History
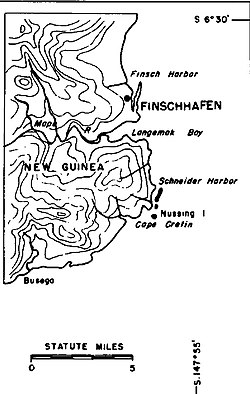
The Imperial Japanese Army took over Finschhafen on March 10, 1942 in the Battle of Finschhafen and the Landing at Scarlet Beach. On October 2, 1943, the Australian Forces recaptured Finschhafen in the Huon Peninsula campaign. On November 2, 1943, members of the US Navy's Seabee 60th Construction Battalion arrived to start work on the Naval Base. The members of the 60th Construction Battalion arrived from Naval Base Woodlark Island, where most work had just been completed. An LST ship did a beach landing of the Seabee crew and the equipment. Work was delayed due to thick mud from a rain storm. On November 16 Seabees began working with 808th Army Aviation Engineer Battalion on the runway. Seabees did grading and mat-laying on the north end of the runway. The runway opened on time on December 5. [1] [3]
On December 9 the 78th Battalion arrived at a point south of the city of Finschhafen and started work on a base camp and the Naval Base. On December 16 the 40th Battalion arrived with the first Liberty ship full of supplies. On January 6, the 46th Battalion arrived on the south side of Langemak Bay and built a camp near the 78th Battalion. [1] [4]
On January 5, 1944, the 808th Army Aviation Engineers departed Finschhafen. The Seabee 60th Battalion took over all maintenance and the remaining construction at the airfield. 60th Battalion built: aviation gasoline tank farm, aviation repair depot, and parking for fighter planes and bombers. The 60th, 78th, and 46th Battalion built the harbor facilities, including a 200-foot pile timber jetty -dock. The PT Boat was opened. Next in 1944, built was: a 30-by-60-foot pier, a torpedo pier, one finger pier, two unloading piers, and an 84-foot repair pier, base camp, supply depot, torpedo shop, and machine shops. By July 1944, the 91st Battalion arrived and improved the base facilities. The 91st Battalion built four 330-foot timber cargo unloading piers for Merchant Navy ships and recreation buildings. Seabee built a 300-bed hospital, Base Hospital 14, and 500 man Navy camp. To refuel the many ships now stopping at the new Naval Base, Seabee built a 10,000-barrel tank farm of Fuel oil. [1] [2] [5] [6]
Finschhafen became a staging camp for upcoming campaigns, and Seabee built a US Army camp for 17,000 Troops. To support the Troops, Seabee built beach ramps to support 14 LST ships and 15 miles of roads. Seabee built a staging camp for 2,500 Navy Troops. The 102nd Battalion arrived in March 1944 ad departed in June 1944. Construction Battalion Maintenance Units 545 and 543 arrived in February and April 1944 to work at the base. During all the construction projects there were delays due to heavy rains. Finschhafen is in the Tropical rainforest climate and can have 4,081 mm (160 inches) of rain a year. There were some enemy bombings from Rabaul, that caused some delay and Seabee casualties. By November 1944 all projects had been completed and by January 1945, some of the base was being shipped to more forward bases. The base was closed at the end of the war. [1]
Naval Base Finschhafen Feet Post Office is FPO# 722 SF Finschhafen.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.