
The Republic of Texas was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. It shared borders with Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, and the United States of America.

The Alamo is a historic Spanish mission and fortress compound founded in the 18th century by Roman Catholic missionaries in what is now San Antonio, Texas, United States. It was the site of the Battle of the Alamo in 1836, a pivotal event of the Texas Revolution in which American folk heroes James Bowie and Davy Crockett were killed. Today it is a museum in the Alamo Plaza Historic District and a part of the San Antonio Missions World Heritage Site.

The Daughters of the Republic of Texas (DRT) is a lineal association dedicated to perpetuating the memory of the founding families and soldiers of the Republic of Texas. The Daughters of the Republic of Texas is best known for its former role as caretakers of The Alamo. In early 2015, Texas Land Commissioner George P. Bush officially removed control of the Alamo to the Texas General Land Office. The DRT were also the custodians of the historic French Legation Museum until 2017, which is owned by the State of Texas and is now operated by the Texas Historical Commission. In addition, they operate a museum in Austin on the history of Texas.

The Texas State Capitol is the capitol and seat of government of the American state of Texas. Located in downtown Austin, Texas, the structure houses the offices and chambers of the Texas Legislature and of the Governor of Texas. Designed in 1881 by architect Elijah E. Myers, it was constructed from 1882 to 1888 under the direction of civil engineer Reuben Lindsay Walker. A $75 million underground extension was completed in 1993. The building was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1970 and recognized as a National Historic Landmark in 1986.

Sixth Street is a historic street and entertainment district in Austin, Texas, located within the city's urban core in downtown Austin. Sixth Street was formerly named Pecan Street under Austin's older naming convention, which had east–west streets named after trees and north–south streets named after Texas rivers.

Congress Avenue is a major thoroughfare in Austin, Texas. The street is a six-lane, tree lined avenue that cuts through the middle of the city from far south Austin and goes over Lady Bird Lake leading to the Texas State Capitol in the heart of Downtown.

The Texas Historical Commission is an agency dedicated to historic preservation within the U.S. state of Texas. It administers the National Register of Historic Places for sites in Texas.

Oakwood Cemetery, originally called City Cemetery, is the oldest city-owned cemetery in Austin, Texas. Situated on a hill just east of I-35 that overlooks downtown Austin, just north of the Swedish Hill Historic District and south of Disch-Falk Field, the once-isolated site is now in the center of the city.

Woodlawn, also known as the Pease Mansion as well as Governor Shivers’ Mansion, is a pre-Civil War mansion located at 30.2871° -97.7581° in Austin, Texas. The Greek Revival style house was owned by two Texas governors. Some notable people that have visited the mansion include Sam Houston, General George Custer, Elisabet Ney, Will Rogers, and Edith Head. Woodlawn was added to the National Register of Historic Places on August 25, 1970.

The Old West Austin Historic District is a residential community in Austin, Texas, United States. It is composed of three neighborhoods located on a plateau just west of downtown Austin: Old Enfield, Pemberton Heights, and Bryker Woods. Developed between 1886 and 1953, the three historic neighborhoods stretch from Mopac Expressway east to Lamar Boulevard, and from 13th Street north to 35th Street. It borders Clarksville Historic District and the West Line Historic District to the south.

Wooldridge Park, also known as Wooldridge Square, is an urban park in downtown Austin, Texas. The park consists of a city block containing a natural basin whose sides slope inward to form an amphitheater with a bandstand at its center. The park was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1979.

After declaring its independence from Mexico in March, 1836, the Republic of Texas had numerous locations as its seat of government. This being seen as a problem attempts were made to select a permanent site for the capital. January, 1839, with Mirabeau B. Lamar as the newly elected president, a site selection commission of five commissioners was formed. Edward Burleson had surveyed the planned townsite of Waterloo, near the mouth of Shoal Creek on the Colorado River, in 1838; it was incorporated January 1839. By April of that year the site selection commission had selected Waterloo to be the new capital. A bill previously passed by Congress in May, 1838, specified that any site selected as the new capital would be named Austin, after the late Stephen F. Austin; hence Waterloo upon selection as the capital was renamed Austin. The first lots in Austin went on sale August 1839.

The Lamar Boulevard Bridge is a historic arch bridge carrying Texas State Highway Loop 343 over Lady Bird Lake in downtown Austin, Texas, United States. The bridge features six open-spandrel concrete arches spanning 659 feet (201 m) and carries tens of thousands of vehicles daily across the lake. Completed in 1942, the Lamar Boulevard Bridge was the second permanent bridge to cross the Colorado River, and one of the last Art Deco-style open-spandrel concrete arch bridges built in Texas. The bridge was named an Austin Landmark in 1993 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1994.

The Southgate–Lewis House is located one mile east of the Texas State Capitol in Austin, Texas, at 1501 East 12th Street. The house was constructed in 1888, and now stands as an African-American historical landmark. It is also a repository for African-American History and Culture in the region of east Austin, which historically became an African-American neighborhood. The City of Austin has now declared this region to be "Austin's Black Cultural District." The Southgate–Lewis House is located in the center of the "African American Cultural Heritage District".

Downtown Austin is the central business district of Austin, Texas, United States. The area of the district is bound by Lamar Boulevard to the west, Martin Luther King Jr. Boulevard to the north, Interstate 35 to the east, and Lady Bird Lake to the south.

The Texas General Land Office (GLO) is a state agency of the U.S. state of Texas, responsible for managing lands and mineral rights properties that are owned by the state. The GLO also manages and contributes to the state's Permanent School Fund. The agency is headquartered in the Stephen F. Austin State Office Building in Downtown Austin.
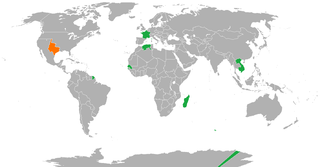
France – Republic of Texas relations refers to the historical foreign relations between the Republic of Texas and France. Relations began in September 1839 when France appointed Alponse Dubois de Saligny to serve as chargé d'affaires. Relations officially ceased upon annexation of Texas by the United States in 1845.

The Westgate Tower is a mixed-use high-rise building in downtown Austin, Texas. The twenty-six-story 261-foot (80 m) tower block was designed in 1962 and completed in 1966; its name reflects its location across the street from the west gate of the Texas State Capitol. Designed by architect Edward Durell Stone, the tower was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2010 and designated a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark in 2012.

The Capitol View Corridors are a series of legal restrictions on construction in Austin, Texas, aimed at preserving protected views of the Texas State Capitol from various points around the city. First established by the Texas Legislature in 1983 and recodified in 2001, the corridors are meant to protect the capitol dome from obstruction by high-rise buildings. While supported by cultural and historical preservation organizations, the corridors have also been criticized for limiting the potential for the development of new tall structures in downtown Austin.




















