
A backplane or backplane system is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications.

In computer architecture, a bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components and software, including communication protocols.

In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and other computer programs to access hardware functions without needing to know precise details about the hardware being used.

An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer: the layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to transmit on, the line code to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified by the physical layer.

AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. These are modified Harvard architecture 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time.

A system on a chip or system-on-chip is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include on-chip central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, input/output devices and interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. SoCs may contain digital and also analog, mixed-signal and often radio frequency signal processing functions.

A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers are commonly made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.

A controller area network (CAN) is a vehicle bus standard designed to enable efficient communication primarily between electronic control units (ECUs). Originally developed to reduce the complexity and cost of electrical wiring in automobiles through multiplexing, the CAN bus protocol has since been adopted in various other contexts. This broadcast-based, message-oriented protocol ensures data integrity and prioritization through a process called arbitration, allowing the highest priority device to continue transmitting if multiple devices attempt to send data simultaneously, while others back off. Its reliability is enhanced by differential signaling, which mitigates electrical noise. Common versions of the CAN protocol include CAN 2.0, CAN FD, and CAN XL which vary in their data rate capabilities and maximum data payload sizes.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a de facto standard for synchronous serial communication, used primarily in embedded systems for short-distance wired communication between integrated circuits.
The System Management Bus is a single-ended simple two-wire bus for the purpose of lightweight communication. Most commonly it is found in chipsets of computer motherboards for communication with the power source for ON/OFF instructions. The exact functionality and hardware interfaces vary with vendors.

An electronic control unit (ECU), also known as an electronic control module (ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle.

Automatic test equipment or automated test equipment (ATE) is any apparatus that performs tests on a device, known as the device under test (DUT), equipment under test (EUT) or unit under test (UUT), using automation to quickly perform measurements and evaluate the test results. An ATE can be a simple computer-controlled digital multimeter, or a complicated system containing dozens of complex test instruments capable of automatically testing and diagnosing faults in sophisticated electronic packaged parts or on wafer testing, including system on chips and integrated circuits.

Kickstart is the bootstrap firmware of the Amiga computers developed by Commodore International. Its purpose is to initialize the Amiga hardware and core components of AmigaOS and then attempt to boot from a bootable volume, such as a floppy disk. Most Amiga models were shipped with the Kickstart firmware stored on ROM chips.
Smart systems are systems which are able to incorporate and perform functions of sensing, actuation, and control in order to analyze a situation, based on acquired data and perform decisions in a predictive or adaptive manner, thereby performing smart actions. In most cases the Intelligence/"smartness" of the system can be attributed to autonomous operation based on closed loop control, resource management, and networking capabilities.

Power management integrated circuits are integrated circuits for power management. Although PMIC refers to a wide range of chips, most include several DC/DC converters or their control part. A PMIC is often included in battery-operated devices and embedded devices to decrease the amount of space required.
The Serial Low-power Inter-chip Media Bus (SLIMbus) is a standard interface between baseband or application processors and peripheral components in mobile terminals. It was developed within the MIPI Alliance, founded by ARM, Nokia, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments. The interface supports many digital audio components simultaneously, and carries multiple digital audio data streams at differing sample rates and bit widths.
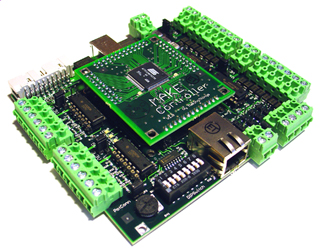
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored program memory and any necessary support ICs. The intention is that the board is immediately useful to an application developer, without requiring them to spend time and effort to develop controller hardware.

The Infineon XC800 family is an 8-bit microcontroller family, first introduced in 2005, with a dual cycle optimized 8051 "E-Warp" core. The XC800 family is divided into two categories, the A-Family for Automotive and the I-Family for Industrial and multi-market applications.
RL78 Family is a 16-bit CPU core for embedded microcontrollers of Renesas Electronics introduced in 2010.














