
Thanatophages, are organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing dead plant biomass. [1]

Thanatophages, are organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing dead plant biomass. [1]
In food webs, thanatophages generally play the roles of decomposers.
The eating of wood, whether live or dead, is known as xylophagy. The activity of animals feeding only on dead wood is called sapro-xylophagy and those animals, sapro-xylophagous.
Saprophyte (-phyte meaning "plant") is a botanical term that is no longer in popular use, as such plants have been discovered to actually be parasitic on fungi. [2] There are no real saprotrophic organisms that are embryophytes,[ citation needed ] and fungi and bacteria are no longer placed in the plant kingdom. Plants that were once considered saprophytes, such as non-photosynthetic orchids and monotropes, are now known to be parasites on fungi. These species are now termed myco-heterotrophs. [3] [4] [5]

A heterotroph is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but not producers. Living organisms that are heterotrophic include all animals and fungi, some bacteria and protists, and many parasitic plants. The term heterotroph arose in microbiology in 1946 as part of a classification of microorganisms based on their type of nutrition. The term is now used in many fields, such as ecology, in describing the food chain.
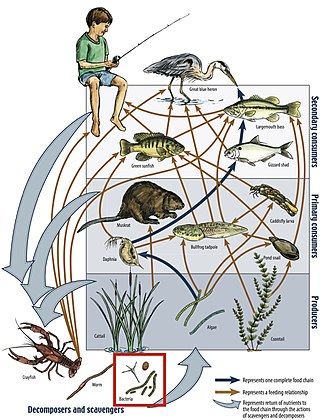
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or heterotrophs. This is a non-binary classification; some organisms occupy the role of mixotrophs, or autotrophs that additionally obtain organic matter from non-atmospheric sources.
This glossary of ecology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts in ecology and related fields. For more specific definitions from other glossaries related to ecology, see Glossary of biology, Glossary of evolutionary biology, and Glossary of environmental science.
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and release the nutrients from the dead matter into the environment around them. Decomposition relies on chemical processes similar to digestion in animals; in fact, many sources use the words digestion and decomposition interchangeably. In both processes, complex molecules are chemically broken down by enzymes into simpler, smaller ones. The term "digestion," however, is commonly used to refer to food breakdown that occurs within animal bodies, and results in the absorption of nutrients from the gut into the animal's bloodstream. This is contrasted with external digestion, meaning that, rather than swallowing food and then digesting it using enzymes located within a GI tract, an organism instead releases enzymes directly onto the food source. After allowing the enzymes time to digest the material, the decomposer then absorbs the nutrients from the environment into its cells. Decomposition is often erroneously conflated with this process of external digestion, probably because of the strong association between fungi, which are external digesters, and decomposition.

Detritivores are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus. There are many kinds of invertebrates, vertebrates, and plants that carry out coprophagy. By doing so, all these detritivores contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles. Detritivores should be distinguished from other decomposers, such as many species of bacteria, fungi and protists, which are unable to ingest discrete lumps of matter. Instead, these other decomposers live by absorbing and metabolizing on a molecular scale. The terms detritivore and decomposer are often used interchangeably, but they describe different organisms. Detritivores are usually arthropods and help in the process of remineralization. Detritivores perform the first stage of remineralization, by fragmenting the dead plant matter, allowing decomposers to perform the second stage of remineralization.

Coarse woody debris (CWD) or coarse woody habitat (CWH) refers to fallen dead trees and the remains of large branches on the ground in forests and in rivers or wetlands. A dead standing tree – known as a snag – provides many of the same functions as coarse woody debris. The minimum size required for woody debris to be defined as "coarse" varies by author, ranging from 2.5–20 cm (1–8 in) in diameter.

The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how it interacts with the environment, plants, and animals.

In biology, detritus is organic matter made up of the decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decompose (remineralise) it. Such microorganisms may be decomposers, detritivores, or coprophages.

Soil biology is the study of microbial and faunal activity and ecology in soil. Soil life, soil biota, soil fauna, or edaphon is a collective term that encompasses all organisms that spend a significant portion of their life cycle within a soil profile, or at the soil-litter interface. These organisms include earthworms, nematodes, protozoa, fungi, bacteria, different arthropods, as well as some reptiles, and species of burrowing mammals like gophers, moles and prairie dogs. Soil biology plays a vital role in determining many soil characteristics. The decomposition of organic matter by soil organisms has an immense influence on soil fertility, plant growth, soil structure, and carbon storage. As a relatively new science, much remains unknown about soil biology and its effect on soil ecosystems.
Saprophyte may refer to:

Myco-heterotrophy is a symbiotic relationship between certain kinds of plants and fungi, in which the plant gets all or part of its food from parasitism upon fungi rather than from photosynthesis. A myco-heterotroph is the parasitic plant partner in this relationship. Myco-heterotrophy is considered a kind of cheating relationship and myco-heterotrophs are sometimes informally referred to as "mycorrhizal cheaters". This relationship is sometimes referred to as mycotrophy, though this term is also used for plants that engage in mutualistic mycorrhizal relationships.

Saprophages are organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing dead plant or animal biomass. They are distinguished from detritivores in that saprophages are sessile consumers while detritivores are mobile. Typical saprophagic animals include sedentary polychaetes such as amphitrites and other terebellids.

Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi and with soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes. Saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes, although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or of other plants. In fungi, the saprotrophic process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae.

The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. A food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level 3 or higher, and typically finish with apex predators at level 4 or 5. The path along the chain can form either a one-way flow or a part of a wider food "web". Ecological communities with higher biodiversity form more complex trophic paths.
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms depend upon other organisms for food to survive. They can't make their own food like Green plants. Heterotrophic organisms have to take in all the organic substances they need to survive.
A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. A consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. Like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. Heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, or decomposers. On the other hand, autotrophs are organisms that use energy directly from the sun or from chemical bonds. Autotrophs are vital to all ecosystems because all organisms need organic molecules, and only autotrophs can produce them from inorganic compounds. Autotrophs are classified as either photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs.

An autotroph is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide, generally using energy from light or inorganic chemical reactions. Autotrophs do not need a living source of carbon or energy and are the producers in a food chain, such as plants on land or algae in water. Autotrophs can reduce carbon dioxide to make organic compounds for biosynthesis and as stored chemical fuel. Most autotrophs use water as the reducing agent, but some can use other hydrogen compounds such as hydrogen sulfide.
Consumer–resource interactions are the core motif of ecological food chains or food webs, and are an umbrella term for a variety of more specialized types of biological species interactions including prey-predator, host-parasite, plant-herbivore and victim-exploiter systems. These kinds of interactions have been studied and modeled by population ecologists for nearly a century. Species at the bottom of the food chain, such as algae and other autotrophs, consume non-biological resources, such as minerals and nutrients of various kinds, and they derive their energy from light (photons) or chemical sources. Species higher up in the food chain survive by consuming other species and can be classified by what they eat and how they obtain or find their food.

A carbon source is a carbon-containing molecule that is used by an organism to synthesise biomass. Such sources may be organic or inorganic. Heterotrophs must use organic molecules as a source of both carbon and energy. In contrast, autotrophs may use inorganic materials as a source for both, such as inorganic chemical energy (chemolithotrophs) or light (photoautotrophs). The carbon cycle, which begins with an inorganic carbon source and progresses through the biological carbon fixation process, includes the biological use of carbon as one of its components.[1]
Saprotrophic bacteria are bacteria that are typically soil-dwelling and utilize saprotrophic nutrition as their primary energy source. They are often associated with soil fungi that also use saprotrophic nutrition and both are classified as saprotrophs.