Nestucca Bay is a bay formed by the confluence of the Nestucca River and the Pacific Ocean in northwest Oregon in the United States. It is near the town of Pacific City, which is in southwestern Tillamook County, about 12 miles (19 km) south of Cape Lookout. The bay is a bar-built estuary and totals 1,000 acres (4.0 km2) in area.

Plum Island is a barrier island located off the northeastern coast of Massachusetts, north of Cape Ann, United States. It is approximately 11 miles (18 km) in length. The island is named for the wild beach plum shrubs that grow on its dunes, but is also famous for the purple sands at high tide, which derive their color from tiny crystals of pink pyrope garnet. It is located in parts of four municipalities in Essex County. From north to south they are the city of Newburyport, and the towns of Newbury, Rowley, and Ipswich.

Humboldt Bay is a natural bay and a multi-basin, bar-built coastal lagoon located on the rugged North Coast of California, entirely within Humboldt County, United States. It is the largest protected body of water on the West Coast between San Francisco Bay and Puget Sound, the second-largest enclosed bay in California, and the largest port between San Francisco and Coos Bay, Oregon. The largest city adjoining the bay is Eureka, the regional center and county seat of Humboldt County, followed by the city of Arcata. These primary cities, together with adjoining unincorporated communities and several small towns, comprise a Humboldt Bay Area with a total population of nearly 80,000 people. This comprises nearly 60% of the population of Humboldt County. The bay is home to more than 100 plant species, 300 invertebrate species, 100 fish species, and 200 bird species. In addition, the bay and its complex system of marshes and grasses support hundreds of thousands of migrating and local shore birds. Commercially, this second-largest estuary in California is the site of the largest oyster production operations on the West Coast, producing more than half of all oysters farmed in California.

The Lower Klamath National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge of the United States on the border between California and Oregon. It is operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. The refuge was designated a National Historic Landmark on October 16, 1965.

Ankeny National Wildlife Refuge is located in the fertile Willamette Valley of northwestern Oregon, 12 miles (19 km) south of Salem. The valley was once a rich mix of wildlife habitats. Valley wetlands were once extensive, with meandering stream channels and vast seasonal marshes. Today, the valley is a mix of farmland and growing cities, with few areas remaining for wildlife.

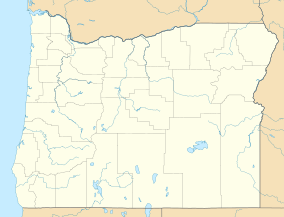
Baskett Slough National Wildlife Refuge is in northwestern Oregon, 10 miles (16 km) west of Salem in Polk County. The Refuge consists of 1,173 acres (4.75 km2) of cropland, which provide forage for wintering geese, 300 acres (1.2 km2) of forests, 550 acres (2.2 km2) of grasslands, and 500 acres (2.0 km2) of shallow water seasonal wetlands and 35 acres (0.14 km2) of permanent open water. In 1965, Baskett Slough National Wildlife Refuge was created to help ensure some of the original habitat remained for species preservation. The refuge is managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior.

Seal Beach National Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife refuge encompassing 965 acres (3.91 km2) located in the California coastal community of Seal Beach. Although it is located in Orange County it is included as part of the San Diego National Wildlife Refuge Complex. It was established in 1972.

The Rachel Carson National Wildlife Refuge is a 9,125-acre (37 km2) National Wildlife Refuge made up of several parcels of land along 50 miles (80 km) of Maine's southern coast. Created in 1966, it is named for environmentalist and author Rachel Carson, whose book Silent Spring raised public awareness of the effects of DDT on migratory songbirds, and of other environmental issues.
The Oregon Coast National Wildlife Refuge Complex consists of six National Wildlife Refuges along the Oregon Coast. It provides wilderness protection to thousands of small islands, rocks, reefs, headlands, marshes, and bays totaling 371 acres spanning 320 miles (515 km) of Oregon's coastline. The areas are all managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.

Bandon Marsh National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge on Oregon's coast. It is one of six National Wildlife Refuges comprising the Oregon Coast National Wildlife Refuge Complex and is renowned among bird watchers for being able to view rare shorebirds including ruff, Hudsonian godwit, and Mongolian plover. The refuge was last expanded in 1999, it now has 889 acres (3.60 km2) in two units: Bandon Marsh and Ni-les'tun.

Siletz Bay National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge on Oregon's coast. It is one of six National Wildlife Refuges (NWRs) comprising the Oregon Coast National Wildlife Refuge Complex. The refuge consists of several discontinuous tracts north and south of the Siletz River where it enters Siletz Bay south of Lincoln City. Previously closed to public use, excluding viewing from outside the refuge boundaries and during special events, the refuge now has a boat launch offering access to non-motorized boats. Alder Island Nature Trail caters to visitors on foot, opened in 2017, and is 0.85 miles (1.37 km) round trip.

Willapa National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located on the shores of Willapa Bay in Washington, United States. It comprises 11,000 acres (45 km2) of sand dunes, sand beaches, mudflats, grasslands, saltwater and freshwater marshes, and coniferous forest. The refuge includes Long Island with stands of old growth Western red cedar and hemlock.

San Pablo Bay National Wildlife Refuge is a 13,190-acre (53.4 km2) National Wildlife Refuge in California established in 1970. It extends along the northern shore of San Pablo Bay, from the mouth of the Petaluma River, to Tolay Creek, Sonoma Creek, and ending at Mare Island.

Moosehorn National Wildlife Refuge is one of the northernmost National Wildlife Refuges in the Atlantic Flyway, a migratory route that follows the eastern coast of North America. The refuge provides important feeding and nesting habitat for many bird species, including waterfowl, wading birds, shorebirds, upland game birds, songbirds, and birds of prey.

Glenn Martin National Wildlife Refuge includes the northern half of Smith Island, which lies 11 miles (18 km) west of Crisfield, Maryland, and Watts Island, which is located between the eastern shore of Virginia and Tangier Island. Both islands are situated in the lower Chesapeake Bay.

Parker River National Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife sanctuary encompassing the majority of Plum Island in northeastern Essex County, Massachusetts, 5 miles southeast of Newburyport. It was established in 1942 primarily to provide feeding, resting, and nesting habitats for migratory birds. Located along the Atlantic Flyway, the refuge is of vital stopover significance to waterfowl, shorebirds, and songbirds during migratory periods.

Seatuck National Wildlife Refuge is located in the hamlet of Islip, New York, on the south shore of Long Island. It is managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as part of the Long Island National Wildlife Refuge Complex. The refuge consists of 196 acres (0.79 km2) bordering the Great South Bay, separated from the Atlantic Ocean only by Fire Island. Situated in a heavily developed urban area along Champlin Creek, the refuge is an oasis for many species of migratory birds and waterfowl.

Humboldt Bay National Wildlife Refuge is located on Humboldt Bay, on the California North Coast near the cities of Eureka and Arcata. The refuge exists primarily to protect and enhance wetland habitats for migratory water birds using the bay area, including tens of thousands of shorebirds, ducks, geese, swans, and the black brant. Humboldt Bay National Wildlife Refuge, along with other public and private lands around Humboldt Bay, is one of the key stopovers for the millions of migratory birds that rely on the Pacific Flyway. More than 200 bird species, including 80 kinds of water birds and four endangered species, regularly feed, rest, or nest on the refuge or other areas around the bay.

Sitka Sedge State Natural Area is an estuary and beach on the north coast of the U.S. state of Oregon in Tillamook County. Sitka Sedge consists of 357 acres (144 ha) of tidal marsh, mudflats, dunes, forested wetlands, and uplands at the south end of the Sand Lake estuary, north of Tierra Del Mar.

The North American Southern Coastal Plain is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in six U.S. states. The region stretches across the Gulf coast from eastern Louisiana to Florida, forms the majority of Florida, and forms the coastlines of Georgia and much of South Carolina. It has been divided into twelve Level IV ecoregions.