
Signy Island is a small subantarctic island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was named by the Norwegian whaler Petter Sørlle (1884–1933) after his wife, Signy Therese.

Powell Island is a narrow island 13 km (8.1 mi) long and 4 km (2.5 mi) wide, lying between Coronation and Laurie Islands in the central part of the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. Its southern end lies 7 km east of the south-western extremity of Coronation Island, between Lewthwaite Strait and Washington Strait.
The Larsen Islands are a small group of islands north-west of Moreton Point, the western extremity of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. They were discovered by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer on the occasion of their joint cruise in December 1821. The islands were named on Petter Sørlle's chart, based upon his survey of the South Orkney Islands in 1912–1913, in honour of Carl Anton Larsen.

The Inaccessible Islands are a group of small precipitous islands ranging from 120 to 215 m high, the westernmost features of the South Orkney Islands, lying 20 km (12 mi) west of Coronation Island in Antarctica. They were discovered in December 1821 by Captain George Powell, a British sealer in the sloop James Monroe, though it is possible they are the "Seal Islands" seen by Nathaniel Palmer a year earlier. The islands were so named by Powell because of their appearance of inaccessibility. They are considered part of the British Antarctic Territory by the United Kingdom and part of the Province of Tierra del Fuego by Argentina.

Cheal Point is a rocky headland 2 km (1.2 mi) east-south-east of Return Point, the south-western extremity of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica.

Christoffersen Island is a small island immediately west of the southern end of Powell Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The name appears on a chart by Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorlle, who made a running survey of these islands in 1912–13.

The Weddell Islands are a group of small islands and rocks lying 1.9 km (1.2 mi) south of Saddle Island and 9 km (5.6 mi) lying north of the western end of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. They were probably first seen during a joint cruise by Captains Nathaniel B. Palmer and George Powell in December 1821. The name first appears on James Weddell's chart resulting from his exploration of the South Orkney Islands in 1823.

Grey Island is 1 km (0.62 mi) south of Michelsen Island and 2 km (1.2 mi) west of the southern part of Fredriksen Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was first charted and named Holmen Graa on a map by the Norwegian whaler Captain Petter Sorlle, who made a running survey of the South Orkney Islands in 1912–13. The anglicised form appears on the chart by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II who surveyed the islands in 1933.

Eillium Island is a small island 2.2 km (1.4 mi) north-west of Rumbo Punta, the north-west tip of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was first seen and roughly charted by Captain George Powell and Captain Nathaniel Palmer during their joint cruise in 1821. It was recharted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under Dr. William S. Bruce, who named it for his son Eillium.
Ellefsen Harbour is a harbour lying at the south end of Powell Island between Christoffersen Island and Michelsen Island, in the South Orkney Islands. It was discovered in the course of a joint cruise by Captain George Powell, a British sealer, and Captain Nathaniel Palmer, an American sealer, in December 1821. Shortly afterward, it was briefly occupied by Sam Pointer. The name first appeared on Powell's chart published in 1822.

Ferrier Peninsula is a narrow peninsula, 2.4 km (1.5 mi) long, forming the eastern end of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was roughly charted in 1823 by a British sealing expedition under James Weddell. It was surveyed in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who named it for his secretary J.G. Ferrier, who was also manager in Scotland of the expedition.
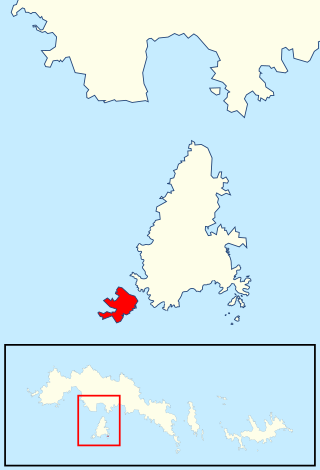
Moe Island is an island 2 km (1.2 mi) long in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica, separated from the south-west end of Signy Island by Fyr Channel. It was charted by Captain Petter Sørlle in 1912–13, and named after M. Thoralf Moe of Sandefjord, Norway, a contemporary whaling captain who worked in this area. The northernmost point of the island is Spaull Point, named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Vaughan W. Spaull, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) biologist on Signy Island, 1969.

Fraser Point is a point between Marr Bay and Mackintosh Cove on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was mapped by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition in 1903, and in 1912–13 by Captain Petter Sorlle. It was remapped in 1933 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II who named it for Francis C. Fraser.

Fredriksen Island is an island 5 km (3.1 mi) long and 1 km (0.62 mi) wide, lying 1 km south-east of Powell Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was discovered by Captains Nathaniel Palmer and George Powell in the course of their joint cruise in December 1821. It was named by Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorlle, who made a running survey of the island in the 1912–13 summer.

Gibbon Bay is a bay 2 km (1.2 mi) long and wide, entered between Rayner Point and The Turret along the east coast of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The bay was first seen in December 1821 by Captain George Powell and Captain Nathaniel Palmer, but was more accurately delineated on a 1912 chart by Captain Petter Sorlle. It was recharted in 1933 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II and named for the ship's surgeon, Dr G.M. Gibbon.
Graptolite Island is an island 0.8 km (0.50 mi) long in the north-east part of Fitchie Bay, lying off the south-east portion of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. James Weddell's chart published in 1825 shows two islands in essentially this position. Existence of a single island was determined in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who so named it because what were thought to be graptolite fossils were found there. Later analysis showed that the fossils on Graptolite Island were merely the remains of ancient plants.

Moreton Point is a point 1 nautical mile (2 km) north of Return Point at the western end of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It was roughly charted by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer in 1821, and was named by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II who charted the islands in 1933.

Matthews Island is the largest of the Robertson Islands in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It lies immediately south-east of Coronation Island, from which it is separated by a narrow channel known as the Divide. Matthews Island was mapped as part of Coronation Island until January 1957 when a Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) party established its insularity. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Drummond H. Matthews, a FIDS geologist at Signy Island in 1956.
Skilling Island is a small island immediately north of Atriceps Island, in the Robertson Islands group of the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. Although roughly charted at a much earlier date, the island was first surveyed in 1933 by DI personnel. It was named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Charles J. Skilling (1931–52) of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), general assistant at Signy Island in 1949, and member of the sledge party which visited the Robertson Islands the same year. Skilling died aboard the John Biscoe on 17 April 1952.

The Southern Powell Island and adjacent islets Specially Protected Area is a 2688 ha site encompassing part of southern Powell Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It includes neighbouring Christoffersen, Fredriksen, Michelsen and Grey Islands, along with some other (unnamed) offshore islets. It was designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area because of its biological values as it supports many plants and animals that exemplify the natural ecology of the South Orkney Islands. It is also a breeding site for Antarctic fur seals.











