
Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F). Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.
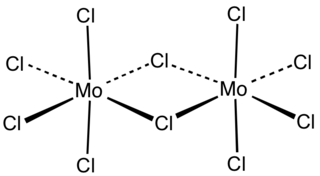
Molybdenum(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl5. This dark volatile solid is used in research to prepare other molybdenum compounds. It is moisture-sensitive and soluble in chlorinated solvents.

Arsenic tribromide is an inorganic compound with the formula AsBr3, it is a bromide of arsenic. Arsenic is a chemical element that has the symbol As and atomic number 33. This pyramidal molecule is the only known binary arsenic bromide. AsBr3 is noteworthy for its very high refractive index of approximately 2.3. It also has a very high diamagnetic susceptibility. The compound exists as colourless deliquescent crystals that fume in moist air.

Vanadium(III) bromide, also known as vanadium tribromide, describes the inorganic compounds with the formula VBr3 and its hydrates. The anhydrous material is a green-black solid. In terms of its structure, the compound is polymeric with octahedral vanadium(III) surrounded by six bromide ligands.

Tantalum(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta2Br10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, TaBr5. It is a diamagnetic, orange solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two TaBr5 units are joined by a pair of bromide bridges. There is no bond between the Ta centres. Niobium(V) chloride, niobium(V) bromide, niobium(V) iodide, tantalum(V) chloride, and tantalum(V) iodide all share this structural motif.
Tin(II) bromide is a chemical compound of tin and bromine with a chemical formula of SnBr2. Tin is in the +2 oxidation state. The stability of tin compounds in this oxidation state is attributed to the inert pair effect.

Copper(I) bromide is the chemical compound with the formula CuBr. This diamagnetic solid adopts a polymeric structure akin to that for zinc sulfide. The compound is widely used in the synthesis of organic compounds and as a lasing medium in copper bromide lasers.
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.
There are three sets of gallium halides, the trihalides where gallium has oxidation state +3, the intermediate halides containing gallium in oxidation states +1, +2 and +3 and some unstable monohalides, where gallium has oxidation state +1.
Titanium(III) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula TiBr3. It is a blue black paramagnetic solid with a reddish reflection. It has few applications, although it is a catalyst for the polymerization of alkenes.
Praseodymium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one praseodymium atom and three bromine atoms.

Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopic and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride.

Samarium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SmBr
2. It is a brown solid that is insoluble in most solvents but degrades readily in air.
Titanium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiI3. It is a dark violet solid that is insoluble in solvents, except upon decomposition.
The telluride bromides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and bromide ions (Br−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.

Californium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, a salt with a chemical formula CfBr3. Like in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3), californium(III) chloride, and californium(III) iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.

Ruthenium(III) bromide is a chemical compound of ruthenium and bromine with the formula RuBr3. It is a dark brown solid that decomposes above 400 °C.

Curium(III) bromide is the bromide salt of curium. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure.
Arsenide bromides or bromide arsenides are compounds containing anions composed of bromide (Br−) and arsenide (As3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the arsenide chlorides, arsenide iodides, phosphide bromides, and antimonide bromides.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.













