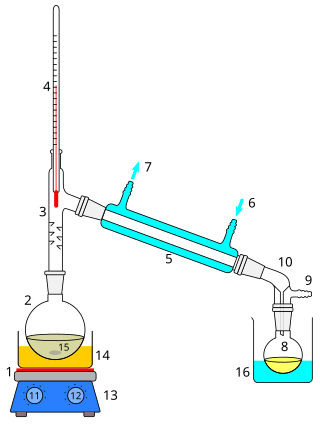
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixture and the condensation of the vapors in a still.

A vacuum pump is a type of pump device that draws gas particles from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke, and was preceded by the suction pump, which dates to antiquity.

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

A dehumidifier is an air conditioning device which reduces and maintains the level of humidity in the air. This is done usually for health or thermal comfort reasons or to eliminate musty odor and to prevent the growth of mildew by extracting water from the air. It can be used for household, commercial, or industrial applications. Large dehumidifiers are used in commercial buildings such as indoor ice rinks and swimming pools, as well as manufacturing plants or storage warehouses. Typical air conditioning systems combine dehumidification with cooling, by operating cooling coils below the dewpoint and draining away the water that condenses.

Pyrolysis is the process of thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere without access to oxygen.

Brazing is a metal-joining process in which two or more metal items are joined by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, with the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal.

Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. The verb form of sublimation is sublime, or less preferably, sublimate. Sublimate also refers to the product obtained by sublimation. The point at which sublimation occurs rapidly is called critical sublimation point, or simply sublimation point. Notable examples include sublimation of dry ice at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and that of solid iodine with heating.

In metallurgy, a flux is a chemical reducing agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.
Outgassing is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen, or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation, as well as desorption, seepage from cracks or internal volumes, and gaseous products of slow chemical reactions. Boiling is generally thought of as a separate phenomenon from outgassing because it consists of a phase transition of a liquid into a vapor of the same substance.

Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to house mold, upholstered furniture, arts and crafts supplies, dry cleaned clothing, and cleaning supplies. VOCs are responsible for the odor of scents and perfumes as well as pollutants. They play an important role in communication between animals and plants, such as attractants for pollinators, protection from predation, and even inter-plant interactions. Some VOCs are dangerous to human health or cause harm to the environment, often despite the odor being perceived as pleasant, such as "new car smell".
Ultra-high vacuum is the vacuum regime characterised by pressures lower than about 1×10−6 pascals. UHV conditions are created by pumping the gas out of a UHV chamber. At these low pressures the mean free path of a gas molecule is greater than approximately 40 km, so the gas is in free molecular flow, and gas molecules will collide with the chamber walls many times before colliding with each other. Almost all molecular interactions therefore take place on various surfaces in the chamber.
An air purifier or air cleaner is a device which removes contaminants from the air in a room to improve indoor air quality. These devices are commonly marketed as being beneficial to allergy sufferers and asthmatics, and at reducing or eliminating second-hand tobacco smoke.

A particulate air filter is a device composed of fibrous, or porous materials which removes particulates such as smoke, dust, pollen, mold, viruses and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbon) may also remove odors and gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds or ozone. Air filters are used in applications where air quality is important, notably in building ventilation systems and in engines.

Space manufacturing or In-space manufacturing is the fabrication, assembly or integration of tangible goods beyond Earth's atmosphere, involving the transformation of raw or recycled materials into components, products, or infrastructure in space, where the manufacturing process is executed either by humans or automated systems by taking advantage of the unique characteristics of space. Synonyms of Space/In-space manufacturing are In-orbit manufacturing, Off-Earth manufacturing, Space-based manufacturing, Orbital manufacturing, In-situ manufacturing, In-space fabrication, In-space production, etc.

Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface. These processes are most commonly used on low-alloy steels. They are also used on titanium, aluminium and molybdenum.

A thermal cooker, or a vacuum flask cooker, is a cooking device that uses thermal insulation to retain heat and cook food without the continuous use of fuel or other heat source. It is a modern implementation of a haybox, which uses hay or straw to insulate a cooking pot.
Ultra-high-purity steam, also called the clean steam, UHP steam or high purity water vapor, is used in a variety of industrial manufacturing processes that require oxidation or annealing. These processes include the growth of oxide layers on silicon wafers for the semiconductor industry, originally described by the Deal-Grove model, and for the formation of passivation layers used to improve the light capture ability of crystalline photovoltaic cells. Several methods and technologies can be employed to generate ultra high purity steam, including pyrolysis, bubbling, direct liquid injection, and purified steam generation. The level of purity, or the relative lack of contamination, affects the quality of the oxide layer or annealed surface. The method of delivery affects growth rate, uniformity, and electrical performance. Oxidation and annealing are common steps in the manufacture of such devices as microelectronics and solar cells.

Materials for use in vacuum are materials that show very low rates of outgassing in vacuum and, where applicable, are tolerant to bake-out temperatures. The requirements grow increasingly stringent with the desired degree of vacuum to be achieved in the vacuum chamber. The materials can produce gas by several mechanisms. Molecules of gases and water can be adsorbed on the material surface. Materials may sublimate in vacuum. Or the gases can be released from porous materials or from cracks and crevices. Traces of lubricants, residues from machining, can be present on the surfaces. A specific risk is outgassing of solvents absorbed in plastics after cleaning.
Weld purging is the act of removing, from the vicinity of the joint; oxygen, water vapour and any other gases or vapours that might oxidize or contaminate a welding joint as it is being welded and immediately after welding.
Thermal cleaning is a combined process involving pyrolysis and oxidation. As an industrial application, thermal cleaning is used to remove organic substances such as polymers, plastics and coatings from parts, products or production components like extruder screws, spinnerets and static mixers. Thermal cleaning is the most common cleaning method in industrial environment. A variety of different methods have been developed so far for a wide range of applications.













