
Tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones are named by various warning centers to simplify communication between forecasters and the general public regarding forecasts, watches and warnings. The names are intended to reduce confusion in the event of concurrent storms in the same basin. Once storms develop sustained wind speeds of more than 33 knots, names are generally assigned to them from predetermined lists, depending on the basin in which they originate. Some tropical depressions are named in the Western Pacific, while tropical cyclones must contain a significant amount of gale-force winds before they are named in the Southern Hemisphere.

The 2005 Pacific typhoon season was the least active typhoon season since 2000, producing 23 named storms, of which 13 became typhoons. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season ran throughout 2005, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Kulap, developed on January 13, while the season's last named storm, Bolaven, dissipated on November 20. The season's first typhoon, Haitang, reached typhoon status on July 13, and became the first super typhoon of the year three days later.

The 2006 Pacific typhoon season was a destructive and deadly season, although it was near-average in terms of activity with a total of 23 named storms, 15 typhoons, and six super typhoons. Compared to the previous season, more typhoons inflicted damage across several countries, particularly China and the Philippines, some of which made landfall at higher intensities. The ratio of intense typhoons to all typhoons is at 0.73, the highest since 1970.

The 2000 Pacific typhoon season marked the first year using names contributed by the World Meteorological Organization. It was a rather below-average season, producing a total of 23 tropical storms, 13 typhoons and 4 intense typhoons. The season ran throughout 2000, though typically most tropical cyclones develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Damrey, developed on May 7, while the season's last named storm, Soulik, dissipated on January 4 of the next year. The Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) index for the 2000 Pacific typhoon season as calculated by Colorado State University using data from the Joint Typhoon Warning Center was 252.9 units.

A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least 119 km/h (74 mph). This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for almost one third of the world's tropical cyclones. The term hurricane refers to a tropical cyclone in the north central and northeast Pacific, and the north Atlantic. In all of the preceding regions, weaker tropical cyclones are called tropical storms. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern, central, and western. The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclone forecasts is in Japan, with other tropical cyclone warning centres for the northwest Pacific in Hawaii, the Philippines, and Hong Kong. Although the RSMC names each system, the main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have territories threatened by typhoons each year.

Tropical cyclones are ranked on one of five tropical cyclone intensity scales, according to their maximum sustained winds and which tropical cyclone basins they are located in. Only a few classifications are used officially by the meteorological agencies monitoring the tropical cyclones, but other scales also exist, such as accumulated cyclone energy, the Power Dissipation Index, the Integrated Kinetic Energy Index, and the Hurricane Severity Index.
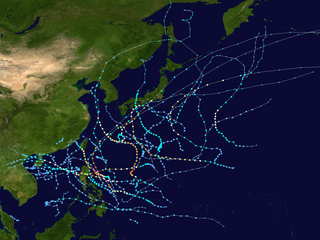
The 2011 Pacific typhoon season was a below average season that produced a total of 21 named storms, 8 typhoons, and four super typhoons. This season was much more active than the previous season, although both seasons were below the Pacific typhoon average of 26. The season ran throughout 2011, though most tropical cyclone tend to develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Aere, developed on May 7 while the season's last named storm, Washi dissipated on December 19.

Throughout 2006, 133 tropical cyclones formed in seven bodies of water known as tropical cyclone basins. Of these, 80 have been named, including two tropical cyclones in the South Atlantic Ocean, and a tropical cyclone in the Mediterranean Sea, by various weather agencies when they attained maximum sustained winds of 65 km/h (40 mph). The strongest storms of the year were Typhoon Yagi in the Western Pacific, and Cyclone Glenda of the Australian region. The deadliest and costliest storms of the year were a series of five typhoons that struck the Philippines and China; Chanchu, Bilis, Saomai, Xangsane, and Durian, with most of the damage being caused by Durian of November. So far, 27 Category 3 tropical cyclones formed, including five Category 5 tropical cyclones in the year. The accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) index for the 2006, as calculated by Colorado State University was 761 units.

Most of the tropical cyclones of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season formed between May and November of that year. The scope of this article is the Pacific Ocean north of the equator, between 100°E and the International Date Line. Tropical storms which form in the Western Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA). Tropical depressions forming in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC). The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility, but these names are not in common use outside the Philippines.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2014 Pacific typhoon season. Most of the tropical cyclones forming between May and November. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. Tropical storms that form in the entire Western Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency. Tropical depressions that form in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center. In addition, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility. These names, however, are not in common use outside of the Philippines.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2015 Pacific typhoon season. Most of the tropical cyclones formed between May and November. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. This area, called the Western Pacific basin, is the responsibility of the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA). They host and operate the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC), located in Tokyo. The Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA) is also responsible for assigning names to all tropical storms that are formed within the basin. However, any storm that enters or forms in the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) will be named by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) using a local name. Also of note - the Western Pacific basin is monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), which gives all Tropical depressions a number with a "W" suffix.

Typhoon Meranti, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Ferdie, was one of the most intense tropical cyclones on record. Impacting the Batanes in the Philippines, Taiwan, as well as Fujian Province in September 2016, Meranti formed as a tropical depression on September 8 near the island of Guam. Tracking to the west northwest, Meranti gradually intensified until September 11, at which point it began a period of rapid intensification. Continuing to rapidly intensify, it became a super typhoon early on September 12, as it passed through the Luzon Strait, ultimately reaching its peak intensity on September 13 with 1-minute sustained winds of 315 km/h (195 mph). Shortly afterwards, it passed directly over the island of Itbayat. Meranti passed to the south of Taiwan as a super typhoon, and began weakening steadily as a result of land interaction. By September 15, it struck Fujian Province as a Category 2-equivalent typhoon, becoming the strongest typhoon on record to impact the province. Upon moving inland, rapid weakening ensued and Meranti became extratropical the next day, dissipating shortly afterwards after it passed to the south of the Korean Peninsula.
The 2025 Pacific typhoon season is an upcoming event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation in the western Pacific Ocean. The season will run throughout 2025, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean to the north of the equator between 100°E and 180th meridian. Within the northwestern Pacific Ocean, there are two separate agencies that assign names to tropical cyclones which can often result in a cyclone having two names. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) will name a tropical cyclone if it has 10-minute sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph) anywhere in the basin. The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N–25°N, regardless of whether or not a tropical cyclone has already been given a name by the JMA. Tropical depressions that are monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) are given a number with a "W" suffix.











