
The 1832 United States presidential election was the 12th quadrennial presidential election, held from Friday, November 2 to Wednesday, December 5, 1832. Incumbent president Andrew Jackson, candidate of the Democratic Party, defeated Henry Clay, candidate of the National Republican Party.

The 1848 United States presidential election was the 16th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1848. In the aftermath of the Mexican–American War, General Zachary Taylor of the Whig Party defeated Senator Lewis Cass of the Democratic Party.

The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott. A third party candidate from the Free Soil party, John P. Hale, also ran and came in third place, but got no electoral votes.
The 1852 Democratic National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from June 1 to June 5 in Baltimore, Maryland. It was held to nominate the Democratic Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1852 election. The convention selected former Senator Franklin Pierce of New Hampshire for president and Senator William R. King of Alabama for vice president.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.
The 1820–21 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 3, 1820, and August 10, 1821. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 17th United States Congress convened on December 3, 1821. They coincided with President James Monroe winning reelection unopposed.

The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810, and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
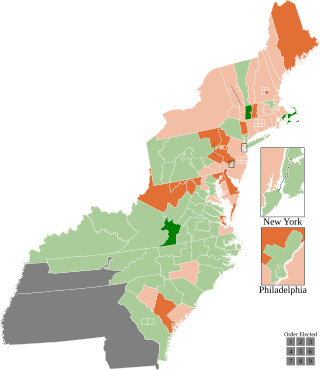
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The 1794–95 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 25, 1794, and September 5, 1795 (Kentucky). Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 4th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1795. They were held during President George Washington's second term. Elections were held for all 105 seats, representing 15 states.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.

The 1788–89 United States House of Representatives elections were the first U.S. House of Representatives elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. Each state set its own date for its congressional elections, ranging from November 24, 1788, to March 5, 1789, before or after the first session of the 1st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1789. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States.

James Adams Weston was a civil engineer, banker, and an American politician from Manchester, New Hampshire, who served as mayor of Manchester for several terms and was the 33rd governor of New Hampshire.

The 1852 Whig National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held from June 16 to June 21, in Baltimore, Maryland. It nominated the Whig Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1852 election. The convention selected General-in-Chief Winfield Scott for president and U.S. secretary of the navy William A. Graham for vice president.

The election of the president and the vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the fifty U.S. states or in Washington, D.C., cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the Electoral College. These electors then cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president, and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for president, the House of Representatives elects the president; likewise if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for vice president, then the Senate elects the vice president.

The 1852–53 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with the 1852 presidential election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1852 and 1853, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1816–17 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1816 and 1817, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1788–1789 United States Senate elections were the first U.S. Senate elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States. As these elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures.

The 1852 United States elections elected the members of the 33rd United States Congress. The election marked the end of the Second Party System, as the Whig Party ceased to function as a national party following this election. Democrats won the presidency and retained control of both houses of Congress.

Following is a table of United States presidential elections in North Carolina, ordered by year. Since its admission to statehood in 1789, North Carolina has participated in every U.S. presidential election except the election of 1864, during the American Civil War, when the state had seceded to join the Confederacy. North Carolina did not participate in the 1788–89 United States presidential election, as it did not ratify the Constitution of the United States until months after the end of that election and after George Washington had assumed office as President of the United States.

The 2020 New Hampshire Republican presidential primary took place on Tuesday, February 11, 2020, as the second nominating contest in the Republican Party presidential primaries for the 2020 presidential election, following the Iowa caucuses the week before. The New Hampshire primary is a semi-closed primary, meaning that only Republicans and independents may vote in this primary.

















