Related Research Articles

The Long Island Rail Road, or LIRR, is a railroad in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. The railroad currently operates a public commuter rail service, with its freight operations contracted to the New York and Atlantic Railway. With an average weekday ridership of 354,800 passengers in 2016, it is the busiest commuter railroad in North America. It is also one of the world's few commuter systems that runs 24/7 year-round. It is publicly owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which refers to it as MTA Long Island Rail Road. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 75,186,900, or about 276,800 per weekday as of the second quarter of 2024.
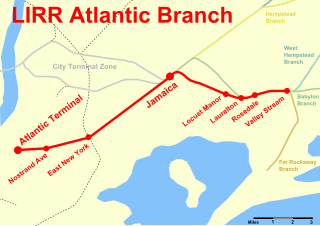
The Atlantic Branch is an electrified rail line owned and operated by the Long Island Rail Road in the U.S. state of New York. It is the only LIRR line with revenue passenger service in the borough of Brooklyn.

The Far Rockaway Branch is an electrified rail line and service owned and operated by the Long Island Rail Road in the U.S. state of New York. The branch begins at Valley Interlocking, just east of Valley Stream station. From Valley Stream, the line heads south and southwest through southwestern Nassau County, ending at Far Rockaway in Queens, thus reentering New York City. LIRR maps and schedules indicate that the Far Rockaway Branch service continues west along the Atlantic Branch to Jamaica. This two-track branch provides all day service in both directions to Grand Central Madison and Penn Station, both in Midtown Manhattan.

The Far Rockaway–Mott Avenue station is the eastern terminal station of the New York City Subway's IND Rockaway Line. Originally a Long Island Rail Road station, it is currently the easternmost station in the New York City Subway. It is served by the A train at all times.

The Montauk Branch is a rail line owned and operated by the Long Island Rail Road in the U.S. state of New York. The line runs the length of Long Island, 115 miles (185 km) from Long Island City to Montauk. However, in LIRR maps and schedules for public use, the term Montauk Branch refers to the line east of Babylon; service from Jamaica to Babylon is covered by separate Babylon Branch schedules, while the line west of Jamaica is currently unused for passenger service. A select number of Montauk Branch trains operate via the Main Line and Central Branch during peak hours.

The Long Beach Branch is an electrified rail line and service owned and operated by the Long Island Rail Road in the U.S. state of New York. The branch begins at Valley Interlocking, just east of Valley Stream station, where it merges with the Far Rockaway Branch to continue west as the Atlantic Branch. East from there the Long Beach Branch parallels the Montauk Branch to Lynbrook station, where it turns south toward Long Beach station. Trains operating on the Long Beach Branch continue west of Valley Stream via the Atlantic Branch to Jamaica station, with most continuing on to Grand Central or Penn Station in Midtown Manhattan. In 2018, the branch recorded an annual ridership of 4,849,085 based on ticket sales, down 1% from 2017.

Island Park is a station on the Long Island Rail Road's Long Beach Branch serving the residents of Island Park, Barnum Island, and Harbor Isle. The station can platform a 12-car train and is fully wheelchair accessible with ramps from street level. Parking facilities are also available. Southwest of the station the train crosses over Reynolds Channel via the Wreck Lead Bridge.
The South Side Railroad of Long Island was a railroad company in the U.S. state of New York. Chartered in 1860 and first opened in 1867 as a competitor to the Long Island Rail Road, it was reorganized in 1874 as the Southern Railroad of Long Island and leased in 1876 to the LIRR. After a reorganization as the Brooklyn and Montauk Railroad in 1879 it was merged in 1889.
The Long Island Rail Road is a railroad owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority in the U.S. state of New York. It is the oldest United States railroad still operating under its original name and charter. It consolidated several other companies in the late 19th century. The Pennsylvania Railroad owned the Long Island Rail Road for the majority of the 20th century and sold it to the State in 1966.

The Long Beach station is an intermodal center and the terminus of the Long Beach Branch of the Long Island Rail Road. It is located at Park Place and Park Avenue in the City of Long Beach, New York, serving as the city's major transportation hub.

East Rockaway is a train station serving the Long Beach Branch of the Long Island Rail Road. It is located at Atlantic and Ocean Avenues in East Rockaway, New York.

Rego Park is a former Long Island Rail Road station. It was made of wood, unlike most other stations that were concrete. The station opened in May 1928 with two side platforms outside the two Rockaway Beach Branch tracks that bracketed the four-track Main Line, so only Rockaway trains stopped there. After the Rockaway Trestle fire in 1950, the line was closed station by station. The station closed on June 8, 1962, one day before the Rockaway Beach Branch was abandoned. Nothing remains at the site today.

Parkside is a former elevated Long Island Rail Road (LIRR) station on the north side of Metropolitan Avenue on the border of the Rego Park, Forest Hills, and Glendale neighborhoods in Queens, New York City. Opened in 1927, the wooden station was part of the Rockaway Beach Branch and was the northernmost station on the branch before the junction with the Main Line at Rego Park Station and the terminus of the line at Grand Street station in Elmhurst. It also had a connecting spur to the Montauk Branch east towards Richmond Hill station. The station was closed in 1962, twelve years after the LIRR had abandoned the Rockaway portions of the line.

Glendale was a Long Island Rail Road station along the Lower Montauk Branch, located in Glendale, Queens at Edsall Avenue and 73rd Street, near Central Avenue, at the All Faiths Monuments factory for the All Faiths Cemetery. This station had two "platforms" which were just strips of pavement besides the tracks signed as the station, and two tracks.

Howard was a former Long Island Rail Road station on the Rockaway Beach Branch. Located on marshland along the coast of Jamaica Bay south of the "WD Tower" near Hawtree Creek, it had no fixed address, and was south of what is today 165th Avenue, evidently within the Gateway National Recreation Area's Hamilton Beach Park.

Hamilton Beach was a former Long Island Rail Road station on the Rockaway Beach Branch in Queens, New York City. It was located between two streets in Hamilton Beach, Queens, one of which no longer exists and is part of land owned by JFK Airport.
The Ocean Electric Railway was a street car line that operated on The Rockaways. It ran parallel to parts of the Rockaway Beach Branch and Far Rockaway Branch of the Long Island Rail Road. The headquarters of the OER were at the Far Rockaway Long Island Rail Road station which was then located across Mott Avenue from the existing Far Rockaway–Mott Avenue subway station. The Office of Superintendent - Trolleys at that location managed all the LIRR's owned trolley operations.
Hammels was a Long Island Rail Road station on the Rockaway Beach Branch in Hammels, Queens. It was located at what is today Beach 84th Street at the west leg of the Hammels Wye.
Beach Channel was a Long Island Rail Road station on the Rockaway Beach Branch in Broad Channel, Queens, New York. It was located on the north end of the Beach Channel Drawbridge across from the north leg of the Hammels Wye.
Wreck Lead was a train station along the Long Beach Branch of the Long Island Rail Road. The station was opened in June 1888 by the New York and Long Beach Railroad to serve numerous fishing clubs and hotels. This station was a flag stop. Wreck Lead consisted of a low cinder platform on the northeast side of the Reynolds Channel. In 1911, a second platform was installed on the west side of the tracks and on January 15, 1927, and Wreck Lead became the terminus of the double-tracking of the Long Beach Branch. Wreck Lead closed on December 31, 1927.
References
- ↑ "LONG ISLAND STATION HISTORY". trainsarefun.com. Archived from the original on 2017-05-26.
- ↑ "The Long Island Rail Road: A Comprehensive History Volume #5(New York, Woodhaven & Rockaway Railroad; New York & Rockaway Beach railway; New York & Long Beach Railroad; New York & Rockaway railroad; Brooklyn rapid transit operation to Rockaway; Over L.I.R.R.)", by Vincent F. Seyfried