This article lists computer monitor screen resolutions that are defined by standards or in common use. Most of them use certain preferred numbers.
This article lists computer monitor screen resolutions that are defined by standards or in common use. Most of them use certain preferred numbers.
| Designation | Usage | W | (px) | H | Aspect ratio | Total pixels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | Display | Pixel | ||||||
| 0.26K1 | Microvision | 16 | × | 16 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 256 |
| 0.46K1 | Timex Datalink USB [1] [2] | 42 | × | 11 | 42∶11 | 1∶1 | 5:9 | 462 |
| 1.02K1 | PocketStation | 32 | × | 32 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1,024 |
| 1.2K3 | Etch A Sketch Animator | 40 | × | 30 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 1,200 |
| 1.34K1 | Epson RC-20 [3] | 42 | × | 32 | 21∶16 | 1∶1 | 0.762 | 1,344 |
| 1.54K2 | GameKing I (GM-218), VMU | 48 | × | 32 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 1,536 |
| 2K3 | Ever DOS computers | 80 | × | 25 | 16∶5 | 4∶3 | 0.417 | 2,000 |
| 2.4K2 | Etch A Sketch Animator 2000 | 60 | × | 40 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 2,400 |
| 2.88K5 | Thumby (console) | 72 | × | 40 | 9∶5 | 7∶5 | 0.778 | 2,880 |
| 4.03K7∶4 | Nokia 3210 and many other early Nokia Phones | 84 | × | 48 | 7∶4 | 2∶1 | 1.143 | 4,032 |
| 4.1K1 | Hartung Game Master | 64 | × | 64 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 4,096 |
| 4.25K3 | Ever DOS computers 2x | 170 | × | 25 | 34∶5 | 4∶3 | 0.196 | 4,250 |
| 4.61K1 | Field Technology CxMP smart watch [2] | 72 | × | 64 | 9∶8 | 1∶1 | 0.889 | 4,608 |
| 4.61K1 | Montblanc e-Strap [4] | 128 | × | 36 | 32∶9 | 1∶1 | 0.281 | 4,608 |
| 4.8K1 | Epoch Game Pocket Computer | 75 | × | 64 | 75∶64 | 1∶1 | 1:1.171875 | 4,800 |
| 0.01M3.75 | Entex Adventure Vision | 150 | × | 40 | 15∶4 | 3.75 | 1∶1 | 6,000 |
| 0.01M2 | First graphing calculators: Casio fx-7000G, TI-81 | 96 | × | 64 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 6,144 |
| 0.01M2 | Pokémon Mini | 96 | × | 64 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 6,144 |
| 0.01M2 | TRS-80 | 128 | × | 48 | 8∶3 | 3∶2 | 0.563 | 6,144 |
| 0.01M2 | Early Nokia colour screen phones | 96 | × | 65 | 96∶65 | 3∶2 | 1.016 | 6,240 |
| 0.01MA | Ruputer | 102 | × | 64 | 51∶32 | 8∶5 | 1.004 | 6,528 |
| 0.01M2 | Pokémon Mini | 108 | × | 70 | 54∶35 | 3∶2 | 0.972 | 7,560 |
| 0.01M4 | Sony Ericsson T68i, T300, T310 and other early colour and black&white screen phones | 101 | × | 80 | 101∶80 | 5∶4 | 0.99 | 8,080 |
| 0.01M2∶1 | Arduboy | 128 | × | 64 | 2∶1 | 2∶1 | 1∶1 | 8,192 |
| 0.01M1 | MetaWatch Strata & Frame watches | 96 | × | 96 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 9,216 |
| 0.01M2 | Pokémon Mini | 128 | × | 96 | 4∶3 | 3∶2 | 1.125 | 12,288 |
| 0.02M3.75 | Atari Portfolio, TRS-80 Model 100 | 240 | × | 64 | 15∶4 | 3.75 | 1∶1 | 15,360 |
| 0.02MA | Atari Lynx | 160 | × | 102 | 80∶51 | 8∶5 | 1.02 | 16,320 |
| 0.02M1 | Sony SmartWatch, Sifteo cubes, early color screen phones (square display), PICO-8 | 128 | × | 128 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 16,384 |
| 0.02M0.8 | Samsung feature phones, e.g., Samsung SGH-S150G and other feature phones such as MobiWire Nakai | 128 | × | 160 | 4∶5 | 4:5 | 1∶1 | 20,480 |
| QQVGA | Quarter Quarter VGA: Nintendo Game Boy Advance LoRes | 160 | × | 120 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 19,200 |
| 0.02M1.111 | Nintendo Game Boy (GB), Game Boy Color (GBC); Sega Game Gear (GG) | 160 | × | 144 | 10∶9 | 10:9 | 1∶1 | 23,040 |
| 0.02M0.857 | Pebble E-Paper Watch | 144 | × | 168 | 6∶7 | 6:7 | 1∶1 | 24,192 |
| 0.02M1.053 | Neo Geo Pocket Color | 160 | × | 152 | 20∶19 | 20:19 | 1∶1 | 24,320 |
| 0.03M1 | Palm LoRes | 160 | × | 160 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 25,600 |
| 0.03M3 | Apple II HiRes (6 color) and Apple IIe Double HiRes (16 color), grouping subpixels | 140 | × | 192 | 35∶48 | 4∶3 | 1.828 | 26,880 |
| 0.03M3 | VIC-II multicolor, IBM PCjr 16-color, Amstrad CPC 16-color | 160 | × | 200 | 4∶5 | 4∶3 | 5∶3 | 32,000 |
| 0.03M9 | WonderSwan | 224 | × | 144 | 14∶9 | 14∶9 | 1∶1 | 32,256 |
| 0.04M13∶11 | Nokia Series 60 smartphones (Nokia 7650, plus First and Second Edition models only) | 208 | × | 176 | 13∶11 | 13∶11 | 1∶1 | 36,608 |
| HQVGA | Half QVGA: Nintendo Game Boy Advance | 240 | × | 160 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 38,400 |
| 0.04M4 | Older Java MIDP devices like Sony Ericsson K600 | 220 | × | 176 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 38,720 |
| 0.04M3 | Acorn BBC 20 column modes | 160 | × | 256 | 5∶8 | 4∶3 | 2.133 | 40,960 |
| 0.04M3 | Apple II HiRes 3 colors | 180 | × | 248 | 45∶62 | 4∶3 | 1.837 | 44,640 |
| 0.04M1 | Nokia 5500 Sport, Nokia 6230i, Nokia 8800 | 208 | × | 208 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 43,264 |
| 0.05M3 | TMS9918 modes 1 (e.g. TI-99/4A) and 2, ZX Spectrum, MSX, Sega Master System, Nintendo DS (each screen) | 256 | × | 192 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 49,152 |
| 0.05M3 | Apple II HiRes (1 bit per pixel) | 280 | × | 192 | 35∶24 | 4∶3 | 0.914 | 53,760 |
| 0.05M3 | MSX2 | 256 | × | 212 | 64∶53 | 4∶3 | 1.104 | 54,272 |
| 0.06M1 | Samsung Gear Fit | 432 | × | 128 | 27∶8 | 1∶1 | 0.296 | 55,296 |
| 0.06M3 | Nintendo Entertainment System, Super Nintendo Entertainment System, Sega Mega Drive | 256 | × | 224 | 8∶7 | 4∶3 | 7∶6 | 57,344 |
| 0.06M1 | Apple iPod Nano 6G, Palm (PDA) | 240 | × | 240 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 57,600 |
| 0.06M3 | PlayStation (e.g. Rockman Complete Works) | 256 | × | 240 | 16∶15 | 4∶3 | 5∶4 | 61,440 |
| 0.06M6 | Atari 8-bit family PAL | 320 | × | 192 | 5∶3 | 5∶3 | 1∶1 | 61,440 |
| 0.06M5∶3 | Atari 8-bit family NTSC | 320 | × | 192 | 5∶3 | 50:35 | 6:7 | 61,440 |
| Color Graphics Adapter (CGA) | CGA 4-color, ATM 16 color, Atari ST 16 color, Nintendo 64 LoRes, Commodore 64, HiRes VIC-II Hires, Amiga OCS NTSC Lowres, Apple IIGS LoRes, MCGA, Amstrad CPC 4-color | 320 | × | 200 | 8∶5 | 4∶3 | 0.833 | 64,000 |
| 0.07M1 | Elektronika BK | 256 | × | 256 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 65,536 |
| 0.07M3 | Sinclair QL | 256 | × | 256 | 1∶1 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 65,536 |
| 0.07M2 | UIQ 2.x based smartphones | 320 | × | 208 | 20∶13 | 3∶2 | 0.975 | 66,560 |
| 0.07M2 | Sega Mega Drive, Sega Nomad, Neo Geo AES | 320 | × | 224 | 10∶7 | 3∶2 | 1.05 | 71,680 |
| QVGA | Quarter VGA: Apple iPod Nano 3G, Nintendo Entertainment System HiRes, Super Nintendo Entertainment System, PlayStation, Nintendo 64, GameCube, Nintendo DS (each screen), Nintendo 3DS (lower screen) | 320 | × | 240 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 76,800 |
| 0.08M4 | Acorn BBC 40 column modes, Amiga OCS PAL Lowres | 320 | × | 256 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 81,920 |
| 0.08M3 | GameCube | 320 | × | 256 | 5∶4 | 4∶3 | 1.066 | 81,920 |
| 0.09M3 | Capcom CP System (CPS, CPS2, CPS3) arcade system boards | 384 | × | 224 | 12∶7 | 4∶3 | 0.778 | 86,016 |
| 0.09M3 | PlayStation (e.g. X-Men vs. Street Fighter ) | 368 | × | 240 | 23∶15 | 4∶3 | 0.869 | 88,320 |
| 0.09M3 | Super Nintendo Entertainment System | 372 | × | 240 | 31∶20 | 4∶3 | 0.86 | 89,280 |
| 0.09M9 | Apple iPod Nano 5G | 376 | × | 240 | 47∶30 | 14∶9 | 0.993 | 90,240 |
| 0.09M0.8 | Apple Watch 38mm | 272 | × | 340 | 4∶5 | 4:5 | 1∶1 | 92,480 |
| WQVGA | Wide QVGA: Common on Windows Mobile 6 handsets, Nintendo 3DS (upper screen in 2D mode), Playdate (console) | 400 | × | 240 | 5∶3 | 5∶3 | 1∶1 | 96,000 |
| 0.1M3 | Timex Sinclair 2068, Timex Computer 2048 | 512 | × | 192 | 8∶3 | 4∶3 | 0.5 | 98,304 |
| 0.1M3 | IGS PolyGame Master arcade system board | 448 | × | 224 | 2∶1 | 4∶3 | 0.667 | 100,352 |
| 0.1M1 | Palm (PDA) HiRes, Samsung Galaxy Gear | 320 | × | 320 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 102,400 |
| WQVGA | Wide QVGA: Apple iPod Nano 7G | 432 | × | 240 | 9∶5 | 9∶5 | 1∶1 | 103,680 |
| 0.11M3 | Apple IIe Double Hires (1 bit per pixel) [5] | 560 | × | 192 | 35∶12 | 4∶3 | 0.457 | 107,520 |
| 0.11M2 | TurboExpress | 400 | × | 270 | 40∶27 | 3∶2 | 1.013 | 108,000 |
| 0.11M3 | MSX2 | 512 | × | 212 | 128∶53 | 4∶3 | 0.552 | 108,544 |
| 0.11M3 | Common Intermediate Format | 384 | × | 288 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 110,592 |
| WQVGA* | Variant used commonly for portable DVD players, digital photo frames, GPS receivers and devices such as the Kenwood DNX-5120 and Glospace SGK-70; often marketed as "16:9" | 480 | × | 234 | 80∶39 | 16∶9 | 0.866 | 112,320 |
| qSVGA | Quarter SVGA: Super Nintendo Entertainment System Selectable in some PC shooters | 400 | × | 300 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 120,000 |
| 0.12M3 | Teletext and Viewdata 40×25 character screens (PAL non-interlaced) | 480 | × | 250 | 48∶25 | 4∶3 | 0.694 | 120,000 |
| 0.12M0.8 | Apple Watch 42mm | 312 | × | 390 | 4∶5 | 4:5 | 1∶1 | 121,680 |
| 0.12M3 | PlayStation (e.g. Tekken and Tekken 2 ) | 512 | × | 240 | 32∶15 | 4∶3 | 0.625 | 122,880 |
| 0.13M3 | Amiga OCS NTSC Lowres interlaced | 320 | × | 400 | 4∶5 | 4∶3 | 5∶3 | 128,000 |
| Color Graphics Adapter (CGA) | Atari ST 4 color, ATM, CGA mono, Amiga OCS NTSC Hires, Apple IIGS HiRes, Nokia Series 80 smartphones, Amstrad CPC 2-color | 640 | × | 200 | 16∶5 | 4∶3 | 0.417 | 128,000 |
| 0.13M9 | Sony PlayStation Portable, Zune HD, Neo Geo X | 480 | × | 272 | 30∶17 | 16∶9 | 1.007 | 130,560 |
| 0.13M2∶1 | Elektronika BK, Poly-Play | 512 | × | 256 | 2∶1 | 2∶1 | 1∶1 | 131,072 |
| 0.13M3 | Sinclair QL | 512 | × | 256 | 2∶1 | 4∶3 | 0.667 | 131,072 |
| 0.15M13∶11 | Nokia Series 60 smartphones (E60, E70, N80, N90) | 416 | × | 352 | 13∶11 | 13∶11 | 1∶1 | 146,432 |
| HVGA | Palm Tungsten T3, Apple iPhone, HTC Dream, Palm (PDA) HiRES+ | 480 | × | 320 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 153,600 |
| HVGA | Handheld PC | 640 | × | 240 | 8∶3 | 8:3 | 1∶1 | 153,600 |
| 0.15M3 | PlayStation, GameCube | 640 | × | 240 | 8∶3 | 4∶3 | 0.5 | 153,600 |
| 0.16M3 | Acorn BBC 80 column modes, Amiga OCS PAL Hires | 640 | × | 256 | 5∶2 | 4∶3 | 0.533 | 163,840 |
| 0.18M2 | Black & white Macintosh (9") | 512 | × | 342 | 256∶171 | 3∶2 | 1.002 | 175,104 |
| 0.18M3 | PlayStation (e.g. Tekken 3 ) (interlaced) | 368 | × | 480 | 23∶30 | 4∶3 | 1.739 | 176,640 |
| 0.19M3 | Sega Model 1 (e.g. Virtua Fighter) and Model 2 (e.g. Daytona USA) arcade system boards | 496 | × | 384 | 31∶24 | 4∶3 | 1.032 | 190,464 |
| 0.19M6 | Nintendo 3DS (upper screen in 3D mode: 2× 400 × 240, one for each eye) | 800 | × | 240 | 10∶3 | 5∶3 | 0.5 | 192,000 |
| 0.2M3 | Macintosh LC (12")/Color Classic (also selectable in many PC shooters) | 512 | × | 384 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 196,608 |
| 0.2M2∶1 | Nokia Series 90 smartphones (7700, 7710) | 640 | × | 320 | 2∶1 | 2∶1 | 1∶1 | 204,800 |
| EGA | Enhanced Graphics Adapter, Apple Macintosh | 640 | × | 350 | 64∶35 | 4∶3 | 0.729 | 224,000 |
| 0.23M9 | nHD, used by Nokia 5800, Nokia 5530, Nokia X6, Nokia N97, Nokia N8 [6] | 640 | × | 360 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 230,400 |
| 0.24M3 | Teletext and Viewdata 40×25 character screens (PAL interlaced) | 480 | × | 500 | 24∶25 | 4∶3 | 1.389 | 240,000 |
| 0.25M3 | Namco System 12 arcade system board (e.g. Soulcalibur, Tekken 3, Tekken Tag Tournament) (interlaced) | 512 | × | 480 | 16∶15 | 4∶3 | 5∶4 | 245,760 |
| 0.25M3 | HGC | 720 | × | 348 | 60∶29 | 4∶3 | 0.644 | 250,560 |
| 0.25M3 | MDA | 720 | × | 350 | 72∶35 | 4∶3 | 0.648 | 252,000 |
| 0.26M3 | Atari ST mono, Amiga OCS NTSC Hires interlaced | 640 | × | 400 | 8∶5 | 4∶3 | 0.833 | 256,000 |
| 0.26M3 | Apple Lisa | 720 | × | 364 | 180∶91 | 4∶3 | 0.674 | 262,080 |
| 0.28M2.273 | Nokia E90 Communicator | 800 | × | 352 | 25∶11 | 25:11 | 1∶1 | 281,600 |
| 0.29M4 | Some older monitors | 600 | × | 480 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 288,000 |
| VGA | Video Graphics Array:MCGA (in monochome), Nintendo 3DS lower screen HiRes, GameCube, Sun-1 color, PlayStation (e.g. Tobal No.1 and Ehrgeiz), Nintendo 64, (e.g. various Expansion Pak enhanced games), 6th Generation Consoles, Nintendo Wii | 640 | × | 480 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 307,200 |
| 0.33M3 | Amiga OCS PAL Hires interlaced | 640 | × | 512 | 5∶4 | 4∶3 | 1.066 | 327,680 |
| WVGA | Wide VGA | 768 | × | 480 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 368,640 |
| WGA | Wide VGA: List of mobile phones with WVGA display | 800 | × | 480 | 5∶3 | 5∶3 | 1∶1 | 384,000 |
| W-PAL | Wide PAL | 848 | × | 480 | 53∶30 | 16∶9 | 1.006 | 407,040 |
| FWVGA | List of mobile phones with FWVGA display | 854 | × | 480 | 427∶240 | 16∶9 | 0.999 | 409,920 |
| SVGA | Super VGA Nintendo Wii, Nintendo 64 HiRes, GameCube HiRes | 800 | × | 600 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 480,000 |
| qHD | Quarter FHD: AACS ICT, HRHD, Motorola Atrix 4G, Sony XEL-1 [7] [ unreliable source? ] | 960 | × | 540 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 518,400 |
| 0.52M3 | Apple Macintosh Half Megapixel [8] | 832 | × | 624 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 519,168 |
| 0.52M9 | PlayStation Vita (PSV) | 960 | × | 544 | 30∶17 | 16∶9 | 1.007 | 522,240 |
| 0.59M9 | PAL 16:9 | 1024 | × | 576 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 589,824 |
| DVGA | Double VGA: Apple iPhone 4S, [9] [ unreliable source? ] [10] 4th Generation iPod Touch [11] | 960 | × | 640 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 614,400 |
| WSVGA | Wide SVGA: 10” netbooks | 1024 | × | 600 | 128∶75 | 16∶9 | 1.041 | 614,400 |
| 0.66MA | Close to WSVGA | 1024 | × | 640 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 655,360 |
| 0.69M3 | Panasonic DVCPRO100 for 50/60 Hz over 720p - SMPTE Resolution | 960 | × | 720 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 691,200 |
| 0.73M9 | Apple iPhone 5, iPhone 5S, iPhone 5C, iPhone SE (1st) | 1136 | × | 640 | 71∶40 | 16∶9 | 1.001 | 727,040 |
| 0.73M9 | Occasional Chromebook resolution with 96 DPI; see HP Chromebook 14A G5. | 1138 | × | 640 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 0.999 | 728,320 |
| XGA | Extended Graphics Array:Common on 14″/15″ TFTs and the Apple iPad | 1024 | × | 768 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 786,432 |
| 0.82M3 | Sun-1 monochrome | 1024 | × | 800 | 32∶25 | 4∶3 | 1.041 | 819,200 |
| 0.83MA | Supported by some GPUs, monitors, and games | 1152 | × | 720 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 829,440 |
| 0.88M2 | Apple PowerBook G4 (original Titanium version) | 1152 | × | 768 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 884,736 |
| WXGA | Wide XGA:Minimum, 720p Nintendo Wii U, Nintendo Switch HDTV | 1280 | × | 720 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 921,600 |
| 0.93M3 | NeXT MegaPixel Display | 1120 | × | 832 | 35∶26 | 4∶3 | 0.99 | 931,840 |
| WXGA | Wide XGA:Average, BrightView Nintendo Wii U, Nintendo Switch | 1280 | × | 768 | 5∶3 | 5∶3 | 1∶1 | 983,040 |
| XGA+ | Apple XGA [note 2] | 1152 | × | 864 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 995,328 |
| 1M9 | Apple iPhone 6, iPhone 6S, iPhone 7, iPhone 8, iPhone SE (2nd) | 1334 | × | 750 | 667∶375 | 16∶9 | 0.999 | 1,000,500 |
| WXGA | Wide XGA:Maximum Nintendo Wii U, Nintendo Switch, Steam Deck | 1280 | × | 800 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 1,024,000 |
| 1.04M32∶25 | Sun-2 Prime Monochrome or Color Video, also common in Sun-3 and Sun-4 workstations | 1152 | × | 900 | 32∶25 | 32∶25 | 1∶1 | 1,036,800 |
| 1.05M1∶1 | Network Computing Devices | 1024 | × | 1024 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1,048,576 |
| WXGA HD | Standardized HDTV 720p/1080i displays or "HD ready", used in most cheaper notebooks Nintendo Wii U | 1366 | × | 768 | 683∶384 | 16∶9 | 0.999 | 1,049,088 |
| 1.09M2 | Apple PowerBook G4 | 1280 | × | 854 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1.001 | 1,093,120 |
| SXGA− | Super XGA "Minus": | 1280 | × | 960 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 1,228,800 |
| 1.23M2.083 | Sony VAIO P series | 1600 | × | 768 | 25∶12 | 25:12 | 1∶1 | 1,228,800 |
| 1.3M0.9 | HTC Vive (per eye) | 1080 | × | 1200 | 9∶10 | 9:10 | 1∶1 | 1,296,000 |
| WSXGA | Wide SXGA | 1440 | × | 900 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 1,296,000 |
| WXGA+ | Wide XGA+ | 1440 | × | 900 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 1,296,000 |
| SXGA | Super XGA | 1280 | × | 1024 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 1,310,720 |
| 1.38M2 | Apple PowerBook G4 | 1440 | × | 960 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 1,382,400 |
| HD+ | 900p Nintendo Wii U, Nintendo Switch | 1600 | × | 900 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 1,440,000 |
| SXGA+ | Super XGA Plus, Lenovo Thinkpad X61 Tablet | 1400 | × | 1050 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 1,470,000 |
| 1.47M5 | Similar to A4 paper format (~123 dpi for A4 size) | 1440 | × | 1024 | 45∶32 | 7∶5 | 0.996 | 1,474,560 |
| 1.56M3 | HDV 1080i | 1440 | × | 1080 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 1,555,200 |
| 1.64M10 | SGI 1600SW | 1600 | × | 1024 | 25∶16 | 25∶16 | 1∶1 | 1,638,400 |
| WSXGA+ | Wide SXGA+ | 1680 | × | 1050 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 1,764,000 |
| 1.78M9 | Available in some monitors | 1776 | × | 1000 | 222∶125 | 16∶9 | 1.001 | 1,776,000 |
| UXGA | Ultra XGA:Lenovo Thinkpad T60 | 1600 | × | 1200 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 1,920,000 |
| 2.05M4 | Sun3 Hi-res monochrome | 1600 | × | 1280 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 2,048,000 |
| FHD | Full HD:1080 HDTV (1080i, 1080p Nintendo Wii U, Nintendo Switch) | 1920 | × | 1080 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 2,073,600 |
| 2.07M1 | Windows Mixed Reality headsets (per eye) | 1440 | × | 1440 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 2,073,600 |
| DCI 2K | DCI 2K | 2048 | × | 1080 | 256∶135 | 1.90∶1 | 1.002 | 2,211,840 |
| WUXGA | Wide UXGA | 1920 | × | 1200 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 2,304,000 |
| QWXGA | Quad WXGA, 2K | 2048 | × | 1152 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 2,359,296 |
| 2.41M3 | Supported by some GPUs, monitors, and games | 1792 | × | 1344 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 2,408,448 |
| FHD+ | Full HD Plus:Microsoft Surface 3 | 1920 | × | 1280 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 2,457,600 |
| 2.46M2.10∶1 | Samsung Galaxy S10e, Xiaomi Mi A2 Lite, Huawei P20 Lite | 2280 | × | 1080 | 2.10∶1 | 2.10∶1 | 1∶1 | 2,462,400 |
| 2.53M2.167 | Samsung Galaxy A8s, Xiaomi Redmi Note 7, Honor Play | 2340 | × | 1080 | 19½:9 | 19½:9 | 1∶1 | 2,527,200 |
| 2.58M3 | Supported by some GPUs, monitors, and games | 1856 | × | 1392 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 2,583,552 |
| 2.59M09? | Samsung Galaxy A70, Samsung Galaxy S21/+, Xiaomi Redmi Note 9S, default for many 3200x1440 phones [12] | 2400 | × | 1080 | 20∶9 | 20∶9 | 1∶1 | 2,592,000 |
| 2.59M4 | Supported by some GPUs, monitors, and games | 1800 | × | 1440 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 2,592,000 |
| CWSXGA | NEC CRV43, [13] Ostendo CRVD, [14] Alienware Curved Display [15] [16] | 2880 | × | 900 | 16∶5 | 16:5 | 1∶1 | 2,592,000 |
| 2.59M9 | HTC Vive, Oculus Rift (both eyes) | 2160 | × | 1200 | 9∶5 | 9∶5 | 1∶1 | 2,592,000 |
| 2.62MA | Supported by some GPUs, monitors, and games | 2048 | × | 1280 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 2,621,440 |
| TXGA | Tesselar XGA | 1920 | × | 1400 | 48∶35 | 7∶5 | 1.021 | 2,688,000 |
| 2.72M1A | Motorola One Vision, Motorola One Action and Sony Xperia 10 IV | 2520 | × | 1080 | 21∶9 | 21∶9 | 1∶1 | 2,721,600 |
| 2.74M2.165 | Apple iPhone X, iPhone XS and iPhone 11 Pro | 2436 | × | 1125 | 812∶375 | 2.165 | 1∶1 | 2,740,500 |
| 2.74M1AD | Avielo Optix SuperWide 235 projector [17] | 2538 | × | 1080 | 2.35∶1 | 2.35∶1 | 1.017 | 2,741,040 |
| 2.76M3 | Supported by some GPUs, monitors, and games | 1920 | × | 1440 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 2,764,800 |
| UW-FHD | UltraWide FHD:Cinema TV from Philips and Vizio, Dell UltraSharp U2913WM, ASUS MX299Q, NEC EA294WMi, Philips 298X4QJAB, LG 29EA93, AOC Q2963PM | 2560 | × | 1080 | 21∶9 | 21∶9 | 1∶1 | 2,764,800 |
| 3.11M2 | Microsoft Surface Pro 3 | 2160 | × | 1440 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 3,110,400 |
| QXGA | Quad XGA:iPad (3rd Generation), iPad Mini (2nd Generation) | 2048 | × | 1536 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 3,145,728 |
| 3.32MA | Maximum resolution of the Sony GDM-FW900, Hewlett Packard A7217A and the Retina Display MacBook | 2304 | × | 1440 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 3,317,760 |
| 3.39MA | Surface Laptop | 2256 | × | 1504 | 3∶2 | 8∶5 | 1.067 | 3,393,024 |
| WQHD | Wide Quad HD:Dell UltraSharp U2711, Dell XPS One 27, Apple iMac | 2560 | × | 1440 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 3,686,400 |
| 3.74M9 | Available in some monitors | 2576 | × | 1450 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 3,735,200 |
| 3.98M3 | Supported by some displays and graphics cards [18] [ unreliable source? ] [19] | 2304 | × | 1728 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 3,981,312 |
| WQXGA | Wide QXGA:Apple Cinema HD 30, Apple 13" MacBook Pro Retina Display, Dell Ultrasharp U3011, Dell 3007WFP, Dell 3008WFP, Gateway XHD3000, Samsung 305T, HP LP3065, HP ZR30W, Nexus 10 | 2560 | × | 1600 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 4,096,000 |
| 4.15M2∶1 | LG G6, LG V30, Pixel 2 XL, HTC U11+, Windows Mixed Reality headsets (both eyes) | 2880 | × | 1440 | 2∶1 | 2∶1 | 1∶1 | 4,147,200 |
| Infinity Display | Samsung Galaxy S8, S8+, S9, S9+, Note 8 | 2960 | × | 1440 | 18½∶9 | 18½∶9 | 1∶1 | 4,262,400 |
| 4.35M2 | Chromebook Pixel | 2560 | × | 1700 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 4,352,000 |
| 4.61M1.422 | Pixel C | 2560 | × | 1800 | 64:45 | 64:45 | 1∶1 | 4,608,000 |
| 4.67M9 | Lenovo Thinkpad W541 | 2880 | × | 1620 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 4,665,600 |
| 4.92M3 | Max. CRT resolution, supported by the Viewsonic P225f and some graphics cards | 2560 | × | 1920 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 4,915,200 |
| Ultra-Wide QHD | LG, Samsung, Acer, HP and Dell UltraWide monitors | 3440 | × | 1440 | 21∶9 | 21∶9 | 1∶1 | 4,953,600 |
| 4.99M2 | Microsoft Surface Pro 4 | 2736 | × | 1824 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 4,990,464 |
| 5.18MA | Apple 15" MacBook Pro Retina Display | 2880 | × | 1800 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 5,184,000 |
| 5.53M2 | Microsoft Surface Pro X | 2880 | × | 1920 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 5,529,600 |
| QSXGA | Quad SXGA: | 2560 | × | 2048 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 5,242,880 |
| 5.6M3 | iPad Pro 12.9" | 2732 | × | 2048 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 0.999 | 5,595,136 |
| WQXGA+ | Wide QXGA+:HP Envy TouchSmart 14, Fujitsu Lifebook UH90/L, Lenovo Yoga 2 Pro | 3200 | × | 1800 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 5,760,000 |
| QSXGA+ | Quad SXGA+: | 2800 | × | 2100 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 5,880,000 |
| 5.9MA | Apple 16" MacBook Pro Retina Display | 3072 | × | 1920 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 5,898,240 |
| 4.26M1.538 | Apple 13" MacBook Air (Apple silicon) Retina Display | 2560 | × | 1664 | 8∶5.2 | 8∶5.2 | 1∶1 | 4,259,840 |
| 5.37M17∶11 | Apple 15" MacBook Air (Apple silicon) Retina Display | 2880 | × | 1864 | 8∶5.178 | 8∶5.178 | 1∶1 | 5,368,320 |
| 5.94M17∶11 | Apple 14" MacBook Pro (Apple silicon) Retina Display | 3024 | × | 1964 | 8∶5.196 | 8∶5.196 | 1∶1 | 5,939,136 |
| 7.72M1.547 | Apple 16" MacBook Pro (Apple silicon) Retina Display | 3456 | × | 2234 | 8∶5.171 | 8∶5.171 | 1∶1 | 7,720,704 |
| 3K | Microsoft Surface Book, Huawei MateBook X Pro [20] | 3000 | × | 2000 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 6,000,000 |
| UW4K | Ultra-Wide 4K: | 3840 | × | 1600 | 2.35∶1 | 21∶9 | 0.988 | 6,144,000 |
| WQSXGA | Wide QSXGA: | 3200 | × | 2048 | 25∶16 | 25∶16 | 1∶1 | 6,553,600 |
| 7M2 | Microsoft Surface Book 2 15" | 3240 | × | 2160 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 6,998,400 |
| DQHD | Dual Quad HD: Philips 499P9H, Dell U4919DW, Samsung C49RG94SSU | 5120 | × | 1440 | 32:9 | 32:9 | 1∶1 | 7,372,800 |
| QUXGA | Quad UXGA: | 3200 | × | 2400 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 7,680,000 |
| 4K UHD-1 | 4K Ultra HD 1:2160p, 4000-lines UHDTV (4K UHD) | 3840 | × | 2160 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 8,294,400 |
| DCI 4K | DCI 4K: | 4096 | × | 2160 | 1.90∶1 | 1.90∶1 | 1.002 | 8,847,360 |
| WQUXGA | Wide QUXGA:IBM T221 | 3840 | × | 2400 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 9,216,000 |
| 9.44M9 | LG Ultrafine 21.5, Apple 21.5" iMac 4K Retina Display | 4096 | × | 2304 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 9,437,184 |
| UW5K (WUHD) | Ultra-Wide 5K:21:9 aspect ratio TVs | 5120 | × | 2160 | 21∶9 | 21∶9 | 1∶1 | 11,059,200 |
| 11.29M9 | Apple 24" iMac 4.5K Retina Display | 4480 | × | 2520 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 11,289,600 |
| HXGA | Hex XGA: | 4096 | × | 3072 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 12,582,912 |
| 13.5M2 | Surface Studio | 4500 | × | 3000 | 3∶2 | 3∶2 | 1∶1 | 13,500,000 |
| 5K | Dell UP2715K, LG Ultrafine 27, Apple 27" iMac 5K Retina Display, Apple Studio Display | 5120 | × | 2880 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 14,745,600 |
| WHXGA | Wide HXGA: | 5120 | × | 3200 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 16,384,000 |
| HSXGA | Hex SXGA: | 5120 | × | 4096 | 5∶4 | 5∶4 | 1∶1 | 20,971,520 |
| 6K | Apple 32" Pro Display XDR [21] 6K Retina Display | 6016 | × | 3384 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 20,358,144 |
| WHSXGA | Wide HSXGA: | 6400 | × | 4096 | 25∶16 | 25∶16 | 1∶1 | 26,214,400 |
| HUXGA | Hex UXGA: | 6400 | × | 4800 | 4∶3 | 4∶3 | 1∶1 | 30,720,000 |
| – | 6480 | × | 3240 | 2∶1 | 2∶1 | 1∶1 | 20,995,200 | |
| 8K UHD-2 | 8K Ultra HD 2:4320p, 8000-lines UHDTV (8K UHD), Dell UltraSharp UP3218K 32" 8K | 7680 | × | 4320 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 33,177,600 |
| WHUXGA | Wide HUXGA: | 7680 | × | 4800 | 8∶5 | 8∶5 | 1∶1 | 36,864,000 |
| 8K Full Format | DCI 8K: | 8192 | × | 4320 | 1.90∶1 | 1.90∶1 | 1.002 | 35,389,440 |
| — | 8192 | × | 4608 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 37,748,736 | |
| UW10K | Ultra-Wide 10K: | 10240 | × | 4320 | 21∶9 | 21∶9 | 1∶1 | 44,236,800 |
| 8K Fulldome | 8K Fulldome | 8192 | × | 8192 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 1∶1 | 67,108,864 |
| 16K | 16K | 15360 | × | 8640 | 16∶9 | 16∶9 | 1∶1 | 132,710,400 |
| 16K Full Format | DCI 16K | 16384 | × | 8640 | 256∶135 | 1.90∶1 | 1.002 | 141,557,760 |
For television, the display aspect ratio (DAR) is shown, not the storage aspect ratio (SAR); analog television does not have well-defined pixels, while several digital television standards have non-square pixels.
| Standard | Resolution [note 3] (dots × lines) | Display aspect ratio, H:V | Total pixels |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCIR System B/G (PAL/SECAM) | ~520 × 576 | 4:3 | ~299,520 |
| CCIR System D/K/L (PAL/SECAM) | ~627 × 576 | 4:3 | ~361,152 |
| CCIR System I (PAL) | ~573 × 576 | 4:3 | ~330,048 |
| CCIR System N (PAL-N) | ~440 × 576 | 4:3 | ~253,440 |
| PALplus | ~520 × 576 | 16:9 | ~300,000 |
| Undecoded PALplus | ~520 × 432 | 16:9 | ~220,000 |
| NTSC, [22] [23] PAL-M | ~440 × 486 | 4:3 | ~213,840 |
| LaserDisc | ~580 × 486 (NTSC) | 4:3 [note 4] | ~268,800 |
| ~570 × 576 (PAL/SECAM) | ~322,560 | ||
| VHS, Betamax, Video8 | ~320 × 486 (NTSC) | 4:3 | ~153,600 |
| ~310 × 576 (PAL/SECAM) | ~178,560 | ||
| Betamax Superbeta | ~380 × 486 (NTSC) | 4:3 | ~182,400 |
| ~370 × 576 (PAL/SECAM) | ~213,120 | ||
| Betacam | ~387 × 486 (NTSC) | 4:3 | ~185,760 |
| ~387 × 576 (PAL) | ~222,912 | ||
| Betacam SP | ~453 × 486 (NTSC) | 4:3 | ~220,158 |
| ~453 × 576 (PAL) | ~260,928 | ||
| S-VHS, Hi8 | ~560 × 486 (NTSC) | 4:3 | ~272,160 |
| ~560 × 576 (PAL) | ~322,560 | ||
| Hi-Vision [24] | ~1920 × 1035 | 16:9 | ~1,987,200 |
| HD-MAC | ~1040 × 1152 | 5:3 | ~1,198,080 |
| 405-line | ~503 × 377 | 4:3 (5:4 before 1950) | ~189,631 |
| 819-line | ~816 × 736 | 4:3 | ~600,576 |
| Standard | Resolution (dots × lines) | Name | Scan | Frame rate (Hz) | Display aspect ratio, H:V | Total pixels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCD (MPEG-1), LDTV (e.g. DMB) | 352 × 240 | SIF 525 | 240i | 30 | 4:3 | 84,480 |
| 352 × 288 | SIF 625 | 288i | 25 | 101,376 | ||
| CVD | 352 × 480 | 480i | 30 | 4:3, 16:9 | 168,960 | |
| 352 × 576 | 576i | 25 | 202,725 | |||
| SVCD (MPEG-2) | 480 × 480 | 480i | 30 | 4:3, 16:9 | 230,400 | |
| 480 × 576 | 576i | 25 | 276,480 | |||
| DVD | 720 × 480 | NTSC | 480i, 480p | 24, 30 | 4:3, 16:9 | 345,600 |
| 720 × 576 | PAL | 576i, 576p | 25 | 4:3, 16:9 | 414,720 | |
| SDTV, EDTV (SMPTE 293M, Rec. 601, e.g. ATSC, DVB, [25] ISDB) | 352 × 480 | 480i, 480p | 30 | 4:3, 16:9 | 168,960 | |
| 480 × 480 | 230,400 | |||||
| 528 × 480 | 253,440 | |||||
| 544 × 480 | 261,120 | |||||
| 640 × 480 | 307,200 | |||||
| 704 × 480 | 4SIF 525 | 337,920 | ||||
| 720 × 480 | NTSC | 345,600 | ||||
| 480 × 576 | 576i, 576p | 25 | 4:3, 16:9 | 276,480 | ||
| 544 × 576 | 313,344 | |||||
| 704 × 576 | 4SIF 625 | 405,504 | ||||
| 720 × 576 | PAL | 414,720 | ||||
| HDTV (Rec. 709; Blu-ray, HD DVD) | 1280 × 720 | HD | 720p | 24, 25, 30, 50, 60 | 16:9 | 921,600 |
| 1280 × 1080 | Full HD, HD Lite | 1080i | 25, 30 | 16:9 | 1,382,400 | |
| 1440 × 1080 | Full HD, HD Lite | 1080i | 25, 30 | 16:9 | 1,555,200 | |
| 1920 × 1080 | Full HD | 1080i, 1080p | 24, 25, 30 | 16:9, 2.21:1 | 2,073,600 | |
| UHDTV (Rec. 2020, Ultra HD Blu-ray) | 3840 × 2160 | 4K UHDTV | 2160p | 24, 25, 30, 50, 60, 100, 120 | 16:9 | 8,294,400 |
| 7680 × 4320 | 8K UHDTV | 4320p | 33,177,600 |
Many of these resolutions are also used for video files that are not broadcast. These may also use other aspect ratios by cropping otherwise black bars at the top and bottom which result from cinema aspect ratios greater than 16∶9, such as 1.85 or 2.35 through 2.40 (dubbed "Cinemascope", "21∶9" etc.), while the standard horizontal resolution, e.g. 1920 pixels, is usually kept. The vertical resolution is usually a multiple of 8 or 16 pixels due to most video codecs processing pixels on such sized blocks. A widescreen FHD video can be 1920 × 800 for a 12∶5 ratio or 1920 × 1040 for roughly 1.85 × 1, for instance.
| Standard | Resolution | Display aspect ratio | Total pixels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital cinema 2× | 2048 × 858 | 2.39:1 | 1,757,184 |
| Digital cinema 2× | 1998 × 1080 | 1.85:1 | 2,157,840 |
| Academy 2× | 1828 × 1332 | 1.37:1 | 2,434,896 |
| Full Aperture Native 2× | 2048 × 1556 | 1.32:1 | 3,186,688 |
| Digital cinema 4× | 4096 × 1714 | 2.39:1 | 7,020,544 |
| Digital cinema 4× | 3996 × 2160 | 1.85:1 | 8,631,360 |
| Digital Cinema Initiatives 4× (native resolution) | 4096 × 2160 | 1.90:1 | 8,847,360 |
| Academy 4× | 3656 × 2664 | 1.37:1 | 9,739,584 |
| Full Aperture 4× | 4096 × 3112 | 1.32:1 | 12,746,752 |
| 6K [26] | 6144 × 3160 | 1.94:1 | 19,415,040 |
| 8K | 7992 × 4320 | 1.85:1 | 34,525,440 |
| 7.2K | 7200 × 3060 | 2.35:1 | 22,032,000 |
| IMAX Digital [27] | 5616 × 4096 | 1.37:1 | 23,003,136 |
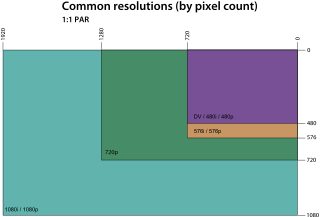
The below distinguish SAR (aspect ratio of pixel dimensions), DAR (aspect ratio of displayed image dimensions), and the corresponding PAR (aspect ratio of individual pixels), though it currently contains some errors (inconsistencies), as flagged.
| Standard | Resolution | Aspect ratio | Total pixels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | Display | Pixel | |||
| DV NTSC | 720 × 480 | 3:2 | 4:3 | 10:11 [ citation needed ] | 345,600 |
| D1 NTSC | 720 × 486 | 40:27 | 4:3 | 9:10 | 349,920 |
| DV PAL | 720 × 576 | 5:4 | 4:3 | 12:11 [ citation needed ] | 414,720 |
| D1 PAL | 720 × 576 | 5:4 | 4:3 | 16:15 | 414,720 |
| Panasonic DVCPRO HD 720p | 960 × 720 | 4:3 | 16:9 | 4:3 | 691,200 |
| Panasonic DVCPRO HD 1080, 59.94i | 1280 × 1080 | 32:27 | 16:9 | 3:2 | 1,382,400 |
| Panasonic DVCPRO HD 1080, 50i | 1440 × 1080 [ citation needed ] | 4:3 [ citation needed ] | 16:9 [ citation needed ] | 3:2 [ citation needed ] | 1,555,200 |
| HDV 1080i/1080p | 1440 × 1080 | 4:3 | 16:9 | 4:3 | 1,555,200 |
| Sony HDCAM (1080) | 1440 × 1080 [ citation needed ] | 4:3 [ citation needed ] | 16:9 [ citation needed ] | 3:2 [ citation needed ] | 1,555,200 |
| Sony HDCAM SR (1080) | 1920 × 1080 | 16:9 | 16:9 | 1:1 | 2,073,600 |
| Academy 2× | 1828 × 1332 | 1.37:1 | 1.37:1 | 1:1 | 2,434,896 |
| Full Aperture Native 2× | 2048 × 1556 | 1.316 | 4:3 | ~1:1 | 3,186,688 |
| Academy 4× | 3656 × 2664 | 1.37:1 | 1.37:1 | 1:1 | 9,739,584 |
| Full Aperture 4× | 4096 × 3112 | 1.316 | 4:3 | ~1:1 | 12,746,752 |
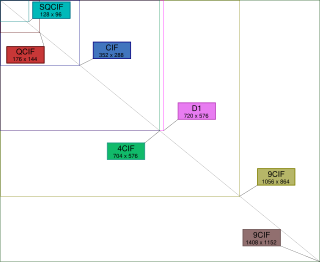
| Standard | Resolution | Storage aspect ratio | Total pixels |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQCIF (Sub Quarter CIF) | 128 × 96 | 1.33:1 | 12,288 |
| QCIF (Quarter CIF) | 176 × 144 | 1.22:1 | 25,344 |
| CIF (or FCIF) | 352 × 288 | 1.22:1 | 101,376 |
| 4CIF (4 × CIF) | 704 × 576 | 1.22:1 | 405,504 |
| 16CIF (16 × CIF) | 1408 × 1152 | 1.22:1 | 1,622,016 |
960H is a resolution used in analog CCTV equipment. 960H represents the number of horizontal pixels in a video signal transmitted from a camera or received by a DVR (Digital Video Recorder). The resolution of 960H depends on whether the equipment is PAL or NTSC based: 960H represents 960 x 576 (PAL) or 960 x 480 (NTSC) pixels. [28] 960H represents an increase in pixels of some 30% over standard D1 resolution, which is 720 x 576 pixels (PAL), or 720 x 480 pixels (NTSC). The increased resolution over D1 comes as a result of a longer horizontal scan. The difference is that whilst D1 has a 4:3 aspect ratio 960H has a 16:9 widescreen aspect ratio. The extra pixels are used to form the increased area to the sides of the D1 image. The pixel density of 960H is identical to standard D1 resolution so it does not give any improvement in image quality, merely a wider aspect ratio.
Alternative analog video transport technologies carrying higher resolutions than 960H include HD-TVI, HDCVI, and AHD.
In digital imaging, a pixel, pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software.

Standard-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. Standard refers to offering a similar resolution to the analog broadcast systems used when it was introduced.

Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types.
CIF, also known as FCIF, is a standardized format for the picture resolution, frame rate, color space, and color subsampling of digital video sequences used in video teleconferencing systems. It was first defined in the H.261 standard in 1988.
Subpixel rendering is a method used to increase the effective resolution of a color display device. It takes advantage of each pixel's composition of individually addressable red, green, and blue components adjacent on the display matrix, called subpixels, and uses them as rendering units instead of pixels.

The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.
480p is the shorthand name for a family of video display resolutions. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The 480 denotes a vertical resolution of 480 pixels, usually with a horizontal resolution of 640 pixels and 4:3 aspect ratio or a horizontal resolution of 854 pixels for an approximate 16:9 aspect ratio. Since a pixel count must be a whole number, in Wide VGA displays it is generally rounded up to 854 to ensure inclusion of the entire image. The frames are displayed progressively as opposed to interlaced. 480p was used for many early plasma televisions. Standard definition has always been a 4:3 aspect ratio with a pixel resolution of 720 × 480 at 60 Hz for NTSC regions, and 720 or 768 × 576 for PAL regions. However, standard definition defines a 15.7k Hz horizontal scanrate, which means that interlacing has to be used for those resolution modes. The lowercase letter "p" in 480p stands for progressive, so the two must not be confused.

720p is a progressive HD signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HD (1.78:1). All major HD broadcasting standards include a 720p format, which has a resolution of 1280×720p.
1080i is a combination of frame resolution and scan type. 1080i is used in high-definition television (HDTV) and high-definition video. The number "1080" refers to the number of horizontal lines on the screen. The "i" is an abbreviation for "interlaced"; this indicates that only the even lines of each frame, then only the odd lines, are drawn alternately, so that only half the number of lines are ever updated at once. A related display resolution is 1080p, which also has 1080 lines of resolution; the "p" refers to progressive scan, which indicates that each full frame appears on the screen in sequence.
Overscan is a behaviour in certain television sets, in which part of the input picture is cut off by the visible bounds of the screen. It exists because cathode-ray tube (CRT) television sets from the 1930s to the early 2000s were highly variable in how the video image was positioned within the borders of the screen. It then became common practice to have video signals with black edges around the picture, which the television was meant to discard in this way.
Source Input Format (SIF) defined in MPEG-1, is a video format that was developed to allow the storage and transmission of digital video.

A Pixel aspect ratio is a mathematical ratio that describes how the width of a pixel in a digital image compared to the height of that pixel.

Large-screen television technology developed rapidly in the late 1990s and 2000s. Prior to the development of thin-screen technologies, rear-projection television was standard for larger displays, and jumbotron, a non-projection video display technology, was used at stadiums and concerts. Various thin-screen technologies are being developed, but only liquid crystal display (LCD), plasma display (PDP) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) have been publicly released. Recent technologies like organic light-emitting diode (OLED) as well as not-yet-released technologies like surface-conduction electron-emitter display (SED) or field emission display (FED) are in development to supercede earlier flat-screen technologies in picture quality.
"21:9" is a consumer electronics (CE) marketing term to describe the ultrawide aspect ratio of 64:27, designed to show films recorded in CinemaScope and equivalent modern anamorphic formats. The main benefit of this screen aspect ratio is a constant display height when displaying other content with a lesser aspect ratio.
PenTile matrix is a family of patented subpixel matrix schemes used in electronic device displays. PenTile is a trademark of Samsung. PenTile matrices are used in AMOLED and LCD displays.

4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 3840 × 2160 with a 16:9 aspect ratio is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 4096 × 2160.
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display.
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as 2.40:1. For the 2.40:1 aspect ratio, the image is 2.40 units wide and 1 unit high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.40:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography. The film was filmed in 2.40:1 widescreen.

5K resolution refers to display formats with a horizontal resolution of around 5,000 pixels. The most common 5K resolution is 5120 × 2880, which has an aspect ratio of 16∶9 with around 14.7 million pixels, with exactly twice the linear resolution of 1440p and four times that of 720p. This resolution is typically used in computer monitors to achieve a higher pixel density, and is not a standard format in digital television and digital cinematography, which feature 4K resolutions and 8K resolutions.

Ultrawide formats refers to photos, videos, and displays with aspect ratios greater than 2. There were multiple moves in history towards wider formats, including one by Disney, with some of them being more successful than others.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)