
Marcello Malpighi was an Italian biologist and physician, who is referred to as the "Founder of microscopical anatomy, histology & Father of physiology and embryology". Malpighi's name is borne by several physiological features related to the biological excretory system, such as the Malpighian corpuscles and Malpighian pyramids of the kidneys and the Malpighian tubule system of insects. The splenic lymphoid nodules are often called the "Malpighian bodies of the spleen" or Malpighian corpuscles. The botanical family Malpighiaceae is also named after him. He was the first person to see capillaries in animals, and he discovered the link between arteries and veins that had eluded William Harvey. Malpighi was one of the earliest people to observe red blood cells under a microscope, after Jan Swammerdam. His treatise De polypo cordis (1666) was important for understanding blood composition, as well as how blood clots. In it, Malpighi described how the form of a blood clot differed in the right against the left sides of the heart.
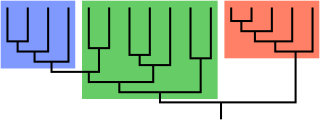
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic with respect to the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic grouping includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants.

In Roman mythology and religion, Quirinus is an early god of the Roman state. In Augustan Rome, Quirinus was also an epithet of Janus, as Janus Quirinus.

Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative or positive qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. Criticism falls into several overlapping types including "theoretical, practical, impressionistic, affective, prescriptive, or descriptive".
Political aspects of Islam are derived from the Quran, ḥadīth literature, and sunnah, the history of Islam, and elements of political movements outside Islam.

Analytical Thomism is a philosophical movement which promotes the interchange of ideas between the thought of Thomas Aquinas, and modern analytic philosophy. It is a branch of analytic scholasticism that draws on other scholastic sources, esp. John Duns Scotus.

The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague was an epidemic that afflicted the entire Mediterranean Basin, Europe, and the Near East, severely affecting the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire, especially Constantinople. The plague is named for the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I, who according to his court historian Procopius contracted the disease and recovered in 542, at the height of the epidemic which killed about a fifth of the population in the imperial capital. The contagion arrived in Roman Egypt in 541, spread around the Mediterranean Sea until 544, and persisted in Northern Europe and the Arabian Peninsula until 549. By 543, the plague had spread to every corner of the empire. As the first episode of the first plague pandemic, it had profound economic, social, and political effects across Europe and the Near East and cultural and religious impact on Eastern Roman society.
International political economy (IPE) is the study of how politics shapes the global economy and how the global economy shapes politics. A key focus in IPE is on the power of different actors such as nation states, international organizations and multinational corporations to shape the international economic system and the distributive consequences of international economic activity. It has been described as the study of "the political battle between the winners and losers of global economic exchange."
Evolutionary medicine or Darwinian medicine is the application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease. Modern biomedical research and practice have focused on the molecular and physiological mechanisms underlying health and disease, while evolutionary medicine focuses on the question of why evolution has shaped these mechanisms in ways that may leave us susceptible to disease. The evolutionary approach has driven important advances in the understanding of cancer, autoimmune disease, and anatomy. Medical schools have been slower to integrate evolutionary approaches because of limitations on what can be added to existing medical curricula. The International Society for Evolution, Medicine and Public Health coordinates efforts to develop the field. It owns the Oxford University Press journal Evolution, Medicine and Public Health and The Evolution and Medicine Review.

Ernesto de Martino was an Italian anthropologist, philosopher and historian of religions. He studied with Benedetto Croce and Adolfo Omodeo, and did field research with Diego Carpitella into the funeral rituals of Lucania and tarantism.

Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however.

Metriorhynchidae is an extinct family of specialized, aquatic metriorhynchoid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous period of Europe, North America and South America. The name Metriorhynchidae was coined by the Austrian zoologist Leopold Fitzinger in 1843. The group contains two subfamilies, the Metriorhynchinae and the Geosaurinae. They represent the most marine adapted of all archosaurs.
Monotheism—the belief that there is only one deity—is the focus of the Abrahamic religions, which like-mindedly conceive God as the all-powerful and all-knowing deity from whom Abraham received a divine revelation, according to their respective narratives. The most prominent Abrahamic religions are Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. They, alongside Samaritanism, Druzism, the Baháʼí Faith, and Rastafari, all share a common core foundation in the form of worshipping Abraham's God, who is identified as Yahweh in Hebrew and called Allah in Arabic. Likewise, the Abrahamic religions share similar features distinguishing them from other categories of religions:
Gender-neutral language or gender-inclusive language is language that avoids reference towards a particular sex or gender. In English, this includes use of nouns that are not gender-specific to refer to roles or professions, formation of phrases in a coequal manner, and discontinuing the collective use of male or female terms. For example, the words policeman and stewardess are gender-specific job titles; the corresponding gender-neutral terms are police officer and flight attendant. Other gender-specific terms, such as actor and actress, may be replaced by the originally male term; for example, actor used regardless of gender. Some terms, such as chairman, that contain the component -man but have traditionally been used to refer to persons regardless of sex are now seen by some as gender-specific. An example of forming phrases in a coequal manner would be using husband and wife instead of man and wife. Examples of discontinuing the collective use of terms in English when referring to those with unknown or indeterminate gender as singular they, and using humans, people, or humankind, instead of man or mankind.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred in Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. The eastern half of the Empire survived the conditions that caused the fall of the West in the 5th century AD, and continued to exist until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in the Mediterranean world. The term "Byzantine Empire" was only coined following the empire's demise; its citizens referred to the polity as the "Roman Empire" and to themselves as "Romans". Due to the imperial seat's move from Rome to Byzantium, the adoption of state Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin, modern historians continue to make a distinction between the earlier Roman Empire and the later Byzantine Empire.
Raffaele Pettazzoni was an Italian anthropologist, archaeologist, professor, and historian of religion. He was one of the first academics to propose a historical approach to the study of religions. He was editor-in-chief of the academic journal Numen published by Brill Academic Publishers, and president of the International Association for the History of Religions from 1950 to 1959.

Ralph Wilbur Hood Jr. is an American psychologist. He serves as Leroy A. Martin Distinguished Professor of Religious Studies at the University of Tennessee at Chattanooga, where he specializes in the psychology of religion.

William Hewat McLeod was a New Zealand scholar who helped establish Sikh Studies as a distinctive field.
Michelle Alexander is a bioarchaeologist with an interest in multi-faith societies and is Senior Lecturer in Bioarchaeology at the University of York.

La Difesa della Razza was a Fascist magazine which was published in Rome between 1938 and 1943 during the Fascist rule in Italy. Its subtitle was Scienza, Documentazione, Polemica. It played a significant role in the implementation of the racial ideology following the invasion of Ethiopia and the introduction of the racial laws in 1938.













