one of America's ten greatest public spaces by the American Planning Association.

Downtown Portland is the central business district of Portland, Oregon, United States. It is on the west bank of the Willamette River in the northeastern corner of the southwest section of the city and where most of the city's high-rise buildings are found.

Oregon Route 6 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Oregon that runs between the city of Tillamook on the Oregon Coast, to the Willamette Valley, near Banks. OR 6 traverses the Wilson River Highway No. 37 of the Oregon state highway system, named after the river paralleling the highway's western segment.

The Mount Hood Highway No. 26 is the Oregon Department of Transportation's designation for a 96.74-mile-long (155.69 km) highway from Portland east around the south side of Mount Hood and north via Bennett Pass to Hood River. It is marked as U.S. Route 26 from Portland to near Mount Hood and Oregon Route 35 the rest of the way to Hood River.

Harbor Drive is a short roadway in Portland, Oregon, spanning a total length of 0.7 miles (1.1 km), which primarily functions as a ramp to and from Interstate 5. It was once much longer, running along the western edge of the Willamette River in the downtown area. Originally constructed from 1942–43, the vast majority of the road was replaced with Tom McCall Waterfront Park in the 1970s. Signed as U.S. Route 99W, it had been the major route through the city and its removal is often cited as the first instance of freeway removal in the U.S. and as a milestone in urban planning; the original road is remembered as the first limited-access highway built in the city.

Oregon Route 58, also known as the Willamette Highway No. 18, is a state highway in the U.S. state of Oregon. The route, signed east–west, runs in a southeast–northwest direction, connecting U.S. Route 97 north of Chemult with Interstate 5 south of Eugene. It links the Willamette Valley and Central Oregon, crossing the Cascade Range at Willamette Pass. OR 58 is generally a modern two-lane highway with a speed limit of 55 mph (88 km/h), built through the Willamette National Forest in the 1930s.

Asa Lawrence Lovejoy was an American pioneer and politician in the region that would become the U.S. state of Oregon. He is best remembered as a founder of the city of Portland, Oregon. He was an attorney in Boston, Massachusetts before traveling by land to Oregon; he was a legislator in the Provisional Government of Oregon, mayor of Oregon City, and a general during the Cayuse War that followed the Whitman massacre in 1847. He was also a candidate for Provisional Governor in 1847, before the Oregon Territory was founded, but lost that election.

Oregon Ballot Measure 37 was a controversial land-use ballot initiative that passed in the U.S. state of Oregon in 2004 and is now codified as Oregon Revised Statutes (ORS) 195.305. Measure 37 has figured prominently in debates about the rights of property owners versus the public's right to enforce environmental and other land use regulations. Voters passed Measure 49 in 2007, substantially reducing the impact of Measure 37.

Oregon pioneer history (1806–1890) is the period in the history of Oregon Country and Oregon Territory, in the present day state of Oregon and Northwestern United States.

Interstate 5 (I-5) in the U.S. state of Oregon is a major Interstate Highway that traverses the state from north to south. It travels to the west of the Cascade Mountains, connecting Portland to Salem, Eugene, Medford, and other major cities in the Willamette Valley and across the northern Siskiyou Mountains. The highway runs 308 miles (496 km) from the California state line near Ashland to the Washington state line in northern Portland, forming the central part of Interstate 5's route between Mexico and Canada.
Audrey Grace McCall was an American activist, environmentalist, politician, and former First Lady of Oregon from January 9, 1967, until January 13, 1975. The widow of former Governor Tom McCall, she became one of the most politically influential first ladies and former first ladies in Oregon's history. Following her husband's death in 1983, Audrey McCall championed a variety of political, social and environmental issues throughout the state. In particular, McCall sought to protect and expand the sweeping statewide land-use laws that had been implemented and signed into law by Governor McCall. She campaigned and fundraised on behalf of both Democratic and Republican political candidates.

The U.S. state of Oregon has had an evolving set of laws affecting land ownership and its restrictions.
The Oregon Land Conservation and Development Act of 1973, formally Oregon Senate Bills 100 and 101 of 1973, were pieces of landmark legislation passed by the Oregon State Senate in 1973 and later signed into law. It created a framework for land use planning across the state, requiring every city and county to develop a comprehensive plan for land use.
The Oregon Beach Bill was a piece of landmark legislation in the U.S. state of Oregon, passed by the 1967 session of the Oregon Legislature. It established public ownership of land along the Oregon Coast from the water up to sixteen vertical feet above the low tide mark.
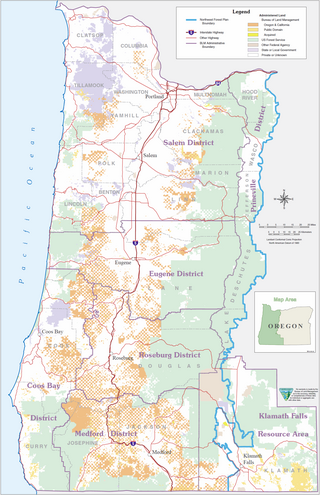
The Oregon and California Railroad Revested Lands, are approximately 2,600,000 acres (1,100,000 ha) of land located in eighteen counties of western Oregon. Originally granted to the Oregon & California Railroad to build a railroad between Portland, Oregon and San Francisco, California, the land was reconveyed to the United States government by act of Congress in 1916 and is currently managed by the United States Bureau of Land Management.

The Native American peoples of Oregon are the set of Indigenous peoples who have inhabited or who still inhabit the area delineated in today's state of Oregon in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. While the state of Oregon currently maintains relations with nine federally recognized tribal groups, the state was previously home to a much larger number of autonomous tribal groups, which today either no longer exist or have been absorbed into these larger confederated entities. Six of the nine tribes gained federal recognition in the late 20th century, after undergoing the termination and restoration of their treaty rights starting in the 1950s.

Willamette Riverkeeper is a non profit organization formed in 1996 in order to protect and restore the water quality and natural habitat of the Willamette River. WR was the 13th Riverkeeper organization formed after the original Hudson Riverkeeper. Today there are over 300 Riverkeeper, Baykeeper, and Coastkeeper organizations in the United States and internationally. Each organization is independent, but subscribes first and foremost to enforcing the Clean Water Act, or related international laws.
The following is a timeline of the history of Oregon in the United States of America.















