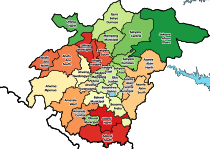
The Ashanti Region is located in the southern part of Ghana and is the third largest of 16 administrative regions, occupying a total land surface of 24,389 km2 (9,417 sq mi) and making up 10.2 percent of the total land area of Ghana. It is the most populated region in Ghana, with a population of 5,440,463 according to the 2021 census, accounting for around one-fifth of Ghana's total population. The Ashanti Region is known for its gold bar and cocoa production. The largest city and capital of Ashanti is Kumasi.

Obuasi is a gold mining community and town which is the capital of the Obuasi Municipal District in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. It lies in the southern part of the Obuasi Municipal, 39 miles south-west of Ashanti capital city Kumasi. Obuasi has a population of 175,043 people. Obuasi mining community has a mixture of the Ashanti people culture and the semi-island exclave Ashantiland.
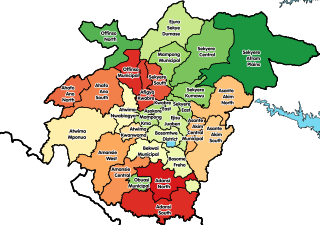
Offinso Municipal District is one of the forty-three districts in Ashanti Region, Ghana. Originally created as an ordinary district assembly in 1988 when it was known as Offinso District, which it was created from the former Offinso District Council; until the northern part of the district was later split off to create Offinso North District on 29 February 2008; while the remaining part was elevated to municipal district assembly status on the same year to become Offinso Municipal District. The municipality is located in the northern part of Ashanti Region and has Offinso as its capital town.
Articles related to Ghana include:

The Akyem are an Akan people. The term Akyem is used to describe a group of four states: Asante Akyem, Akyem Abuakwa, Akyem Kotoku, and Akyem Bosome. These nations are located primarily in the eastern region in south Ghana. The term is also used to describe the general area where the Akyem ethnic group clusters. The Akyem ethnic group make up between 3-4 percent of Ghana's population depending on how one defines the group and are very prominent in all aspects of Ghanaian life. The Akyem are a matrilineal people. The history of this ethnic group is that of brave warriors who managed to create a thriving often influential and relatively independent state within modern-day Ghana. When one talks of Ghanaian history, there is often mention of The Big Six. These were six individuals who played a big role in the independence of Ghana. Of the big six, people of Akyem descent made up the majority.
Agogo is a town in the Asante Akim North Municipal District of the Ashanti Region of Ghana. Agogo is approximately 80 kilometers east of Kumasi, the capital of the Ashanti Region, and had a population of 28,271 in the 2000 census. Computer projections estimate that the 2007 population was 32,859.
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Konongo–Mampong is a diocese located in the city of Konongo–Mampong in the ecclesiastical province of Kumasi in Ghana.

The Asante Empire, today commonly called the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted from 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana and also parts of Ivory Coast and Togo. Due to the empire's military prowess, wealth, architecture, sophisticated hierarchy and culture, the Ashanti Empire has been extensively studied and has more historic records written by European, primarily British, authors than any other indigenous culture of sub-Saharan Africa.

The Mining industry of Ghana accounts for 5% of the country's GDP and minerals make up 37% of total exports. Gold contributes over 90% of the total mineral exports. Thus, the main focus of Ghana's mining and minerals development industry remains focused on gold. Ghana is Africa's largest gold producer, producing 80.5 t in 2008. Ghana is also a major producer of bauxite, manganese and diamonds. Ghana has 20 large-scale mining companies producing gold, diamonds, bauxite and manganese; over 300 registered small scale mining groups; and 90 mine support service companies. Other mineral commodities produced in the country are natural gas, petroleum, salt, and silver.

Asante Akim North District is one of the forty-three districts in Ashanti Region, Ghana. Originally it was formerly part of the then-larger and original Asante Akim North District in 1988, which it was created from the former Asante Akim District Council. Later, it was elevated to municipal district assembly status to become Asante Akim North Municipal District in November 2007. However, in July 2012, the northern part of the district was split off to create a new Asante Akim North District; thus the remaining part has been renamed to become Asante Akim Central Municipal District. The district assembly is located in the eastern part of Ashanti Region and has Agogo as its capital town.

Ofori Panin Senior High School (OPASS) is a co-educational second cycle institution at Kukurantumi in the Eastern Region of Ghana. Ofori Panin School, is a co-educational boarding school located at Tafo in Akyem, Eastern Region, Ghana. The school was founded in 1961 by Kwame Nkrumah. The foundation stone of the building was laid on 19 May 1962 by Hon. Kofi Asante Ofori Attah, M.P. for Akim Abuakwa and Minister of Justice at that time. An alumnus/alumna of Ofori Panin is known as an "Opassian".
Konongo Odumase Senior High School is a coeducational second-cycle institution at Konongo-Odumase in the Asante Akim Central District of the Ashanti Region of Ghana.

The economy of the Ashanti Region in southern Ghana is largely self-sufficient, being driven by its service sector as well as by natural resources. The region is also known for its production of manganese, bauxite and agricultural commodities such as cocoa and yam, with the region having low levels of taxation and without much need for foreign direct investment. The Ashanti Region spans an area of 24,389 km2, and according to the 2000 census, the region had a population of 3,612,950, most of whom (94.2%) were ethnic Akans, of whom 82.9% were ethnic Ashanti. The capital of the region is Kumasi, which with a population of 2,069,350 as of 2013 represents a high level of urbanisation within the state.

Asante Akim Central Municipal District is one of the forty-three districts in Ashanti Region, Ghana. Originally created as an ordinary district assembly in 1988 as the 1st Asante Akim North District, which it was created from the former Asante Akim District Council. Later it was elevated to municipal district assembly status to become Asante Akim North Municipal District in November 2007. However, in July 2012, the northern part of the district was split off to create a new Asante Akim North District; thus the remaining part has been renamed to become Asante Akim Central Municipal District. The municipality is located in the eastern part of Ashanti Region and has Konongo as its capital town.

Asante-Akim Central is one of the constituencies represented in the Parliament of Ghana. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first past the post system of election. Asante-Akim Central is located in the Asante Akim North district of the Ashanti Region of Ghana. The member of parliament for the constituency is Kwame Anyimadu-Antwi.
Charles de Graft-Dickson (1913–1997) was a Ghanaian educationist and a politician. He served as a minister of State and a member of parliament in the first republic. Prior to politics, he was the chairman of Asante Kotoko S.C.
Ernest Papa Arko was a Ghanaian footballer. He played as a forward for Asante Kotoko and the Ghana national team.

The Economy of the Ashanti Empire was largely a pre-industrial and agrarian economy. The Ashanti established different procedures for mobilizing state revenue and utilizing public finance. Ashanti trade extended upon two main trade routes; one at the North and the other at the South. The Northern trade route was dominated by the trade in Kola nuts and at the South, the Ashanti engaged in the Atlantic Slave Trade. A variety of economic industries such as cloth-weaving and metal working industries existed. The Ashanti originally farmed in subsistence until agriculture became extensive during the 19th century.