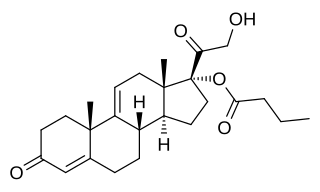
| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CB-03-01; 11-Deoxycortisol 17α-propionate; 17α-(Propionyloxy)- deoxycorticosterone; 21-Hydroxy-3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-17-yl propionate |
| Routes of administration | Topical (cream) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H34O5 |
| Molar mass | 402.531 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cortexolone 17α-propionate (developmental code name CB-03-01; tentative brand names Breezula (for acne), Winlevi (for androgenic alopecia)), or 11-deoxycortisol 17α-propionate, is a synthetic steroidal antiandrogen – specifically, an androgen receptor antagonist – that is under development by Cassiopea and Intrepid Therapeutics for use as a topical medication in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions including acne vulgaris and androgenic alopecia (male-pattern hair loss). [1] [2] [3] It is the C17α propionate ester of 11-deoxycortisol (cortexolone); [2] C17α esters of 11-deoxycortisol were unexpectedly found to possess antiandrogen activity, and cortexolone 17α-propionate was selected for development based on its optimum drug profile. [2]

A steroidal antiandrogen (SAA) is an antiandrogen with a steroidal chemical structure. They are typically antagonists of the androgen receptor (AR) and act both by blocking the effects of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and by suppressing gonadal androgen production. SAAs lower concentrations of testosterone through simulation of the negative feedback inhibition of the hypothalamus. SAAs are used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions in men and women, and are also used in veterinary medicine for the same purpose. They are the converse of nonsteroidal antiandrogens (NSAAs), which are antiandrogens that are not steroids and are structurally unrelated to testosterone.
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.

A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers. In pharmacology, antagonists have affinity but no efficacy for their cognate receptors, and binding will disrupt the interaction and inhibit the function of an agonist or inverse agonist at receptors. Antagonists mediate their effects by binding to the active site or to the allosteric site on a receptor, or they may interact at unique binding sites not normally involved in the biological regulation of the receptor's activity. Antagonist activity may be reversible or irreversible depending on the longevity of the antagonist–receptor complex, which, in turn, depends on the nature of antagonist–receptor binding. The majority of drug antagonists achieve their potency by competing with endogenous ligands or substrates at structurally defined binding sites on receptors.
Contents
In rats, the drug has been found to possess strong local antiandrogen activity, but negligible systemic antiandrogen activity when administered via subcutaneous injection. [2] In addition, cortexolone 17α-propionate is not progonadotropic, suggesting that it is peripherally selective. [2] In a bioassay, the topical potency of the drug was greater than that of progesterone, flutamide, and finasteride and was equivalent to that of cyproterone acetate. [2]

A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, collectively referred to as the cutis. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering vaccines and medications such as insulin, morphine, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous injection of recreational drugs is referred to as "skin popping." Subcutaneous administration may be abbreviated as SC, SQ, sub-cu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut.Subcut is the preferred abbreviation for patient safety.

A bioassay is an analytical method to determine concentration or potency of a substance by its effect on living cells or tissues. Bioassays were used to estimate the potency of agents by observing their effects on living animals or tissues.

Progesterone (P4) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is a progestogen and is used in combination with estrogens mainly in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in women to support pregnancy and fertility and to treat gynecological disorders. Progesterone can be taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection into muscle or fat, among other routes. A progesterone vaginal ring and progesterone intrauterine device used for birth control also exist in some areas of the world.
A pilot clinical trial in 2011 of men treated with topical cortexolone 17α-propionate 1% cream for acne found that the drug was very well-tolerated and significantly reduced symptoms of acne. [3] Moreover, its effectiveness was significantly greater than that of the active comparator, tretinoin 0.05% cream. [3] As of 2017, the drug is in phase III clinical trials for acne vulgaris and phase II clinical trials for androgenic alopecia. [1]
Clinical trials are experiments or observations done in clinical research. Such prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants are designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial – their approval does not mean that the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.
A cream is a preparation usually for application to the skin. Creams for application to mucous membranes such as those of the rectum or vagina are also used. Creams may be considered pharmaceutical products as even cosmetic creams are based on techniques developed by pharmacy and unmedicated creams are highly used in a variety of skin conditions (dermatoses). The use of the finger tip unit concept may be helpful in guiding how much topical cream is required to cover different areas.

Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin disease that occurs when hair follicles are clogged with dead skin cells and oil from the skin. It is characterized by blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects areas of the skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.