
The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LACMTA), branded as Metro, is the county agency that plans, operates, and coordinates funding for most of the public transportation system in Los Angeles County, California, the most populated county in the United States.

Los Angeles has a complex multimodal transportation infrastructure, which serves as a regional, national and international hub for passenger and freight traffic. The system includes the United States' largest port complex; an extensive freight and passenger rail infrastructure, including light rail lines and rapid transit lines; numerous airports and bus lines; vehicle for hire companies; and an extensive freeway and road system. People in Los Angeles rely on cars as the dominant mode of transportation, but since 1990 the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority has built over one hundred miles (160 km) of light and heavy rail serving more and more parts of Los Angeles and the greater area of Los Angeles County; Los Angeles was the last major city in the United States to get a permanent rail system installed.

Crenshaw Boulevard is a north-south thoroughfare that runs through Crenshaw and other neighborhoods along a 23-mile route in the west-central part of Los Angeles, California, United States.

The Los Angeles Metro Rail is an urban rail transit system serving Los Angeles County, California, United States, consisting of six lines: four light rail lines and two rapid transit lines, serving a total of 102 stations. The system connects with the Metro Busway bus rapid transit system, the Metrolink commuter rail system, as well as several Amtrak lines. Metro Rail is owned and operated by the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro).

Hollywood/Highland station is an underground rapid transit station on the B Line of the Los Angeles Metro Rail system. It is located under Hollywood Boulevard at its intersection with Highland Avenue, after which the station is named, in the Los Angeles neighborhood of Hollywood.
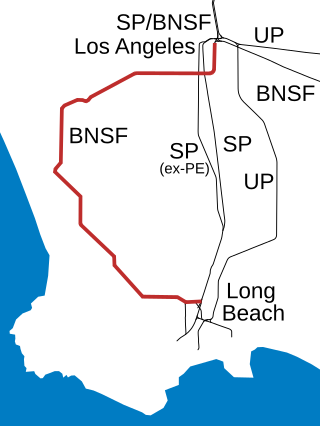
The Harbor Subdivision is a single-track main line of the BNSF Railway which stretches 53 miles (85 km) between rail yards near downtown Los Angeles and the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach across southwestern Los Angeles County. It was the primary link between two of the world's busiest harbors and the national rail network. Mostly displaced with the April 15, 2002 opening of the more direct Alameda Corridor, the Harbor Sub takes a far more circuitous route from origin to destination, owing to its growth in segments over the decades. The subdivision was built in this fashion beginning in the early 1880s to serve the ports and the various businesses that developed along it.

The C Line is a 17.8-mile (28.6 km) light rail line running between the Los Angeles neighborhood of Westchester and the city of Norwalk within Los Angeles County, California. It is one of six lines forming the Los Angeles Metro Rail system and opened on August 12, 1995. Along the route, the line also serves the cities of Downey, Hawthorne, and Lynwood, as well as several unincorporated communities in the South Los Angeles region including Athens, Del Aire, and Willowbrook. The fully grade-separated route runs mainly in the median strip of Interstate 105 for its latitude portion and in a mixture of viaducts, embankments, and an open trench for its western leg. A free shuttle bus to Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) is available at Aviation/LAX and Aviation/Century stations.

Aviation/LAX station is an elevated light rail station on the C Line of the Los Angeles Metro Rail system. It is located over Aviation Boulevard, after which the station is named, near its intersection with Imperial Highway and south of Century Freeway in the Westchester neighborhood of Los Angeles, California and immediately adjacent to the Del Aire neighborhood. It opened as part of the Green Line on August 12, 1995. The station was initially named Aviation Blvd/I-105, but in 2003, it was renamed Aviation/LAX to highlight its proximity to Los Angeles International Airport.
This article covers streets in Los Angeles, California between and including 41st Street and 250th Street. Major streets have their own linked articles; minor streets are discussed here.
Measure R was a ballot measure during the November 2008 elections in Los Angeles County, California, that proposed a half-cent sales taxes increase on each dollar of taxable sales for thirty years in order to pay for transportation projects and improvements. The measure was approved by voters with 67.22% of the vote, just over the two-thirds majority required by the state of California to raise local taxes. The project was touted as a way to "improve the environment by getting more Angelenos out of their cars and into the region's growing subway, light rail, and bus services." It will result in the construction or expansion of a dozen rail lines in the county.

Expo/Crenshaw station is a light rail station in the Los Angeles Metro Rail system located in the Jefferson Park neighborhood of Los Angeles at the intersection of Crenshaw and Exposition Boulevards. During construction, it was known as the Crenshaw station. The station is the transfer point between the E Line, which stops at two street-level platforms alongside Exposition Boulevard, and the K Line, which has its northern terminus at a single island platform under Crenshaw Boulevard.
Aviation Boulevard is a major north–south thoroughfare in western and the South Bay region of Los Angeles County, California.

The D Line Subway Extension Project is a construction project in Los Angeles County, California, extending the rapid transit D Line of the Los Angeles Metro Rail system from its current terminus at Wilshire/Western in Koreatown, Los Angeles, to the Westside region. The project is being supervised by the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro). The subway has been given high priority by Metro in its long-range plans, and funding for the project was included in two county sales tax measures, Measure R and Measure M.

The Sepulveda Transit Corridor is a two-phased planned transit corridor that aims to connect the Los Angeles Basin to the San Fernando Valley through Sepulveda Pass in Los Angeles, California, by supplementing the existing I-405 freeway through the pass. The corridor would partly parallel I-405, and proposed alternatives include heavy rail rapid transit or a monorail line connecting the G Line in the Valley to the D Line and E Line on the Westside, and the K Line near Los Angeles International Airport.

Aviation/Century station is an elevated light rail station on the C and K lines of the Los Angeles Metro Rail system. It is located alongside Aviation Boulevard above its intersection with Century Boulevard, located in the Westchester neighborhood of Los Angeles.

LAX/Metro Transit Center station is an under construction light rail transport hub in the Los Angeles Metro Rail system, located near Aviation Boulevard and 96th Street in the Westchester district of Los Angeles. The station was designed as a station for the C and K lines. It will serve as the transfer point between Metro Rail and the LAX Automated People Mover (APM) serving the Los Angeles International Airport terminals and facilities. Additionally, the station will have connections to Metro Bus, other municipal bus lines, a customer service center, and a Metro Bike Share hub. Metro is scheduled to start serving the station sometime in 2025, although the APM connection is not scheduled to open until early 2026.

The K Line Northern Extension, formerly known as the Crenshaw Northern Extension, is a project planning a Los Angeles Metro Rail light rail transit corridor extension connecting Expo/Crenshaw station to Hollywood/Highland station in Hollywood. The corridor is a fully underground, north-south route along mostly densely populated areas on the western side of the Los Angeles Basin; it would be operated as part of the K Line. The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro) is prioritizing the project along with pressure from the West Hollywood residents. Construction is slated to start in 2041 and begin service by 2047 unless means to accelerate the project are found.
The history of the Los Angeles Metro Rail and Busway system begins in the early 1970s, when the traffic-choked region began planning a rapid transit system. The first dedicated busway opened along I-10 in 1973, and the region's first light rail line, the Blue Line opened in 1990. Today the system includes over 160 miles (260 km) of heavy rail, light rail, and bus rapid transit lines, with multiple new lines under construction as of 2019.
The Lincoln Boulevard Transit Corridor is a proposed 10-mile (16 km) bus rapid transit or light rail line in the public transport network of the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority in Los Angeles County, California. It is planned to operate on a north to south route on Lincoln Boulevard between the C and K Line's LAX/Metro Transit Center station with the E Line's Downtown Santa Monica station on the Los Angeles Metro Rail system. A proposed completion date of 2047 for BRT and an unknown date for rail conversion. It is funded by Measure M and Measure R. The route will have signal priority at traffic lights and will have a dedicated right of way.



























