
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.

Refrigeration is any of various types of cooling of a space, substance, or system to lower and/or maintain its temperature below the ambient one. Refrigeration is an artificial, or human-made, cooling method.

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

A dehumidifier is an air conditioning device which reduces and maintains the level of humidity in the air. This is done usually for health or thermal comfort reasons, or to eliminate musty odor and to prevent the growth of mildew by extracting water from the air. It can be used for household, commercial, or industrial applications. Large dehumidifiers are used in commercial buildings such as indoor ice rinks and swimming pools, as well as manufacturing plants or storage warehouses. Typical air conditioning systems combine dehumidification with cooling, by operating cooling coils below the dewpoint and draining away the water that condenses.

A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated due to their toxicity, flammability and the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and that of HFC refrigerants to climate change.

A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid coolant via a vapor-compression, adsorption refrigeration, or absorption refrigeration cycles. This liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment, or another process stream. As a necessary by-product, refrigeration creates waste heat that must be exhausted to ambience, or for greater efficiency, recovered for heating purposes. Vapor compression chillers may use any of a number of different types of compressors. Most common today are the hermetic scroll, semi-hermetic screw, or centrifugal compressors. The condensing side of the chiller can be either air or water cooled. Even when liquid cooled, the chiller is often cooled by an induced or forced draft cooling tower. Absorption and adsorption chillers require a heat source to function.

A refrigerator, colloquially fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so that its inside is cooled to a temperature below the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential food storage technique around the world. The low temperature lowers the reproduction rate of bacteria, so the refrigerator reduces the rate of spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. The optimal temperature range for perishable food storage is 3 to 5 °C. A freezer is a specialized refrigerator, or portion of a refrigerator, that maintains its contents’ temperature below the freezing point of water. The refrigerator replaced the icebox, which had been a common household appliance for almost a century and a half. The United States Food and Drug Administration recommends that the refrigerator be kept at or below 4 °C (40 °F) and that the freezer be regulated at −18 °C (0 °F).

Cold chain is a set of rules and procedures that ensure the systematic coordination of activities for ensuring temperature-control of goods while in storage and transit. The objective of a cold chain is to preserve the integrity and quality of goods such as pharmaceutical products or perishable good from production to consumption. Cold chain management earned its name as a "chain" because it involves linking a set of storage locations and special transport equipment, required for ensuring that temperature conditions for goods are met, while they are in storage or in transit from production to consumption, akin to the interconnected links of a physical chain.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.

Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature and in some cases also strictly controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or by other methods, including passive cooling and ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners, but use a reversing valve to allow them both to heat and to cool an enclosed space.

Thermodynamic heat pump cycles or refrigeration cycles are the conceptual and mathematical models for heat pump, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. A heat pump is a mechanical system that transmits heat from one location at a certain temperature to another location at a higher temperature. Thus a heat pump may be thought of as a "heater" if the objective is to warm the heat sink, or a "refrigerator" or “cooler” if the objective is to cool the heat source. The operating principles in both cases are the same; energy is used to move heat from a colder place to a warmer place.
Natural refrigerants are considered substances that serve as refrigerants in refrigeration systems. They are alternatives to synthetic refrigerants such as chlorofluorocarbon (CFC), hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC), and hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) based refrigerants. Unlike other refrigerants, natural refrigerants can be found in nature and are commercially available thanks to physical industrial processes like fractional distillation, chemical reactions such as Haber process and spin-off gases. The most prominent of these include various natural hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, ammonia, and water. Natural refrigerants are preferred actually in new equipment to their synthetic counterparts for their presumption of higher degrees of sustainability. With the current technologies available, almost 75 percent of the refrigeration and air conditioning sector has the potential to be converted to natural refrigerants.
HVAC is a major sub discipline of mechanical engineering. The goal of HVAC design is to balance indoor environmental comfort with other factors such as installation cost, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. The discipline of HVAC includes a large number of specialized terms and acronyms, many of which are summarized in this glossary.

Pumpable icetechnology (PIT) uses thin liquids, with the cooling capacity of ice. Pumpable ice is typically a slurry of ice crystals or particles ranging from 5 micrometers to 1 cm in diameter and transported in brine, seawater, food liquid, or gas bubbles of air, ozone, or carbon dioxide.
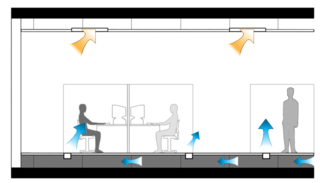
Underfloor air distribution (UFAD) is an air distribution strategy for providing ventilation and space conditioning in buildings as part of the design of a HVAC system. UFAD systems use an underfloor supply plenum located between the structural concrete slab and a raised floor system to supply conditioned air to supply outlets, located at or near floor level within the occupied space. Air returns from the room at ceiling level or the maximum allowable height above the occupied zone.

The International Institute of Refrigeration (IIR), is an independent intergovernmental science and technology-based organization which promotes knowledge of refrigeration and associated technologies and applications on a global scale that improve quality of life in a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable manner, including:

Automotive air conditioning systems use air conditioning to cool the air in a vehicle.

The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers is an American professional association seeking to advance heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration (HVAC&R) systems design and construction. ASHRAE has over 50,000 members in more than 130 countries worldwide.
The Institute of Refrigeration is an organisation in the UK that supports the refrigeration and air-conditioning industry.
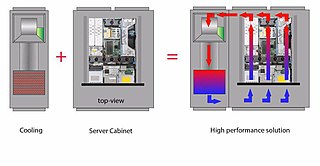
Close Coupled Cooling is a last generation cooling system particularly used in data centers. The goal of close coupled cooling is to bring heat transfer closest to its source: the equipment rack. By moving the air conditioner closer to the equipment rack a more precise delivery of inlet air and a more immediate capture of exhaust air is ensured.

















