Anti-infective medicines
Anthelminthics
Intestinal anthelminthics
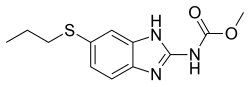
Antifilarials
Antischistosomals and other antinematode medicines
Complementary:
Cysticidal medicines
Complementary:
Antibacterials
Access group antibiotics
- Amikacin
- Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (amoxicillin + clavulanic acid)
- Ampicillin
- Benzathine benzylpenicillin
- Benzylpenicillin
- Cefalexin
- Cefazolin [note 27]
- Chloramphenicol [note 28]
- Clindamycin
- Cloxacillin [note 29] [note 30]
- Doxycycline [note 31]
- Gentamicin
- Metronidazole
- Nitrofurantoin
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin (penicillin V)
- Procaine benzylpenicillin [note 32]
- Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim)
- Trimethoprim
Watch group antibiotics
- Azithromycin
- Cefixime
- Cefotaxime [note 33]
- Ceftriaxone [note 20] [note 21]
- Cefuroxime
- Ciprofloxacin
- Clarithromycin [note 34]
- Piperacillin/tazobactam (piperacillin + tazobactam)
- Vancomycin [note 35]
Complementary:
Reserve group antibiotics
Complementary:
Antileprosy medicines
Antituberculosis medicines
- Amikacin
- Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (amoxicillin + clavulanic acid) [note 37]
- Bedaquiline
- Clofazimine
- Cycloserine
- Delamanid
- Ethambutol
- Ethionamide [note 38]
- Isoniazid
- Isoniazid/pyrazinamide/rifampicin (isoniazid + pyrazinamide + rifampicin)
- Isoniazid/rifampicin (isoniazid + rifampicin)
- Isoniazid/rifapentine (isoniazid + rifapentine)
- Levofloxacin
- Linezolid
- Meropenem [note 39]
- Moxifloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
- P-aminosalicylate sodium
- Pyrazinamide
- Rifampicin
- Rifapentine
- Streptomycin
Antifungal medicines
- Amphotericin B
- Fluconazole
- Flucytosine
- Griseofulvin
- Itraconazole [note 40]
- Nystatin
- Voriconazole [note 41]
Complementary:
Antiviral medicines
Antiherpes medicines
Antiretrovirals
Nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors
Fixed-dose combinations of antiretroviral medicines
Medicines for prevention of HIV-related opportunistic infections
Other antivirals
Complementary:
Antihepatitis medicines
Medicines for hepatitis B
Nucleoside/Nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Medicines for hepatitis C
Pangenotypic direct-acting antiviral combinations
Non-pangenotypic direct-acting antiviral combinations
No listings in this section.
Other antivirals for hepatitis C
No listings in this section.
Antiprotozoal medicines
Antiamoebic and antigiardiasis medicines
Antileishmaniasis medicines
Antimalarial medicines
Medicines for curative treatment
- Artemether [note 55]
- Artemether/lumefantrine (artemether + lumefantrine)
- Artesunate [note 55] [note 56]
- Artesunate/amodiaquine (artesunate + amodiaquine)
- Artesunate/mefloquine (artesunate + mefloquine)
- Artesunate/pyronaridine tetraphosphate (artesunate + pyronaridine tetraphosphate)
- Artesunate + sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine (Co-packaged)
- Chloroquine [note 57]
- Dihydroartemisinin/piperaquine phosphate (dihydroartemisinin + piperaquine phosphate)
- Primaquine [note 58]
- Quinine [note 55]
Medicines for chemoprevention
- Amodiaquine + sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine (Co-packaged)
- Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine (sulfadoxine + pyrimethamine)
Medicines for chemoprophylaxis in travellers
Antipneumocystosis and antitoxoplasmosis medicines
Antitrypanosomal medicines
African trypanosomiasis
Medicines for the treatment of 1st stage African trypanosomiasis
Medicines for the treatment of 2nd stage African trypanosomiasis
Complementary:
American trypanosomiasis
Medicines for ectoparasitic infections
Medicines for Ebola virus disease
Medicines for COVID-19
No listings in this section.