
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops or to the binding site within transmembrane helices. They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed.

Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors.

The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: A1, A2A, A2B and A3; each is encoded by a different gene.
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors, or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder.

Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors, which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER).
PlayStation Network (PSN) is a digital media entertainment service provided by Sony Interactive Entertainment. Launched in November 2006, PSN was originally conceived for the PlayStation video game consoles, but soon extended to encompass smartphones, tablets, Blu-ray players and high-definition televisions. This service is the account for PlayStation consoles, accounts can store games and other content.

P2Y receptors are a family of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors, stimulated by nucleotides such as adenosine triphosphate, adenosine diphosphate, uridine triphosphate, uridine diphosphate and UDP-glucose.To date, 8 P2Y receptors have been cloned in humans: P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y4, P2Y6, P2Y11, P2Y12, P2Y13 and P2Y14.
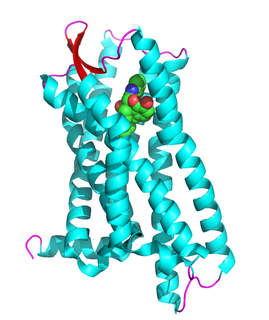
The ∆-opioid receptor, also known as delta opioid receptor or simply delta receptor, abbreviated DOR or DOP, is an inhibitory 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and has enkephalins as its endogenous ligands. The regions of the brain where the ∆-opioid receptor is largely expressed vary from species model to species model. In humans, the ∆-opioid receptor is most heavily expressed in the basal ganglia and neocortical regions of the brain.

The nuclear receptor 4A3 (NR4A3) also known as neuron-derived orphan receptor 1 (NOR1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A3 gene. NR4A3 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.

Valerenic acid is a sesquiterpenoid constituent of the essential oil of the valerian plant.

The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR1) also known G-protein coupled receptor 19 (GPCR19), membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR) or TGR5 as is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPBAR1 gene.

G protein-coupled receptor 119 also known as GPR119 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the GPR119 gene.

Taste receptor type 1 member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAS1R2 gene.

G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 (GRK4) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GRK4 gene.

Olfactory receptor 3A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR3A1 gene.

Olfactory Receptor 2G3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR2G3 gene.

Probable G-protein coupled receptor 61 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR61 gene.

AR-231,453 is an agonist for the suggested novel cannabinoid receptor GPR119.

PSN-375,963 is a selective ligand for the suggested novel cannabinoid receptor GPR119.















